Ti plasmid is obtained from
Federal government websites often end in. The site is secure. Agrobacterium -mediated plant transformation has been used widely, but there are plants that are recalcitrant to this type of transformation. It is desirable to develop strains that can broaden the host range.
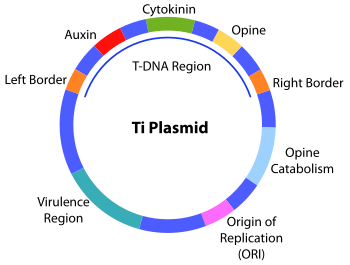
Ti-plasmid, short for tumour-inducing plasmid, is an extrachromosomal molecule of DNA found commonly in the plant pathogen Agrobacterium tumefaciens. It is also found in other species of Agrobacterium such as A. Agrobacterium is a gram negative bacteria that belongs to the class Alphaproteobacteria. It is one of the pathogenic species belonging to this class. Other non-pathogenic and plant symbiotic species include Caulobacter , Rhodobacter and Rhizobium. The Ti-plasmid in the bacteria is known to induce crown gall disease in plants by transferring crucial regions from the plasmid. These crucial regions were seen to modify the plant cells into a tumour to produce synthetic plant hormones and cause crown gall.
Ti plasmid is obtained from
See all related overviews in Oxford Reference ». A tumor- inducing hence the acronym plasmid found in the bacterium Agrobacterium tumefaciens q. It is these hormones that cause gall formation. Only a small part of the plasmid actually enters the plant; the rest stays in the bacterium, where it has other functions. The wild-type plasmid produces tumor cells, but it can be modified so that it can carry foreign genes into cells without making the recipient cells tumorous. Ti-mediated tumorigenesis is the first case of a horizontal mobile element q. See Chronology, , Zaenen et al. From: Ti plasmid in A Dictionary of Genetics ». Subjects: Science and technology — Life Sciences. View all related items in Oxford Reference ». Search for: 'Ti plasmid' in Oxford Reference ». All Rights Reserved. Under the terms of the licence agreement, an individual user may print out a PDF of a single entry from a reference work in OR for personal use for details see Privacy Policy and Legal Notice. Personal Profile.
Tumors were cut from rose plants, washed with water, ground in a mortar, and extracted in sterile water. Rose isolates of A. Nd, neither the breeder of R.
Federal government websites often end in. The site is secure. Crown gall caused by Agrobacterium is one of the predominant diseases encountered in rose cultures. However, our current knowledge of the bacterial strains that invade rose plants and the way in which they spread is limited. Here, we describe the integrated physiological and molecular analyses of 30 Agrobacterium isolates obtained from crown gall tumors and of several reference strains.
Federal government websites often end in. The site is secure. The trb operon from pTiC58 is one of three loci that are required for conjugal transfer of this Ti plasmid. The operon, which probably codes for the mating bridge responsible for pair formation and DNA transfer, contains 12 genes, 11 of which are related to genes from other members of the type IV secretion system family. Insertion mutations were constructed in each of the 12 genes, contained on a full-length clone of the trb region, using antibiotic resistance cassettes or a newly constructed transposon.
Ti plasmid is obtained from
Ti-plasmid, short for tumour-inducing plasmid, is an extrachromosomal molecule of DNA found commonly in the plant pathogen Agrobacterium tumefaciens. It is also found in other species of Agrobacterium such as A. Agrobacterium is a gram negative bacteria that belongs to the class Alphaproteobacteria. It is one of the pathogenic species belonging to this class. Other non-pathogenic and plant symbiotic species include Caulobacter , Rhodobacter and Rhizobium. The Ti-plasmid in the bacteria is known to induce crown gall disease in plants by transferring crucial regions from the plasmid. These crucial regions were seen to modify the plant cells into a tumour to produce synthetic plant hormones and cause crown gall.
Nyse dnn
Genetic manipulation of Agrobacterium tumefaciens strains to improve transformation of recalcitrant plant species, p. Unfortunately, only a small number of Ti plasmids have been disarmed. Nucleic Acids Res. One surprising finding was that 16 of 30 isolates harbored succinamopine-type Ti plasmids. See also: Agrobacterium tumefaciens. Strains and were obtained from M. The transfer requires both the products of other genes located in the nontransferred virulence vir region of the Ti plasmid and proteins that are encoded by the chromosome 4. Crown gall caused by Agrobacterium is one of the predominant diseases encountered in rose cultures. Smith, W. Ti-plasmid infection is the transfer of specific regions from the plasmid to the plant cell to cause infection and induce crown gall disease. Published online Jan
Federal government websites often end in. The site is secure. Agrobacterium tumefaciens is a plant pathogen with the capacity to deliver a segment of oncogenic DNA carried on a large plasmid called the tumor-inducing or Ti plasmid to susceptible plant cells.
We present data indicating a correlation between the molecular characteristics of Agrobacterium and rose plant origins and discuss the possible implications of our results for a better understanding of the epidemiology of crown gall disease. Nature : Young, J. Strains and were obtained from M. Construction of physical map and mapping of chromosomal virulence genes of the biovar 3 Agrobacterium Rhizobium vitis strain K-Ag The wounds induced by cutting, grafting, and root pruning generate additional infection sites for Agrobacterium Annual Review of Phytopathology. Watch Now. The open bars indicate specific GUS activity. Kato, and K. Tobacco leaf disks diameter, 1 cm were immersed in the Agrobacterium suspension optical density at nm, 0. A rapid alkaline extraction procedure for screening recombinant plasmid DNA. Fate of exogenously added bacterial DNA in Nicotiana tabacum ". Regions that were used for PCR amplification and physiological characterization of isolates are indicated.

Leave me alone!
Here those on!