What is the specific heat of a substance
If a swimming pool and wading pool, both full of water at the same temperature, were subjected to the same input of heat energy, the wading pool would certainly rise in temperature more quickly than the swimming pool. The heat capacity of an object depends both on its mass and its chemical composition.
When summer hits, you might end up going to the beach to cool down. While the ocean waves may feel cool, the sand, unfortunately, is red-hot. If you aren't wearing shoes, it's possible to actually burn your feet! Explore our app and discover over 50 million learning materials for free. But how can the water be so cold, but the sand be so hot?
What is the specific heat of a substance
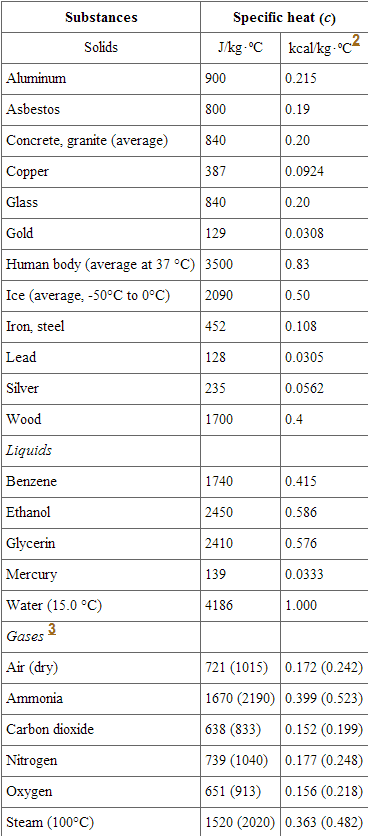
In thermodynamics , the specific heat capacity symbol c of a substance is the heat capacity of a sample of the substance divided by the mass of the sample, also sometimes referred to as massic heat capacity or as the specific heat. Specific heat capacity often varies with temperature, and is different for each state of matter. The specific heat capacity of a substance, especially a gas, may be significantly higher when it is allowed to expand as it is heated specific heat capacity at constant pressure than when it is heated in a closed vessel that prevents expansion specific heat capacity at constant volume. Specific heat capacity is also related to other intensive measures of heat capacity with other denominators. One of the first scientists to use the concept was Joseph Black , an 18th-century medical doctor and professor of medicine at Glasgow University. He measured the specific heat capacities of many substances, using the term capacity for heat. These parameters are usually specified when giving the specific heat capacity of a substance. Specific heat capacity is an intensive property of a substance, an intrinsic characteristic that does not depend on the size or shape of the amount in consideration. The qualifier "specific" in front of an extensive property often indicates an intensive property derived from it. Two particular choices are widely used:.
An equal mass of water under the same sun exposure will not become nearly as hot.
Heat capacity is an extensive property, so it scales with the size of the system. For example, if it takes 1, J to heat a block of iron, it would take 2, J to heat a second block of iron with twice the mass as the first. The heat capacity of most systems is not a constant. Rather, it depends on the state variables of the thermodynamic system under study. In particular, it is dependent on temperature itself, as well as on the pressure and the volume of the system, and the ways in which pressures and volumes have been allowed to change while the system has passed from one temperature to another. The temperature dependence is why the definition a calorie is formally the energy needed to heat 1 g of water from Different measurements of heat capacity can therefore be performed, most commonly at constant pressure and constant volume.
In equation form, this can be represented as the following:. That is if a constant has units, the variables must fit together in an equation that results in the same units. So C equals something with energy in the numerator and temperature in the denominator. Now, you need to use some common sense here, as we are adding heat, not work, and adding heat changes the temperature, it does not make the temperature. In words, heat capacity is the substance's ability to resist change in temperature upon exposure to a heat source.
What is the specific heat of a substance
Specific heat describes the amount of thermal energy required to raise the temperature of one unit mass of a substance by one degree Celsius or Kelvin. It plays a crucial role in understanding how different materials respond to changes in temperature and their ability to store or release thermal energy. The specific heat formula calculates the amount of heat transferred into and out of a system. In this formula, q represents the amount of heat transferred. It is measured in Joules J or calories cal. The variable m denotes the mass of the substance being heated or cooled.
Neutrogena healthy skin anti aging perfector
The constant-volume and constant-pressure changes are only two particular directions in this space. Register for Free I'll do it later. This method allows up to calculate the heat exchange q as well as the specific heat of whatever substance we choose. Quantum mechanics predicts that, at room temperature and ordinary pressures, an isolated atom in a gas cannot store any significant amount of energy except in the form of kinetic energy. Free energy Free entropy. This article covers specific heat. However, not all energy provided to a sample of a substance will go into raising its temperature, exemplified via the equipartition theorem. These experiments mark the foundation of thermochemistry. Knowledge of the heat capacity of the surroundings, and careful measurements of the masses of the system and surroundings and their temperatures before and after the process allows one to calculate the heat transferred as described in this section. Confusingly, there are two common units with that name, respectively denoted cal and Cal :. When an endothermic reaction occurs, the heat required is absorbed from the thermal energy of the solution, which decreases its temperature. Nature Communications. Water g. True or False: Specific heat is dependent on state of matter. It is a simple equation relating the heat capacities under constant temperature and under constant pressure.
Heat capacity is an extensive property, so it scales with the size of the system. For example, if it takes 1, J to heat a block of iron, it would take 2, J to heat a second block of iron with twice the mass as the first. The heat capacity of most systems is not a constant.
Provided by : Wiktionary. If you aren't wearing shoes, it's possible to actually burn your feet! Specific Heat The specific heat is an intensive property that describes how much heat must be added to a particular substance to raise its temperature. The energy produced by the reaction is trapped in the steel bomb and the surrounding water. Studying with content from your peer. Non-necessary Non-necessary. The specific heat capacity can be defined also for materials that change state or composition as the temperature and pressure change, as long as the changes are reversible and gradual. Rather, it depends on the state variables of the thermodynamic system under study. The first learning app that truly has everything you need to ace your exams in one place. Calorimetry is the measurement of the heat of chemical reactions or physical changes. One of the strengths of the Debye model is that unlike the preceding Einstein model it predicts the proper mathematical form of the approach of heat capacity toward zero, as absolute zero temperature is approached.

All above told the truth. We can communicate on this theme. Here or in PM.