Sigma bond and pi bond examples
Forgot password? New user?
When you hear the words sigma and pi bond, you might think of Greek life in college. But actually, sigma and pi bonds are types of covalent bonds. Covalent bonds happen when atoms share electrons. They are found in single, double, and triple bonds. They only exist in double and triple bonds.
Sigma bond and pi bond examples
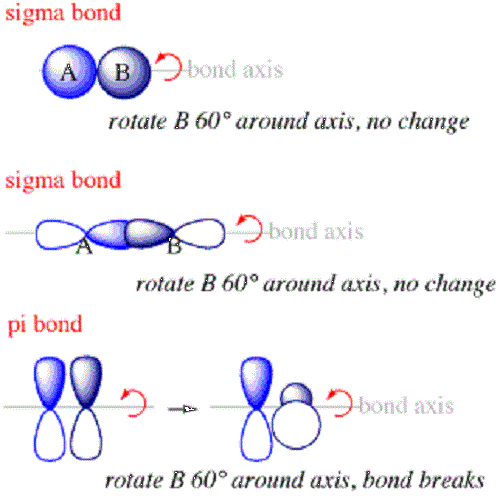
Sigma and Pi bonds are the two types of covalent bonds found in molecules and compounds. Sigma and Pi Bonds play a crucial role in understanding the structure, stability, and reactivity of a wide range of chemical species. Sigma bonds are characterized by their head-on overlap, greater electron density along the bond axis, and the ability to rotate freely. Pi bonds, on the other hand, involve parallel p-orbital overlap, electron density above and below the internuclear axis, and restrict rotation to some degree. In this article, we will discuss the concept of sigma and pi bonds including their various examples, characteristics, and key differences between both the bonds. By the end of this article, you will have a solid understanding of these essential covalent bonds i. Sigma bond is formed by end-to-end overlapping of bonding orbitals along the internuclear axis. This is called head-on overlap or axial overlap. The overlap of s orbitals, as well as the overlap of p orbitals in a single bond, results in sigma bonds. Sigma bonds allow for free rotation around the bond axis because the electron density is concentrated along the bond axis. There are various examples of sigma bonds as all single bonds are simaga bonds only. Some common examples are:. Sigma bonds can be categorized into different types based on the nature of the atomic orbitals involved and the way they overlap.
They will first fill the lower energy orbitals, and then they will fill the higher energy orbitals. Whereas sigma bond and pi bond examples one sigma bonding MO is possible, the pi bonding MOs can exist either in the vertical plane or the horizontal plane, and so two pi bonds are possible. Sigma bonds are generally stronger than pi bonds due to the greater overlap of orbitals in sigma bonds.
Sigma and pi bonds are types of covalent bonds that differ in the overlapping of atomic orbitals. Covalent bonds are formed by the overlapping of atomic orbitals. Sigma bonds are a result of the head-to-head overlapping of atomic orbitals whereas pi bonds are formed by the lateral overlap of two atomic orbitals. Various bond parameters such as bond length, bond angle, and bond enthalpy depend on the way the overlapping of atomic orbital takes place. This overlap occurs in two major ways, giving rise to two primary types of covalent bonds , i. This type of covalent bond is formed by head-on positive same phase overlap of atomic orbitals along the internuclear axis.
We mentioned in the previous post that covalent bonds are formed as a result of sharing two valence electrons in overlapping orbitals of two atoms. For example , the following Lewis structures represent covalent bonds together with some lone pairs of electrons:. In short, you can remember that single bonds are sigma bonds. For example, the single bond between the two carbons in ethane C 2 H 6 is a sigma bond because it is formed by overlapping two sp 3 orbitals of the adjacent carbon atoms:. On the other hand, in ethene, or ethylene C 2 H 4 , there is one sigma and one pi bond between the two carbon atoms:. The pi bond is formed by a side-to-side overlap of two p orbitals provided by adjacent atoms.
Sigma bond and pi bond examples
Our minds can handle two electrons interacting with one another in a sphere of space. But then we start putting in double bonds and triple bonds. So we need a more complex picture that works for all these electrons. The hybridization model helps explain molecules with double or triple bonds see figure below. The entire molecule is planar. As can be seen in the figure below, the electron domain geometry around each carbon independently is trigonal planar.
Loto-québec me connecter
Sigma bonds are generally stronger and more stable than pi bonds. Pi bonds are formed by the sidewise positive same phase overlap of atomic orbitals along a direction perpendicular to the internuclear axis. To understand sigma and pi bonds, you need to know a little about atomic orbitals and hybridization. There is a defined optimal distance between the nuclei in which the potential energy is at a minimum, meaning that the combined attractive and repulsive forces add up to the greatest overall attractive force. This optimal internuclear distance is the bond length. Column Chromatography. Did not receive OTP? Download Now. Log in with Facebook Log in with Google Log in with email. Note that there are four single bonds, one double bond, and one triple bond in an acrylonitrile molecule. First, sigma bonds are stronger than pi bonds. Atomic orbitals are spaces where electrons are likely to be found. Sigma and Pi Bonds. Sigma and pi bonds are types of covalent bonds that differ in the overlapping of atomic orbitals. Condensation Polymers.
Forgot password? New user?
Thank you for your valuable feedback! It has absolutely nothing to do with any actual heads but instead this difference refers to where the bonding between orbitals actually occurs. Reaction Quotient. Double bonds are comprised of one sigma and one pi bond. The three most common overlap conditions that result in sigma bonds are:. Valence bond theory is most often used to describe bonding in organic molecules. Empirical and Molecular Formula. How many people do you think are squeezed on this street? Review What is the hybridization around each carbon in ethene? Complete Tutorials. This article is being improved by another user right now. Avogadro Constant. Polar and Non-Polar Covalent Bonds.

0 thoughts on “Sigma bond and pi bond examples”