Shape of becl2 according to vsepr theory
Study material notes on the linear shape of molecules. This theory is dependent on the premise that repulsion stickers between the valence electrons in each atom, shape of becl2 according to vsepr theory, and all atoms will rearrange themselves in a way that the electron pair repulsion is minimised on its own. The VSEP number is responsible for describing the molecule shape, as described in the table below. The atoms come in contact with each other to build molecules, whereas molecules come in contact to form compounds and elements.
Submitted by Brian S. We will assign your question to a Numerade educator to answer. Your personal AI tutor, companion, and study partner. Ask unlimited questions and get video answers from our expert STEM educators. Millions of real past notes, study guides, and exams matched directly to your classes. Predict the shape of the following molecule o ion: AsH4 trigonal pyramidal trigonal planar linear tetrahedral bent.
Shape of becl2 according to vsepr theory
Views: 5, Connect with our Chemistry tutors online and get step by step solution of this question. Are you ready to take control of your learning? American National Curriculum. High School. All topics. Question asked by Filo student. Views: 5, students. First, find the number of valence electrons of each atom. The Beryllium Be has 2 valence electrons, and each Chlorine Cl atom has 7 valence electrons. Step 2: Draw the Lewis structure of BeCl2. Start by placing Beryllium Be at the center as it has the lowest electronegativity. Then, attach two Chlorine atoms to Be by single bonds.
Three hydrogens are bonded to a central oxygen. With no lone pair repulsions, we do not expect any bond angles to deviate from the ideal. Each chlorine has three electron pairs.
Theoretical Physical Chemistry Revision Notes. The Shapes of Molecules and Ions and bond angles related to their Electronic Structure - mainly inorganic molecules on this page. Part 1 from diatomic molecules to polyatomic molecules. All by structure and chemical bonding revision notes All my advanced A level inorganic chemistry notes Index of all my GCSE level chemistry notes The shapes and bond angles of a variety of molecules are described, explained and discussed using valence shell electron pair repulsion theory VSEPR theory and patterns of shapes deduced for 2, 3, 4, 5 and 6 groups of bonding electrons or non-bonding electrons in the valence shell of the central atom of the molecule or ion. So, this page is all about how to work out molecule shapes and work out bond angles is described and explained! Sub-index for 'shapes of molecules' pages. Consider bonding pairs and lone non-bonding pairs of electrons as charge clouds that repel each other remember that like electrical charges repel.
The Lewis electron-pair approach can be used to predict the number and types of bonds between the atoms in a substance, and it indicates which atoms have lone pairs of electrons. This approach gives no information about the actual arrangement of atoms in space, however. Keep in mind, however, that the VSEPR model, like any model, is a limited representation of reality; the model provides no information about bond lengths or the presence of multiple bonds. The VSEPR model can predict the structure of nearly any molecule or polyatomic ion in which the central atom is a nonmetal, as well as the structures of many molecules and polyatomic ions with a central metal atom. The premise of the VSEPR theory is that electron pairs located in bonds and lone pairs repel each other and will therefore adopt the geometry that places electron pairs as far apart from each other as possible. This theory is very simplistic and does not account for the subtleties of orbital interactions that influence molecular shapes; however, the simple VSEPR counting procedure accurately predicts the three-dimensional structures of a large number of compounds, which cannot be predicted using the Lewis electron-pair approach. We can use the VSEPR model to predict the geometry of most polyatomic molecules and ions by focusing only on the number of electron pairs around the central atom , ignoring all other valence electrons present.
Shape of becl2 according to vsepr theory
To use the VSEPR model, one begins with the Lewis dot picture to determine the number of lone pairs and bonding domains around a central atom. For example, in either the hypervalent or octet structure of the I 3 - ion above, there are three lone pairs on the central I atom and two bonding domains. We then follow these steps to obtain the electronic geometry :.
Paper cup decoration ideas
Frequently in the text I've used the abbreviated term ' lone pair ' meaning a pair of non-bonding electrons - in exams its a good idea to initially define any abbreviations you may use several times and then you shouldn't lose any marks - take care! The dipole moment of a molecule is therefore the vector sum of the dipole moments of the individual bonds in the molecule. The central atom has one lone pair and there are two bond pairs. JEE Advanced Syllabus. AX 5 Molecules: PCl 5 1. The valence-shell electron-pair repulsion VSEPR model allows us to predict which of the possible structures is actually observed in most cases. Shape determination: VSEPR model works better for simple halides of the p-block elements but can also be used with other substituents. For CCl 4 in the dot and cross diagram the four crosses represent carbon's outer shell valence electrons and the four sets of seven dots represent the original chlorine outer shell valence electrons. JEE Coaching Centres. Sign Up for Free.
BeCl2 referred to as Beryllium Chloride, is an inorganic compound.
Therefore, the shape of the molecules are arranged so that the energy is minimized. This gives a stable 'octet' of electrons around both the nitrogen and boron atoms. Last introduction point: Be very careful when describing your deduction of a molecular shape to distinguish between the electron pair geometry and the actual molecular geometry of the molecule i. There are two bonding pairs and one lone pair, so the structure is designated as AX 2 E. The three lone pairs of electrons have equivalent interactions with the three iodine atoms, so we do not expect any deviations in bonding angles. JEE Eligibility Criteria Copying of website material is NOT permitted. Zeolites have small, fixed-size openings that allow small molecules to pass through easily but not larger molecules; this is why they are sometimes referred to as molecular sieves. Problems 1. SiCl: This molecule has four atoms bonded to the central Si atom, with no lone pairs.

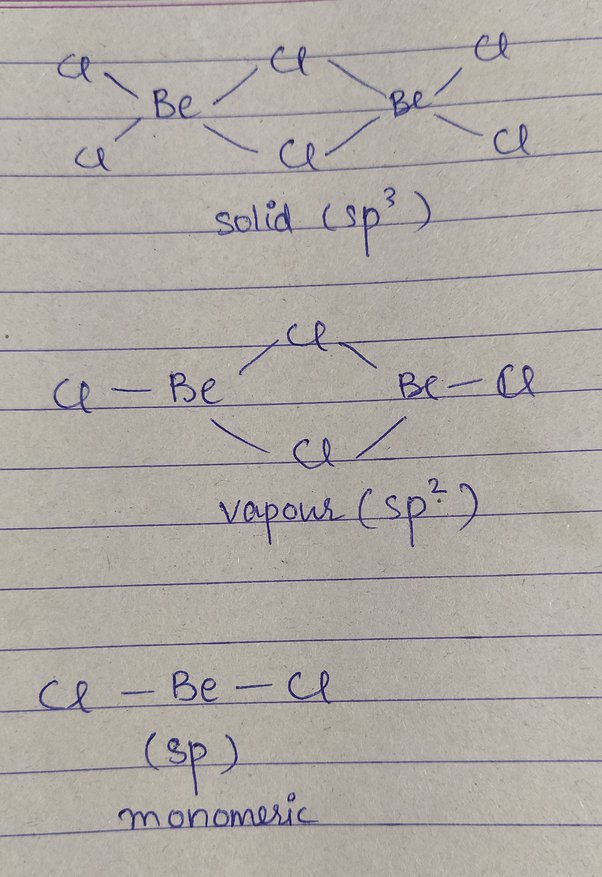
Prompt, where I can find it?
Bravo, what words..., a brilliant idea
You, maybe, were mistaken?