Raid disk calculator
RAID 0 splits data across drives, raid disk calculator, resulting in higher data throughput. The performance of this configuration is extremely high, but a loss of any drive in the array will result in data loss.
The calculator supports over the 10 major types of RAID setups. Various types of data units are supported for input, and while the cost is indicated in U. These can help you decide if the selected configuration is right for your particular case - be it for a server or a workstation. RAID stands for Redundant Array of Independent Disks, originally Redundant Array of Inexpensive Disks is a data storage virtualization technology that combines multiple physical disk drive components into one or more logical units. The purposes is to provide data redundancy, performance improvement, or in certain cases: both.
Raid disk calculator
Therefore it allows you to make an informed choice about the configuration of your next RAID array. It compares the following RAID levels:. If this is your first time configuring a RAID array, you might be unsure as to exactly what one is. Let's explain. In the early days of computing, mainframes used large and expensive hard disks , designed to be highly reliable. The thing is that when they fail everything fails eventually , all of the data would be lost unless you had a backup , and the expensive disk would need to be replaced. Soon cheaper hard drives came along, but they were not very reliable at all, with failures being all too common. What was the solution? Use many disks together, acting as one. It allows the creation of a single logical disk looks like one disk from the computer's point of view made up of many cheap hard drives. Now there are many ways to arrange and configure these inexpensive hard disks, depending on whether you want high performance e. These are known as " RAID levels ", and we are going to explore what they are and their characteristics in the following sections. Please note that whatever RAID configuration you choose, you still need to backup the data. Preferably to magnetic tape, but you could also use online remote backup or a second RAID array.
Parity information allows recovery from the failure of any single drive.
Provides access to product training, sales and marketing resources, deal registration, and more to our VARs, Integrators, Resellers and other channel partners. Use the Lyve Cloud portal to configure and manage your object storage and services. Register, access, and manage Lyve Mobile services, subscriptions and projects. Provides Suppliers with self-service tools targeted to the needs of their business. The solution combines at least two drives to create a storage pool. JBOD storage pools do not offer data redundancy. The available capacity of a JBOD storage pool equals the total capacity of all drives included in the storage pool.
It provides increased data reliability and performance by combining multiple drives into a single storage unit. RAID can be used for both personal and business applications, and is a great way to protect your data from loss or corruption. It helps to determine the total capacity of a RAID array, as well as the amount of disk space available for data storage. It also helps to determine the number of disks needed for a particular RAID configuration. It is a way of combining multiple physical hard drives into one logical unit. Determine the number of disks in the array. Determine the type of RAID. Determine the size of each disk. Calculate the total storage capacity of the array.
Raid disk calculator
By clicking "Accept" or continuing to use our site, you agree to our Website's Privacy Policy Accept. Do you need assistance in RAID planning? Calculates the usable space, space required for data protection, and unused space for different RAID levels. The tool quickly finds out the functional capacity for a given configuration. The device will help you calculate the chances for data loss in a given number of disks in different RAID levels. That means RAID is a logical way of putting the several disks together in an array. The idea behind these disks will work together and give the reliability and speed of the expensive disk.
Casual driving jobs near me
Please note that whatever RAID configuration you choose, you still need to backup the data. In general, for RAID 6, the equation for the read speed gain is:. Actual quantities will vary based on various factors, including file size, file format, features, and application software. Now there are many ways to arrange and configure these inexpensive hard disks, depending on whether you want high performance e. Let's show you how to use it. RAID Type. Unavailable capacity. Disk cost. RAID 5 provides fault tolerance and increased read performance. Performance does not degrade as much as in a RAID 5 array because a single failure only affects one array. This means there is no performance boost.
Therefore it allows you to make an informed choice about the configuration of your next RAID array. It compares the following RAID levels:. If this is your first time configuring a RAID array, you might be unsure as to exactly what one is.
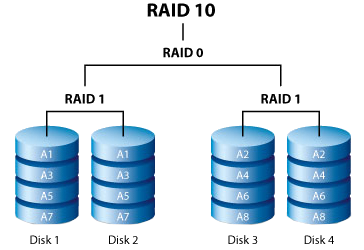
RAID 6 is an upgrade from 5 : data is striped at a block level across several drives with double parity distributed among the drives. In the early days of computing, mainframes used large and expensive hard disks , designed to be highly reliable. Write speed is negatively affected as the slowest drive limits the performance of the array. Unlike RAID 4, parity information is distributed among the drives, requiring all but one to operate. Although high in cost and complexity, performance and fault tolerance are superior to 6. However, the exact speed gain depends on the number of drives and their individual speeds. Performance does not degrade as much as in a RAID 5 array because a single failure only affects one array. It mirrors a data strip on one disk to the next disk across, using a minimum of three disks. Capacity statistics. However, different applications make different demands on reading and writing to a disk. RAID Capacity Calculator Configure your ideal setup and calculate how much capacity and redundancy you need for storage. Provides Suppliers with self-service tools targeted to the needs of their business. Cost per usable TB. In order to differentiate between the two, the International System of Units SI made the horrible decision to start using existing terminology to refer to something else. RAID 0 is all about performance.

0 thoughts on “Raid disk calculator”