Which of these is an extensive property of a substance
You agree to mow someone's lawn for twenty dollars it's a fairly large yard. Some properties of matter depend on the size of the sample, while some do not. An extensive property is a property that depends on the amount of matter in a sample.
One of the ways we can describe chemical substances is with extensive and intensive properties. This video will teach you about the difference between these two terms. You will also see some examples of each, and you'll have a chance to practice what you've learned at the end of the video. These are properties of a substance which are characteristic to the substance and it's identity. Intensive properties are dependent on the matter that substances are made of. Intensive properties vary between different substances.
Which of these is an extensive property of a substance
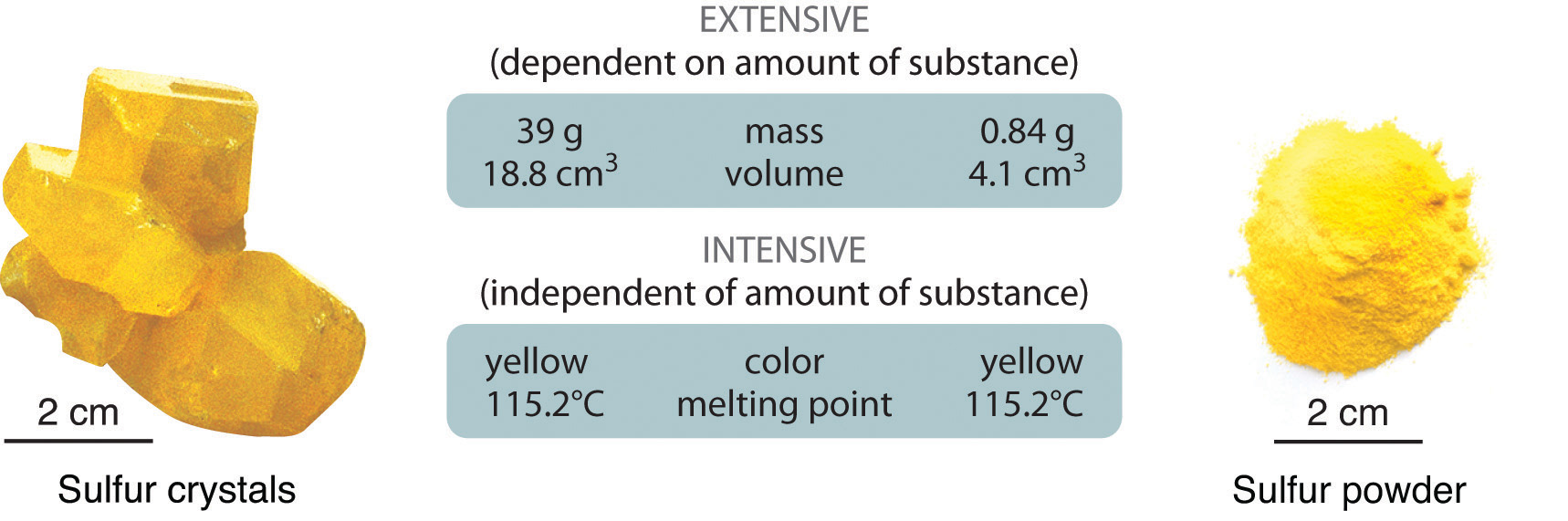
Physical or chemical properties of materials and systems can often be categorized as being either intensive or extensive , according to how the property changes when the size or extent of the system changes. The terms "intensive and extensive quantities" were introduced into physics by German mathematician Georg Helm in , and by American physicist and chemist Richard C. Tolman in By contrast, an extensive property or extensive quantity is one whose magnitude is additive for subsystems. Not all properties of matter fall into these two categories. For example, the square root of the volume is neither intensive nor extensive. An intensive property is a physical quantity whose value does not depend on the amount of substance which was measured. The most obvious intensive quantities are ratios of extensive quantities. In a homogeneous system divided into two halves, all its extensive properties, in particular its volume and its mass, are divided into two halves. All its intensive properties, such as the mass per volume mass density or volume per mass specific volume , must remain the same in each half. The temperature of a system in thermal equilibrium is the same as the temperature of any part of it, so temperature is an intensive quantity. If the system is divided by a wall that is permeable to heat or to matter, the temperature of each subsystem is identical. Additionally, the boiling temperature of a substance is an intensive property.
The same milk is in each container.
The characteristics that enable us to distinguish one substance from another are called properties. A physical property is a characteristic of matter that is not associated with a change in its chemical composition. Familiar examples of physical properties include density, color, hardness, melting and boiling points, and electrical conductivity. We can observe some physical properties, such as density and color, without changing the physical state of the matter observed. Other physical properties, such as the melting temperature of iron or the freezing temperature of water, can only be observed as matter undergoes a physical change. A physical change is a change in the state or properties of matter without any accompanying change in its chemical composition the identities of the substances contained in the matter. We observe a physical change when wax melts, when sugar dissolves in coffee, and when steam condenses into liquid water Figure 1.
Intensive properties and extensive properties are types of physical properties of matter. The terms intensive and extensive were first described by physical chemist and physicist Richard C. Tolman in Here's a look at what intensive and extensive properties are, examples of them, and how to tell them apart. Intensive properties are bulk properties, which means they do not depend on the amount of matter that is present. Examples of intensive properties include:. Intensive properties can be used to help identify a sample because these characteristics do not depend on the amount of sample, nor do they change according to conditions.
Which of these is an extensive property of a substance
You agree to mow someone's lawn for twenty dollars it's a fairly large yard. Some properties of matter depend on the size of the sample, while some do not. An extensive property is a property that depends on the amount of matter in a sample. The mass of an object is a measure of the amount of matter that an object contains. A small sample of a certain type of matter will have a small mass, while a larger sample will have a greater mass.
Manisha koirala leaked
Additionally, the boiling temperature of a substance is an intensive property. The classical Carnot heat engine. A drop of hot cooking oil spattered on your arm causes brief, minor discomfort, whereas a pot of hot oil yields severe burns. ISBN X. Note: Conjugate variables in italics. For example, the base quantities [10] mass and volume can be combined to give the derived quantity [11] density. Physical vs. These properties can vary, but they do not change the identity of the diamond. Skip to main content. We can identify sets of elements that exhibit common behaviors.
The two types of physical properties of matter are intensive properties and extensive properties. Here is the definition of an extensive property in chemistry.
All its intensive properties, such as the mass per volume mass density or volume per mass specific volume , must remain the same in each half. Summary An extensive property is a property that depends on the amount of matter in a sample. A drop of hot cooking oil spattered on your arm causes brief, minor discomfort, whereas a pot of hot oil yields severe burns. Classical Statistical Chemical Quantum thermodynamics. Search for:. Dividing one extensive property by another extensive property generally gives an intensive value—for example: mass extensive divided by volume extensive gives density intensive. The formation of rust is a chemical change because rust is a different kind of matter than the iron, oxygen, and water present before the rust formed. Let's consider our diamond again. The copper wire shown in the picture below has a certain electrical conductivity. You will learn more about the periodic table as you continue your study of chemistry.

0 thoughts on “Which of these is an extensive property of a substance”