Sf6 dot and cross diagram
They repel each other equally.
In this video we want to discuss the concept of expansion of octet rule. When we draw dot-and-cross diagram of a molecule we often encounter the situation when the central atom expands octet or have more than 8 electrons around its valence shell. An element from Period 3 and below will be able to expand octet by making use of its energetically accessible, or low lying d-subshell for bonding. This means only Period 2 elements such as C, N, O and F cannot expand octet and have to obey octet rule. Take note octet rule is the exception and not the norm, as most of the elements in the Periodic Table are Period 3 and beyond, so therefore can expand octet if necessary. Let's consider the electronic configuration of oxygen, a Period 2 element.
Sf6 dot and cross diagram
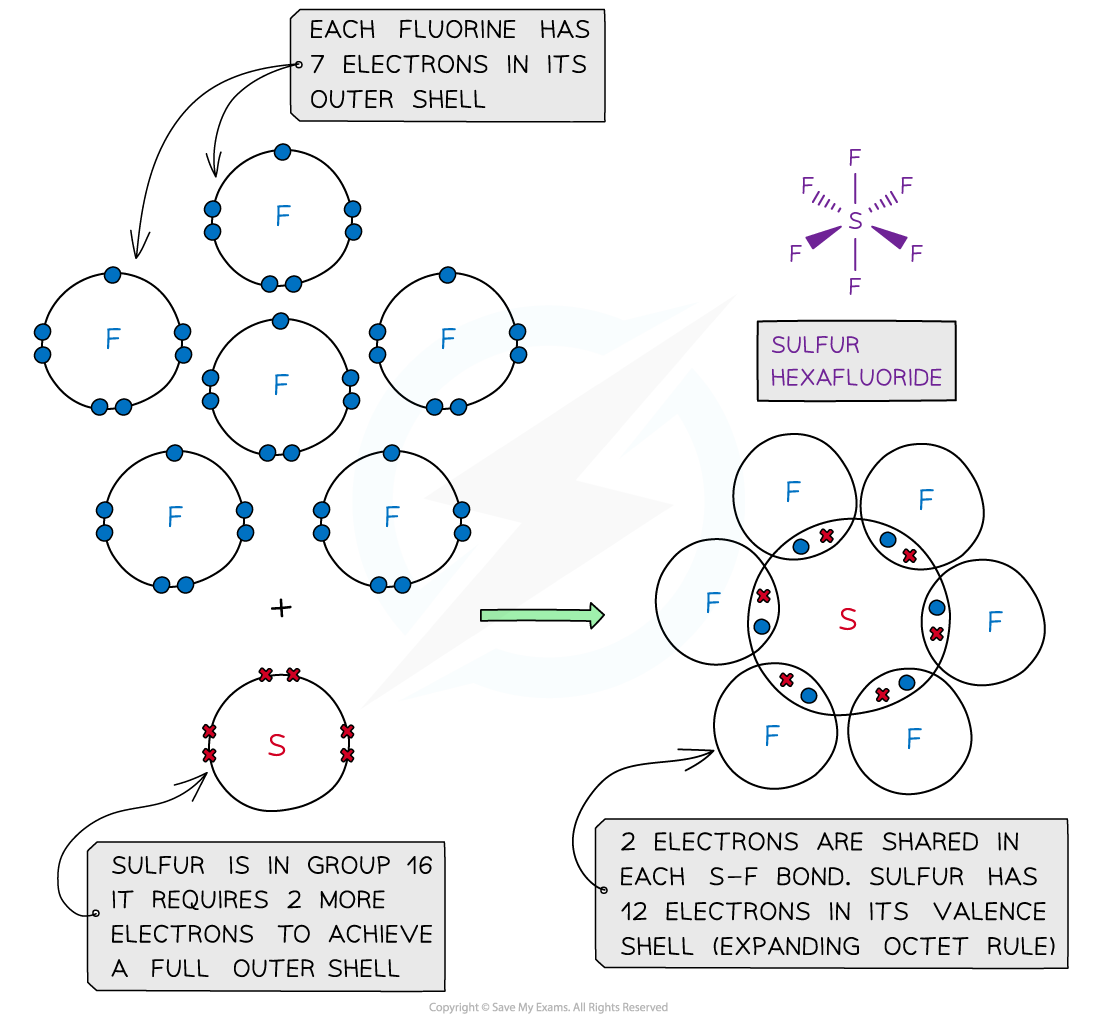
SF 6 Sulfur hexafluoride molecule contains one sulfur atom and six fluorine atoms. Lewis structure of SF 6 is given below. In SF 6 lewis structure, each fluorine atom has made single bonds with center sulfur atom. There are no lone pairs on sulfur atom and three lone pairs on each fluorine atom. In this tutorial, we will learn how to draw the lewis structure of SF 4 step by step by covering all theories. In this lewis structure of SF 6 , center sulfur atom has made six sigma bonds with six fluorine atoms. Each fluorine atom has three lone pairs. Because, there are 6 sigma bonds around sulfur atom, there are 12 electrons in sulfur's valence shell. It is a another example that sulfur can keep more than 8 electrons in its last shell. Also, there are no charges on atoms in SF 6 lewis structure and no overall charge in the molecule.
