Schwann cell
Federal government websites often end in. Schwann cell site is secure. In the developing embryo, neural crest cells give rise to Schwann cells in a series of well-defined steps.
Schwann cells or neurolemmocytes named after German physiologist Theodor Schwann are the principal glia of the peripheral nervous system PNS. Glial cells function to support neurons and in the PNS, also include satellite cells , olfactory ensheathing cells , enteric glia and glia that reside at sensory nerve endings, such as the Pacinian corpuscle. The two types of Schwann cells are myelinating and nonmyelinating. The Schwann cell promoter is present in the downstream region of the human dystrophin gene that gives shortened transcript that are again synthesized in a tissue-specific manner. During the development of the PNS, the regulatory mechanisms of myelination are controlled by feedforward interaction of specific genes, influencing transcriptional cascades and shaping the morphology of the myelinated nerve fibers.
Schwann cell
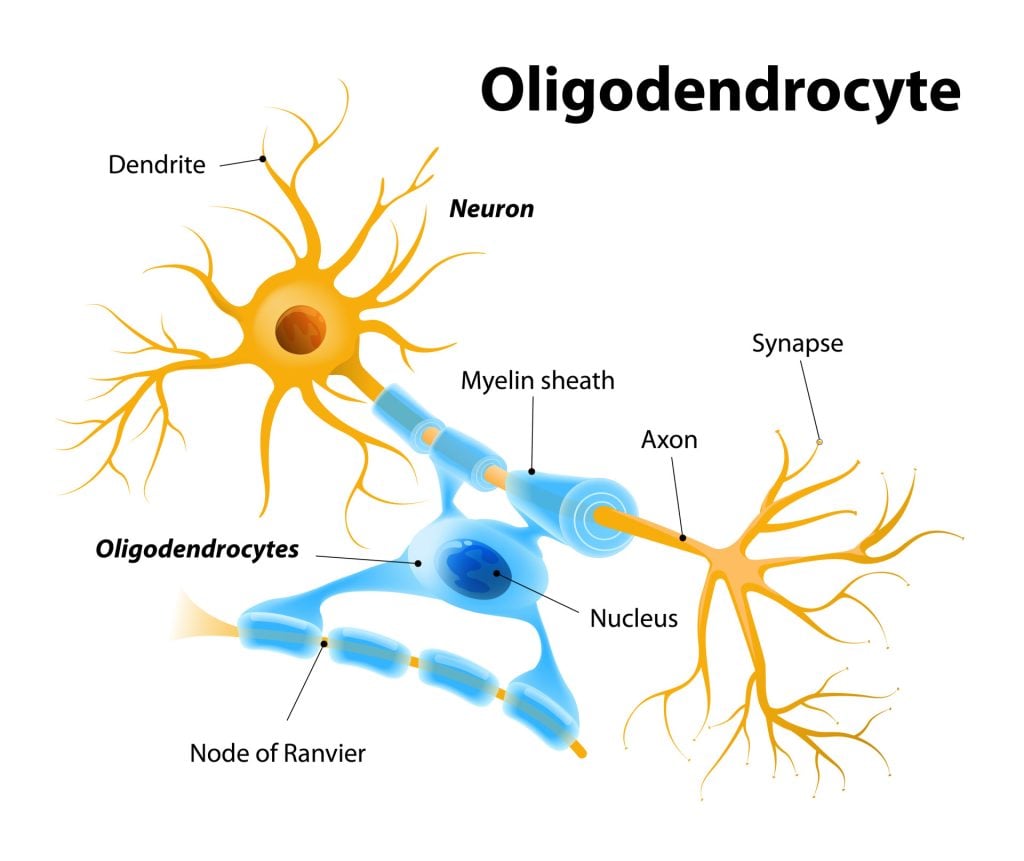
Federal government websites often end in. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you're on a federal government site. The site is secure. NCBI Bookshelf. Matthew Fallon ; Prasanna Tadi. Authors Matthew Fallon ; Prasanna Tadi 1. Schwann cells embryologically derive from the neural crest. They myelinate peripheral nerves and serve as the primary glial cells of the peripheral nervous system PNS , insulating and providing nutrients to axons. Myelination increases conduction velocity along the axon, allowing for the saltatory conduction of impulses. Each Schwann cell makes up a single myelin sheath on a peripheral axon, with each ensuing myelin sheath made by a different Schwann cell, such that numerous Schwann cells are needed to myelinate the length of an axon. This arrangement is in contrast to oligodendrocytes, the myelinating cell of the central nervous system CNS , which form myelin sheaths for multiple surrounding axons. Schwann cells are surrounded by a basal lamina, while oligodendrocytes are not. Between adjacent myelin sheaths, there are gaps of approximately 1 micrometer, called nodes of Ranvier. There is a concentration of voltage-gated sodium channels at the node, which is the site of saltatory conduction. They contain a high density of gap junctions and other cell junctions, serving a role in communication and maintenance of the Schwann cell.
Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you're on a federal government site. Salzer JL. Role of N-cadherin in Schwann cell schwann cell of growing nerves.
.
If you're seeing this message, it means we're having trouble loading external resources on our website. To log in and use all the features of Khan Academy, please enable JavaScript in your browser. Donate Log in Sign up Search for courses, skills, and videos. Neural cell types. About About this video Transcript. This video describes the structure and function of Schwann cells. Schwann cells are a type of cell that support nerve cells.
Schwann cell
Schwann cells are named after Theodor Schwann, a German physiologist who discovered these types of cells in the 19th century. Schwann cell, also called neurilemma cell, are a type of large neurological cell responsible for forming the myelin sheath around the neurons of the peripheral nervous system , and supplying nutrients to individual axons. Myelin sheath functions to insulate and protect the axons of neurons and is, therefore, important for enhancing the transmission of electrical impulses. Each Schwann cell comprises a single myelin sheath on an axon. Therefore, numerous Schwann cells are required to myelinate the length of an axon. However, Schwann cells can be either myelinating or non-myelinating.
Tpa3116d2
Correspondence: Email: ku. The diagram shows both developmental and injury-induced transitions. CMT1 is characterized by segmental demyelination and remyelination, causing onion skin appearance on biopsy, and greatly reduced conduction velocity of nerves. Pax3: A paired domain gene as a regulator in PNS myelination. Brain Behav Immun 21 : — This review describes the signals that control the embryonic phase of this process and the organogenesis of peripheral nerves. Neuron 83 : — What Drives Schwann Cell Proliferation? Mol Neurobiol. You are not required to obtain permission to distribute this article, provided that you credit the author and journal. It is often associated with a preceding infection of the gastrointestinal or respiratory tract, particularly C. Gene profiling and bioinformatics analysis of Schwann cell embryonic development and myelination. PMC Microscopy, Light Under light microscopy, Schwann cell nuclei and myelin sheath are visible, as well as their basal laminae and associated axons. Cell Rep 5 : —
Federal government websites often end in. The site is secure.
The PNS has satellite cells and Schwann cells. Invariant mantling of growth cones by Schwann cell precursors characterize growing peripheral nerve fronts. Schwann cell—specific Notch inactivation results in a substantial reduction in DNA synthesis and Schwann cell numbers in neonatal nerves Woodhoo et al. Epoxy is preferable for smaller nerve branches and visualization with electron microscopy. Diminished Schwann cell repair responses underlie age-associated impaired axonal regeneration. Nat Rev Neurosci 6 : — Am J Pathol. The two types of Schwann cells are myelinating and nonmyelinating. Rescue of the cardiac defect in ErbB2 mutant mice reveals essential roles of ErbB2 in peripheral nervous system development. These columns form tracks from the injury site to the nerve target areas, with the Bungner Schwann cells providing essential substrate and guidance cues for regenerating axons Fig.

In it something is. Thanks for the help in this question. I did not know it.
You have hit the mark. It is excellent thought. I support you.