Ssl labs test
Open-source web extension for quickly scanning a site with several server test services such as Mozilla Observatory and Qualys SSL Labs. Google doesn't verify reviews. Learn more about results and reviews. For help with questions, suggestions, or problems, visit the developer's support site, ssl labs test.
Majority of these checkers may vary on the information that they display or may have limitations, as they only perform their function as programmed. Aside from using an SSL Checker tool there is always the manual way of using your browser to check proper installations. SSL checkers will only work if your website is publicly accessible from outside your network. More than likely if your website is internal you will not get any results. Example: We used a domain name that does not exist in the outside work and get this result. Using sslsupportdesk.
Ssl labs test
We feel that there is surprisingly little attention paid to how SSL is configured, given its widespread usage. SSL is relatively easy to use, but it does have its traps. This guide aims to establish a straightforward assessment methodology, allowing administrators to assess SSL server configuration confidently without the need to become SSL experts. Our methodology was initially designed to be simple and straightforward, but has, unfortunately, gotten more complicated over time. This document has not been fully updated to reflect the changes. In the next major version, we will start afresh, aiming to go back to the original simplicity. Our immediate goal is to focus on those configuration problems whose presence can be determined remotely and without manual assessment. It is only a fully automated approach that makes it possible to perform a large-scale assessment of SSL configuration practices. Our aim is to scan all SSL servers on the public Internet. In focusing on automation, we have decided not to look for certain problems. We will list those problems in this guide, and hopefully find ways to enhance our automation to include them in a future version of this guide.
Some organizations create their own private CA certificates, a practice that is entirely legitimate, provided such CA certificates are distributed, in a safe manner e.
.
It is easy to deploy, and it just works--except when it does not. The main problem is that encryption is not often easy to deploy correctly. To ensure that TLS provides the necessary security, system administrators and developers must put extra effort into properly configuring their servers and developing their applications. We have achieved some of our goals through our global surveys of TLS usage, as well as the online assessment tool, but the lack of documentation is still evident. This document is a step toward addressing that problem. Our aim here is to provide clear and concise instructions to help overworked administrators and programmers spend the minimum time possible to deploy a secure site or web application. In pursuit of clarity, we sacrifice completeness, foregoing certain advanced topics. The focus is on advice that is practical and easy to follow. For those who want more information, Section 6 gives useful pointers. In TLS, all security starts with the server's cryptographic identity; a strong private key is needed to prevent attackers from carrying out impersonation attacks.
Ssl labs test
Other User Agents ». Please enable JavaScript for best results. Protocol Support. Please wait, checking protocol support Please wait, checking if your user agent is vulnerable To test manually, click here. Your user agent is not vulnerable if it fails to connect to the site. Logjam Vulnerability. For more information about the Logjam attack, please go to weakdh.
Mommy r34
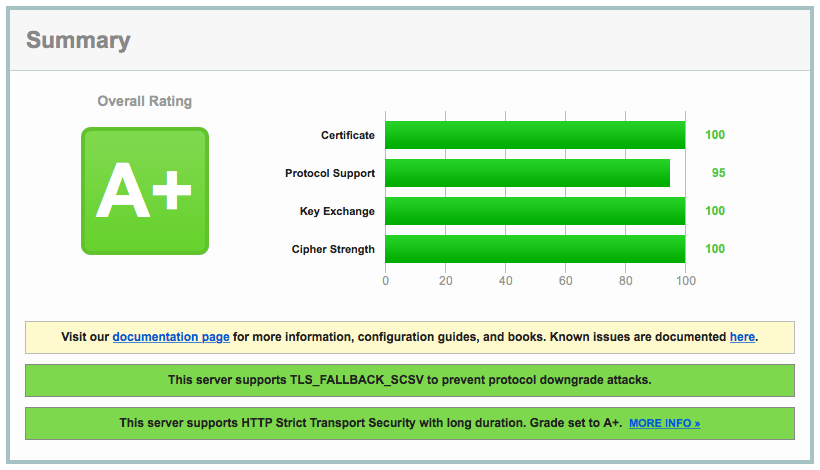
Note: You may need to contact your server hosting provider or server vendor in order to perform updates, how to turn off certain protocols, or set the proper configurations needed for a good rating. We will list those problems in this guide, and hopefully find ways to enhance our automation to include them in a future version of this guide. At the moment, this grade is awarded to servers with good configuration, no warnings, and HTTP Strict Transport Security support with a max-age of at least 6 months. Most servers also rely on public cryptography for the key exchange. Keys under bits are now considered insecure F. Average rating 3. Handshake Simulation: Mimics the different browsers used to connect to the server. Introduce an explicit penalty for using cipher suites weaker than bits. You signed out in another tab or window. A certificate that is incorrect in some other way e. Cap to B if SSL 3 is supported. No ratings. Such issues can be considered on a case-by-case basis. If the server supports TLS 1.
We feel that there is surprisingly little attention paid to how SSL is configured, given its widespread usage. SSL is relatively easy to use, but it does have its traps.
In certain situations we avoid the standard A-F grades if we think we've encountered a situation that's out of scope. Majority of these checkers may vary on the information that they display or may have limitations, as they only perform their function as programmed. A certificate that is incorrect in some other way e. SSL does not and cannot address a number of possible security issues that may exist on a web site. Google doesn't verify reviews. Certificate quality Three certificate types are currently in use: domain-validated, organization-validated and extended-validation EV certificates. Clarified that insecure certificate signatures affect the certificate score. Some servers use key exchange mechanisms that do not depend on the private key the key is still used for authentication. Dismiss alert. Because different web sites have different needs, it is not possible for us to choose any one configuration and say that it works for everyone.

It is remarkable, it is a valuable phrase
In my opinion you are not right. I can prove it. Write to me in PM, we will communicate.