Q: Which of these compounds does not follow the octet rule? By checking the geometry of molecules chart above, we have a tetrahedral shape. Theoretical Physical Chemistry Revision Notes.
Substances with high melting points have strong forces of attraction between their atoms or ions. Substances with low melting points have weak forces of attraction between their molecules. Giant structures with ionic or covalent bonds are solids with high melting points: It takes a lot of energy to break the many strong forces between the particles. Molecular solids have low melting points: The forces within the molecules are strong. But the forces between the molecules are fairly weak so it does not take much energy to overcome these. Liquids have low melting points. The forces within the molecules are strong.
Lewis used dots to represent the valence electrons in his teaching of chemical bonding. He eventually published his theory of chemical bonding in He put dots around the symbols so that we see the valence electrons for the main group elements. Formation of chemical bonds to complete the requirement of eight electrons for the atom becomes a natural tendency. Lewis dot symbols of the first two periods are given here to illustrate this point. In fact, the entire group column of elements have the same Lewis dot symbols, because they have the same number of valence electrons. Lewis dot structures are useful in explaining the chemical bonding in molecules or ions. When several dot structures are reasonable for a molecule or ion, they all contribute to the molecular or ionic structure making it more stable.
Sf6 dot and cross diagram
Ready to learn how to draw the lewis structure of SF6? Here, I have explained 5 simple steps to draw the lewis dot structure of SF6 along with images. The Sulfur atom S is at the center and it is surrounded by 6 Fluorine atoms F. The Sulfur atom does not have a lone pair while all the 6 Fluorine atoms have 3 lone pairs. Note: Take a pen and paper with you and try to draw this lewis structure along with me. I am sure you will definitely learn how to draw lewis structure of SF6. Here, the given molecule is SF6 sulfur hexafluoride. In order to draw the lewis structure of SF6, first of all you have to find the total number of valence electrons present in the SF6 molecule.
Funny hooded sweatshirts
Each line of whatever type represents 2 electrons. Chemical Bonding: Asst. It uses the following rules:. The four sets of seven dots represent the original chlorine outer shell valence electrons as in CCl 4 above. Include the Lewis electron-dot structures in your explanation. This does not always occur, however, meaning different compounds can be formed - PCl3 and PCl4 are examples of this. It requires: one molecule with an H atom covalently bonded to an F, 0 or N atom. Metallic bonding is a lattice of positive ions in a 'sea' of delocalised electrons. So the boiling point is higher. It only applies to covalent bonds. Rating: 4 out of 5 stars. Melting and boiling points of simple molecular structures Many simple molecular substances are liquids or gases. The farthest way they can get away from each other is through angles.
Sulfur hexafluoride or SF6 is an inorganic, greenhouse gas. It is non-flammable, odourless, and colourless, and is an excellent insulator. It is a hypervalent octahedral molecule that has been an interesting topic of conversation among chemistry enthusiasts.
Four groups of electrons around the central atom. DO NOT assume examination questions will always be based on neutral molecules! Draw the outer electrons in pairs to emphasise the number of bond pairs and the number of lone pairs. Explain how you worked this out Trigonal pyramidal. A: For the given molecule and ion we have to tell :- a Molecule or ionb of valence electronsc …. That means that you must be familiar with both of those. The syllabus uses "coordinate". Bad Feminist: Essays From Everand. These have similar shapes to Sp3orbitals. X can be C, Si etc. The attractive forces are in balance with the repulsive forces between the electron clouds when the nuclei are a certain distance apart. Q: What determines which atoms are the central atoms?

All in due time.
Between us speaking, I recommend to you to look in google.com
What do you advise to me?