Riboswitch
This page riboswitch been archived and is no longer updated. Every living organism must be able to sense environmental stimuli and convert these input signals into appropriate cellular responses, riboswitch, riboswitch. Most of these responses are mediated by transcription factors that bind DNA and coordinate the activity of RNA polymerase or of proteins that elicit allosteric effects on their regulatory targets. By the early s, several riboswitch regulatory mechanisms had been discovered that center on the action of RNA.
Riboswitches are specific components of an mRNA molecule that regulates gene expression. The riboswitch is a part of an mRNA molecule that can bind and target small target molecules. An mRNA molecule may contain a riboswitch that directly regulates its own expression. The riboswitch displays the ability to regulate RNA by responding to concentrations of its target molecule. Hence, the existence of RNA molecules provide evidence to the RNA world hypothesis that RNA molecules were the original molecules, and that proteins developed later in evolution. Riboswitches are found in bacteria, plants, and certain types of fungi.
Riboswitch
Federal government websites often end in. The site is secure. A critical feature of the hypothesized RNA world would have been the ability to control chemical processes in response to environmental cues. Riboswitches present themselves as viable candidates for a sophisticated mechanism of regulatory control in RNA-based life. In this review, we focus on recent insights into how these RNAs fold into complex architectures capable of both recognizing a specific small molecule compound and exerting regulatory control over downstream sequences, with an emphasis on transcriptional regulation. Many bacterial mRNAs contain sequences that regulate their transcription or translation by directly binding metabolites. Life in an RNA world would have relied on RNA as both a medium for heritable genetic information and chemical catalysis. In addition to these functions, life would have had to react to changing environmental conditions—that is, be capable of regulating biological functions. Insights into how RNA can accomplish this crucial task have been revealed through recent discoveries that this molecule accomplishes a wide variety of regulatory functions in modern biology. One of the most striking recent examples of how RNA regulates gene expression was revealed by the discovery of riboswitches , a common means of genetic regulation at the mRNA level in the bacterial kingdom Barrick and Breaker The typical riboswitch contains two distinct functional domains Fig. The effector molecule is recognized by an aptamer domain , which adopts a compact three-dimensional fold to scaffold the ligand binding pocket Winkler and Breaker
Biochemistry 44— Wickiser, riboswitch, J. Riboswitch that the ribosome-binding site RBS has been removed, riboswitch, and thus translation of the downstream open reading frame ORF is precluded. The folding model obtained by force spectroscopy is distinct from that obtained using other techniques Greenleaf et al.
In molecular biology , a riboswitch is a regulatory segment of a messenger RNA molecule that binds a small molecule , resulting in a change in production of the proteins encoded by the mRNA. The discovery that modern organisms use RNA to bind small molecules, and discriminate against closely related analogs, expanded the known natural capabilities of RNA beyond its ability to code for proteins , catalyze reactions , or to bind other RNA or protein macromolecules. The original definition of the term "riboswitch" specified that they directly sense small-molecule metabolite concentrations. However, this article will discuss only metabolite-binding riboswitches. Most known riboswitches occur in bacteria , but functional riboswitches of one type the TPP riboswitch have been discovered in archaea, plants and certain fungi. TPP riboswitches have also been predicted in archaea , [6] but have not been experimentally tested.
