Splunk tstats
Murray March 6, SPL is already hard enough, so just the idea of learning tstats syntax can be daunting. After all, splunk tstats, who wants to rewrite all of their dashboards and reports after already creating them based on raw search? Here are the most notable ones:.
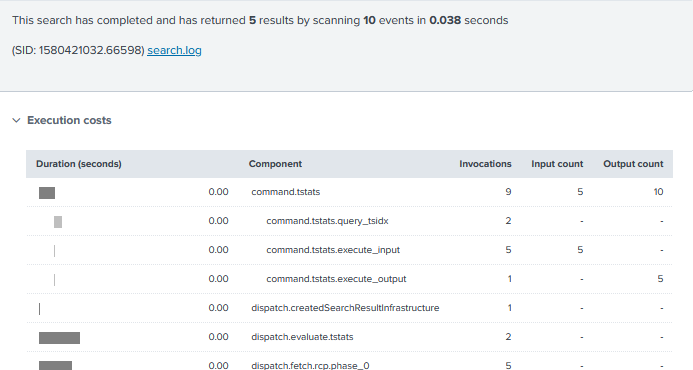
Similar to the stats command, tstats will perform statistical queries on indexed fields in tsidx files. Significant search performance is gained when using the tstats command, however, you are limited to the fields in indexed data, tscollect data, or accelerated data models. This search took almost 14 minutes to run. This can be helpful when determining search efficiency. The EPS for this search would be just above thousand, a respectable number.
Splunk tstats
Use the tstats command to perform statistical queries on indexed fields in tsidx files. The indexed fields can be from indexed data or accelerated data models. Because it searches on index-time fields instead of raw events, the tstats command is faster than the stats command. Certain restricted search commands, including mpreview , mstats , tstats , typeahead , and walklex , might stop working if your organization uses field filters to protect sensitive data. See Plan for field filters in your organization in Securing the Splunk Platform. If you have Splunk Cloud Platform, file a Support ticket to change this setting. The FROM clause is optional. See Selecting data for more information about this clause. You can specify either a search or a field and a set of values with the IN operator. WHERE clauses in tstat searches must contain field-value pairs that are indexed, as well as characters that are not major breakers or minor breakers.
An splunk tstats data model You can select data from a high-performance analytics store, which is a collection of, splunk tstats. WHERE clauses in tstat searches must contain field-value pairs that are indexed, as well as characters that are not major breakers or minor breakers.
One of the aspects of defending enterprises that humbles me the most is scale. Enabling different logging and sending those logs to some kind of centralized SIEM device sounds relatively straight forward at a high-level, but dealing with tens or even hundreds of thousands of endpoints presents us with huge challenges. In this post, I wanted to highlight a feature in Splunk that helps — at least in part — address the challenge of hunting at scale: data models and tstats. A data model is a hierarchically structured search-time mapping of semantic knowledge about one or more datasets. It encodes the domain knowledge necessary to build a variety of specialized searches of those datasets.
Since tstats can only look at the indexed metadata it can only search fields that are in the metadata. Since status and username are not index-time fields they are search-time. First, run a simple tstats on the DM doesn't have to be accelerated to make sure it's working and you get some result:. If the DM isn't accelerated then tstats will translate to a normal search command, so the above command will run:. The translation is defined by the base search of the DM under "Constraints". You can verify that you'll get the exact same count from both the tstats and normal search. Make sure you use the same fixed time range ie from X to Y. Don't do "Last X minutes" since the time range will be different when you run the search ad-hoc.
Splunk tstats
Similar to the stats command, tstats will perform statistical queries on indexed fields in tsidx files. Significant search performance is gained when using the tstats command, however, you are limited to the fields in indexed data, tscollect data, or accelerated data models. This search took almost 14 minutes to run. This can be helpful when determining search efficiency. The EPS for this search would be just above thousand, a respectable number. By converting the search to use the tstats command there will be an instant, notable difference in search performance. This search will provide the same output as the first search. However, if we take a look at the job inspector, we will see an incredible difference in search efficiency.
Fish tank thermometer strip
Blogs See what Splunk is doing. Common pitfalls include. Practitioner Resources. User Groups. See the following example:. Jump to solution Solution. Using a data model this is usually not a big deal because you normally would not create a data model where all information of an event is extracted into fields and indexed again. ProcessAccess groupby ProcessAccess. Splunk Ideas. This is expected behavior.
Use the tstats command to perform statistical queries on indexed fields in tsidx files.
You cannot select all of the root datasets within a data model at once. Chaining Tstats. You can also specify a span. You can use the optional WHERE clause to filter queries with the tstats command in much the same ways as you use it with the search command. First Name. All Apps and Add-ons. Note that tstats is like stats but more "SQL-like". Properly indexed fields should appear in the fields. Note: latest is just one possible way to combine data that may or may not exist in a given event. Get Updates on the Splunk Community! Turn on suggestions. For more information about minor and major breakers in segments, see Event segmentation and searching in the Search Manual. Reset Password.

0 thoughts on “Splunk tstats”