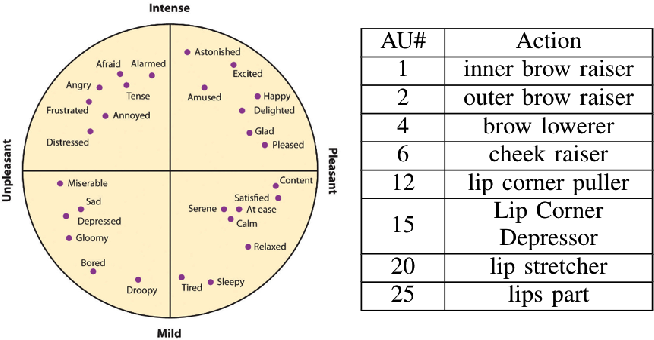
Valence and arousal
The main prediction of the Uncanny Valley Hypothesis UVH is that observation of humanlike characters valence and arousal are difficult to distinguish from the human counterpart will evoke a state of negative affect, valence and arousal. LPP and EMG provided direct psychophysiological indices of affective state during passive observation and the SAM provided self-reported indices of affective state during explicit cognitive evaluation of static facial stimuli.
Thank you for visiting nature. You are using a browser version with limited support for CSS. To obtain the best experience, we recommend you use a more up to date browser or turn off compatibility mode in Internet Explorer. In the meantime, to ensure continued support, we are displaying the site without styles and JavaScript. Since discrete emotional classes such as anger, happiness, sadness and so on are not representative of the full spectrum of emotions displayed by humans on a daily basis, psychologists typically rely on dimensional measures, namely valence how positive the emotional display is and arousal how calming or exciting the emotional display looks like.
Valence and arousal
Thank you for visiting nature. You are using a browser version with limited support for CSS. To obtain the best experience, we recommend you use a more up to date browser or turn off compatibility mode in Internet Explorer. In the meantime, to ensure continued support, we are displaying the site without styles and JavaScript. The built environment represents the stage surrounding our everyday life activities. To investigate how architectural design impacts individuals' affective states, we measured subjective judgments of perceived valence pleasant and unpleasant and arousal after the dynamic experience of a progressive change of macro visuospatial dimensions of virtual spaces. To this aim, we developed a parametric model that allowed us to create 54 virtual architectural designs characterized by a progressive change of sidewalls distance, ceiling and windows height, and color of the environment. Decreasing sidewalls distance, ceiling height variation, and increasing windows height significantly affected the participants' emotional state within virtual environments. Indeed, such architectural designs generated high arousing and unpleasant states according to subjective judgment. Overall, we observed that valence and arousal scores are affected by all the dynamic form factors which modulated the spaciousness of the surrounding. Showing that the dynamic experience of virtual environments enables the possibility of measuring the emotional impact of macro spatial architectural features, the present findings may lay the groundwork for future experiments investigating the effects that the architectural design has on individuals' mental state as a fundamental factor for the creation of future spaces. A crucial but largely unexplored issue of human experience concerns how affective states are influenced by the dynamical change of spatial features when walking through a built environment. Previous studies using static 2D representations showed that several architectural features massively impact the observer's affective states, typically measured in valence and arousal 1. Valence represents the extent to which an architectural space makes an occupant feel good or bad.
Toward a general psychobiological theory of emotions.
Federal government websites often end in. The site is secure. A growing body of literature shows that the emotional content of verbal material affects reading, wherein emotional words are given processing priority compared to neutral words. Human emotions can be conceptualised within a two-dimensional model comprised of emotional valence and arousal intensity. These variables are at least in part distinct, but recent studies report interactive effects during implicit emotion processing and relate these to stimulus-evoked approach-withdrawal tendencies.
Federal government websites often end in. The site is secure. Several theories conceptualise emotions along two main dimensions: valence a continuum from negative to positive and arousal a continuum that varies from low to high. These dimensions are typically treated as independent in many neuroimaging experiments, yet recent behavioural findings suggest that they are actually interdependent. This result has impact on neuroimaging design, analysis and theoretical development. We were interested in determining the extent of this interdependence both behaviourally and neuroanatomically, as well as teasing apart any activation that is specific to each dimension. While we found extensive overlap in activation for each dimension in traditional emotion areas bilateral insulae, orbitofrontal cortex, amygdalae , we also found activation specific to each dimension with characteristic relationships between modulations of these dimensions and BOLD signal change. Increases in arousal ratings were related to increased activations predominantly in voice-sensitive cortices after variance explained by valence had been removed.
Valence and arousal
Federal government websites often end in. The site is secure. The circumplex model of affect proposes that all affective states arise from cognitive interpretations of core neural sensations that are the product of two independent neurophysiological systems. This model stands in contrast to theories of basic emotions, which posit that a discrete and independent neural system subserves every emotion. We propose that basic emotion theories no longer explain adequately the vast number of empirical observations from studies in affective neuroscience, and we suggest that a conceptual shift is needed in the empirical approaches taken to the study of emotion and affective psychopathologies. The circumplex model of affect is more consistent with many recent findings from behavioral, cognitive neuroscience, neuroimaging, and developmental studies of affect. Moreover, the model offers new theoretical and empirical approaches to studying the development of affective disorders as well as the genetic and cognitive underpinnings of affective processing within the central nervous system. The reigning experimental paradigm in affective neuroscience research posits that emotions can be divided into discrete and independent categories and that specific neural structures and pathways subserve each of these emotional categories. This theory of basic emotions has yielded significant advances in the understanding of affect and yet, in the fields of clinical psychology and psychiatry, it has left unsettled many important questions. The theory of basic emotions, for example, has not explained the near ubiquitous comorbid illnesses among mood disorders, nor has it resolved confusion over the neurophysiological underpinnings of affective disorders.
At&t 30 dollar plan
As an alternative to ad hoc scales, and in keeping with the foregoing considerations on arousal and valence, well-validated measures such as the Self-Assessment Manikin SAM , e. All participants were native or fluent speakers of Standard German, consistently right-handed Annett, , and had no previous experience designing or modifying computer-generated characters in, for example, virtual reality-based role-playing games, second life, or virtual reality environments, or experience using such environments e. Weinberg, A. Lewis and J. This is likely one reason we see increased rates of anxiety among people with alexithymia. Erlbaum; Hillsdale, NJ: Franz, G. Hence, each design was proposed in two colors: a warm reddish and cold bluish. Figure 4. Too real for comfort? It has been suggested that this difference might relate to the use of novel and thus salient perceptual information as a readily identifiable feature of avatar faces e. You will use a scale to rate how you felt while reading each word.
Federal government websites often end in.
Arousal, on the other hand, is still thought of as a linear continuum with activations increasing with increased arousal ratings. Immersive virtual environments versus physical built environments: A benchmarking study for building design and user-built environment explorations. Similar effects might apply for the psychophysiological and for the SAM-based measures of valence and arousal. The results provide no support for the notion that category ambiguity along the DHL is specifically associated with enhanced experience of negative affect. Hum Comput Stud. Not all negative words slow down lexical decision and naming speed: Importance of word arousal. The code was written by A. Neural systems subserving valence and arousal during the experience of induced emotion. Error bars represent standard errors of the mean. No significant difference among valence scores was observed for the factor Color. Furlanello, T. Guidelines for human electromyographic research. Neural correlates of processing valence and arousal in affective words. Data collection began on March 14, , and was completed May 30, Sci Rep 12 ,

0 thoughts on “Valence and arousal”