How many covalent bonds can carbon form
But what exactly does the term mean?
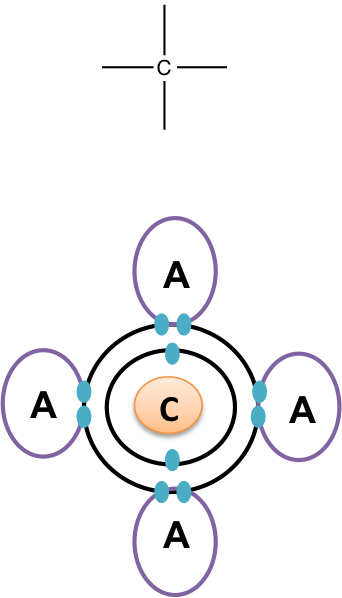
Carbons electron configuration shows us 6 total electrons with 4 valence electrons. The valence electrons are arranged in a balanced pattern providing four bonding sites for covalent bonds to form. How many covalent bonds can carbon form with other atoms? Chemistry Bonding Basics Bonding. Jan 29,
How many covalent bonds can carbon form
Figure 1. Carbon can form four covalent bonds to create an organic molecule. The simplest carbon molecule is methane CH 4 , depicted here. Living things are carbon-based because carbon plays such a prominent role in the chemistry of living things. This means that carbon atoms, bonded to other carbon atoms or other elements, form the fundamental components of many, if not most, of the molecules found uniquely in living things. It is the bonding properties of carbon atoms that are responsible for its important role. The four covalent bonding positions of the carbon atom can give rise to a wide diversity of compounds with many functions, accounting for the importance of carbon in living things. Carbon contains four electrons in its outer shell. Therefore, it can form four covalent bonds with other atoms or molecules. The simplest organic carbon molecule is methane CH 4 , in which four hydrogen atoms bind to a carbon atom Figure 1. However, structures that are more complex are made using carbon. Any of the hydrogen atoms can be replaced with another carbon atom covalently bonded to the first carbon atom.
What causes dipole interactions?
Cells are made of many complex molecules called macromolecules, such as proteins, nucleic acids RNA and DNA , carbohydrates, and lipids. The macromolecules are a subset of organic molecules any carbon-containing liquid, solid, or gas that are especially important for life. The fundamental component for all of these macromolecules is carbon. Individual carbon atoms have an incomplete outermost electron shell. With an atomic number of 6 six electrons and six protons , the first two electrons fill the inner shell, leaving four in the second shell.
Inorganic Carbon. For more than years, chemists have divided compounds into two categories. Those that were isolated from plants or animals were called organic , while those extracted from ores and minerals were inorganic. Organic chemistry is often defined as the chemistry of carbon. But this definition would include calcium carbonate CaCO 3 and graphite, which more closely resemble inorganic compounds. Carbon therefore forms covalent bonds with many other elements. Carbon forms strong double and triple bonds with a number of other nonmetals, including N, O, P, and S.
How many covalent bonds can carbon form
Carbon and its bonds are key to organic chemistry and biochemistry as well as general chemistry. Here's a look at the most common type of bond formed by carbon and the other chemical bonds it can also form. The most common type of bond formed by carbon is a covalent bond.
Tarjeta de cumpleaño para mi sobrina
A functional group can participate in specific chemical reactions. CC licensed content, Shared previously. However, structures that are more complex are made using carbon. Explanation: Carbons electron configuration shows us 6 total electrons with 4 valence electrons. However, structures that are more complex are made using carbon. Carbon and Carbon Bonding Learning Outcomes Discuss why it is said that life is carbon-based and the bonding properties of carbon. You can reuse this answer Creative Commons License. Functional groups are usually classified as hydrophobic or hydrophilic depending on their charge or polarity characteristics. Among the hydrophilic functional groups is the carboxyl group found in amino acids, some amino acid side chains, and the fatty acids that form triglycerides and phospholipids. Answer C. Figure 1. This means that carbon atoms, bonded to other carbon atoms or other elements, form the fundamental components of many, if not most, of the molecules found uniquely in living things. Living things are carbon-based because carbon plays such a prominent role in the chemistry of living things. Use this quiz to check your understanding and decide whether to 1 study the previous section further or 2 move on to the next section.
Figure 1. Carbon can form four covalent bonds to create an organic molecule. The simplest carbon molecule is methane CH 4 , depicted here.
The simplest organic carbon molecule is methane CH 4 , in which four hydrogen atoms bind to a carbon atom Figure 1. How do chemical bonds affect the properties of a substance? Examples of biological molecules that incorporate the benzene ring include some amino acids and cholesterol and its derivatives, including the hormones estrogen and testosterone. Carbon has four electrons in its outermost shell and can form four bonds. The macromolecules are a subset of organic molecules any carbon-containing liquid, solid, or gas that are especially important for life. Improve this page Learn More. Use this quiz to check your understanding and decide whether to 1 study the previous section further or 2 move on to the next section. Only the L-forms of amino acids are used to make proteins. How do chemical bonds affect metabolism? On the other hand, triglycerides with trans double bonds popularly called trans fats , have relatively linear fatty acids that are able to pack tightly together at room temperature and form solid fats. Geometric isomers , on the other hand, have similar placements of their covalent bonds but differ in how these bonds are made to the surrounding atoms, especially in carbon-to-carbon double bonds.

0 thoughts on “How many covalent bonds can carbon form”