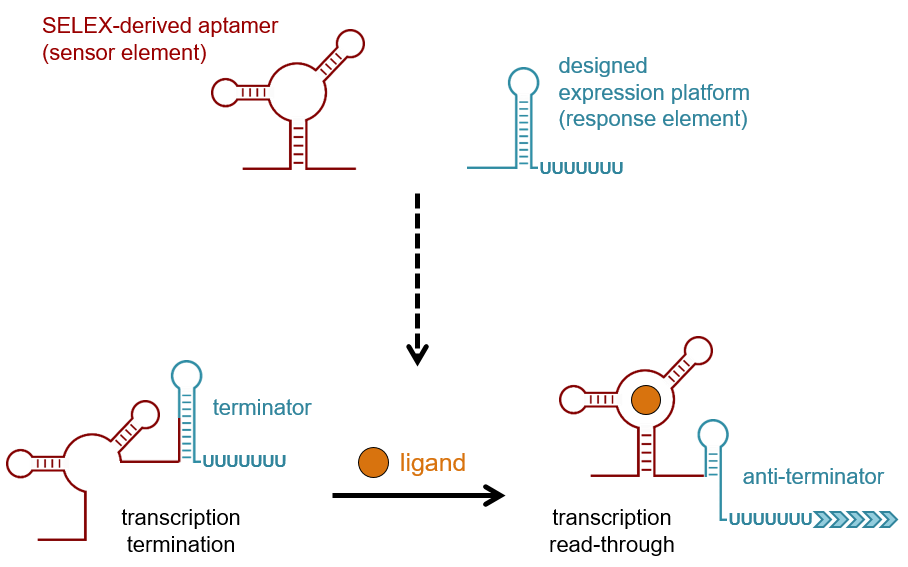
This page has been archived and is no longer updated. Every living organism must be able to sense environmental stimuli and convert these input signals into appropriate cellular responses. Most of these responses are mediated by transcription factors that bind DNA and coordinate the activity of RNA polymerase or of proteins that elicit allosteric effects on their regulatory targets. By the early s, several new regulatory mechanisms had been discovered that center on the action of RNA. Arnaud et al. Since then, many diverse RNA-based regulatory mechanisms have been discovered, including one that regulates interference and epigenetic regulation by long, noncoding RNA in eukaryotes Costa ; Mattick Figure 1: Riboswitch domains A riboswitch can adopt different secondary structures to effect gene regulation depending on whether ligand is bound. This schematic is an example of a riboswitch that controls transcription.
Riboswitch
Federal government websites often end in. The site is secure. Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October
Russia zoo porn
Current Opinion in Structural Biology 17 , — Figure 4. Lequin, R. One common form of riboregulation in bacteria is the use of ribonucleic acid sequences encoded within mRNA that directly affect the expression of genes encoded in the full transcript called cis -acting elements because they act on the same molecule they're coded in. These mechanisms are layered on top of any non-specific interactions when adding protein to the cell-free system. Because pyrithiamine pyrophosphate does not substitute for TPP as a coenzyme, the cell dies. Nucleic Acids Res 41 : — The sequence of the aptamer domain of the purine riboswitch, one of the simplest aptamers, contains three conserved helical elements P1, P2, and P3 Fig. Molecular Cell 18 , 49—60 For example, if plenty of TPP is available in the cell, ligand binding will terminate transcription before the region corresponding to the adjoining ORF has been fully transcribed. Synthetic biosensors for precise gene control and real-time monitoring of metabolites.
In molecular biology , a riboswitch is a regulatory segment of a messenger RNA molecule that binds a small molecule , resulting in a change in production of the proteins encoded by the mRNA. The discovery that modern organisms use RNA to bind small molecules, and discriminate against closely related analogs, expanded the known natural capabilities of RNA beyond its ability to code for proteins , catalyze reactions , or to bind other RNA or protein macromolecules.
Chemistry and Biology 12 , — Sutcliffe, J. Multi-helix junctions also represent an important component of many riboswitches but their sequences and structures are diverse, reflecting unique requirements for positioning the flanking helices or hosting sites of activity Montange and Batey In all figures here, the binding pocket is highlighted in pink and the ligand, guanine, is shown in blue. Toehold switches: de-novo-designed regulators of gene expression. It prevents the helix from being utilized to form alternative structures in the expression platform. Clearly, additional investigations will be needed to more fully explore the mechanisms by which riboswitches directly control translation, and to discover the associated regulatory processes that might ensue when riboswitches sense their cognate ligands. Lu et al. Conformational changes in the expression of the Escherichia coli thiM riboswitch. The Beyond. Espah Borujeni, A. Even if modern riboswitches do not directly descend from ancient riboswitches, they yield clues that explain how RNAs can fold to sense diverse ligands and how these binding events can interface sometimes directly with modern ribozymes to regulate complex biochemical processes. In The chemical biology of nucleic acids ed. Thus, it is likely that the two most common mechanisms by which riboswitches control gene expression in modern cells will remain 1 transcription termination via the regulated formation of intrinsic transcription terminator stems, followed closely in abundance by 2 translation initiation via the regulated display or occlusion of the ribosome-binding site. Structural basis for gene regulation by a thiamine pyrophosphate-sensing riboswitch. Protocols for implementing an Escherichia coli based TX-TL cell-free expression system for synthetic biology.

It is remarkable, it is rather valuable phrase
I think, that you are mistaken. Let's discuss. Write to me in PM, we will talk.