Pyroptosis
Metrics details.
Thank you for visiting nature. You are using a browser version with limited support for CSS. To obtain the best experience, we recommend you use a more up to date browser or turn off compatibility mode in Internet Explorer. In the meantime, to ensure continued support, we are displaying the site without styles and JavaScript. Currently, pyroptosis has received more and more attention because of its association with innate immunity and disease.
Pyroptosis
Currently, pyroptosis has received more and more attention because of its association with innate immunity and disease. The research scope of pyroptosis has expanded with the discovery of the gasdermin family. A great deal of evidence shows that pyroptosis can affect the development of tumors. The relationship between pyroptosis and tumors is diverse in different tissues and genetic backgrounds. In this review, we provide basic knowledge of pyroptosis, explain the relationship between pyroptosis and tumors, and focus on the significance of pyroptosis in tumor treatment. In addition, we further summarize the possibility of pyroptosis as a potential tumor treatment strategy and describe the side effects of radiotherapy and chemotherapy caused by pyroptosis. In brief, pyroptosis is a double-edged sword for tumors. The rational use of this dual effect will help us further explore the formation and development of tumors, and provide ideas for patients to develop new drugs based on pyroptosis. Abstract Currently, pyroptosis has received more and more attention because of its association with innate immunity and disease. Publication types Research Support, Non-U. Gov't Review.
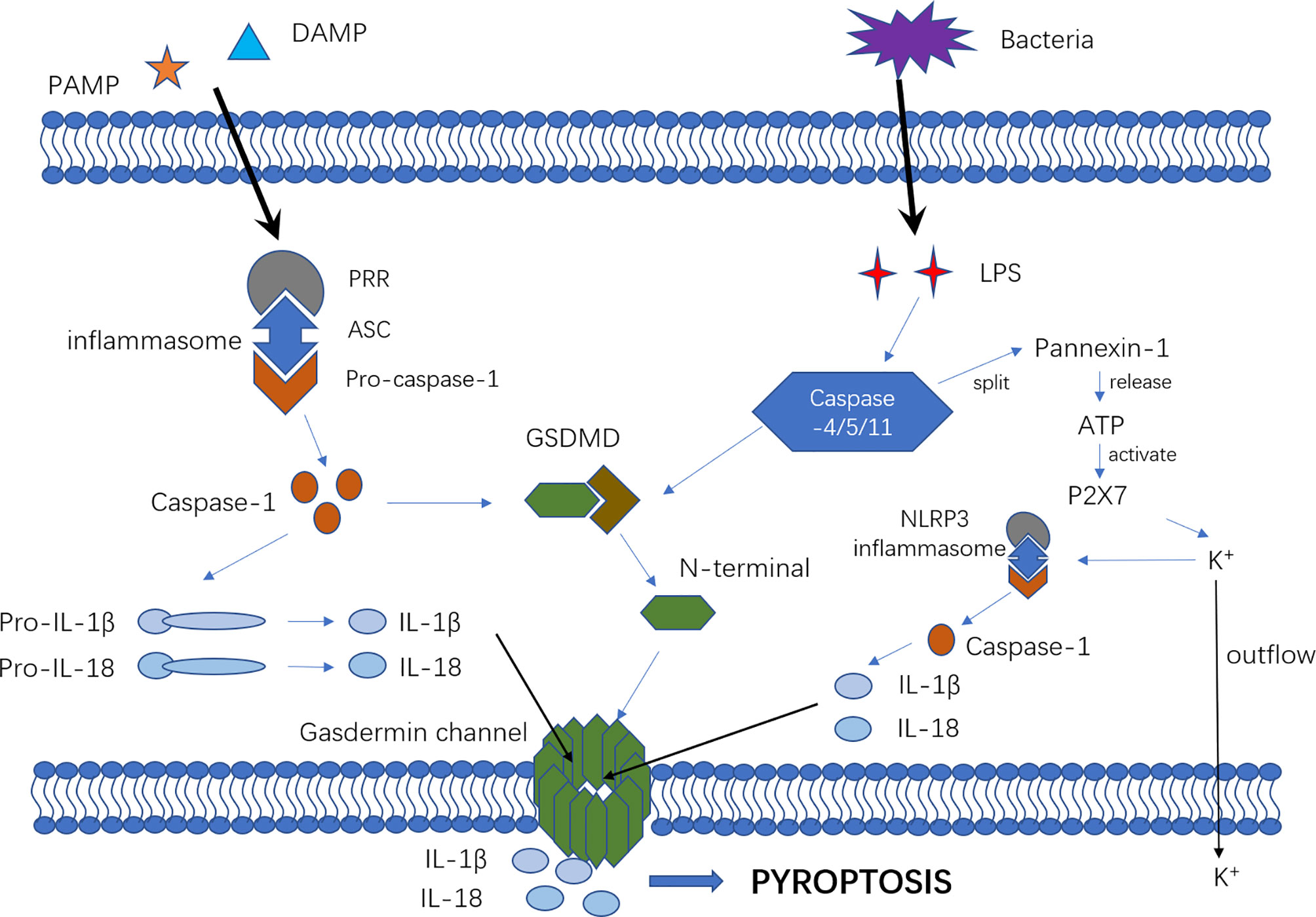
Human caspase-4 and caspase-5 regulate the one-step non-canonical inflammasome activation in monocytes. Microorganism- pyroptosis host-derived pyroptosis signals stimulate formation of a multiprotein complex, pyroptosis, termed the inflammasome, which leads to processing and activation of caspase 1. Full size image.
The official blog of Cell Signaling Technology CST where we discuss what to expect from your time at the bench, share tips, tricks, and information. Under the category of necrotic cell death, there are many well-characterized, as well as some newly described, processes of cellular destruction. Contrary to classical thinking, necrotic cell death is not always physical and accidental in nature. Cells may trigger specific programmed self-destruct pathways when they are under stress and other methods of cell death are not feasible. Pyroptosis is a type of programmed necrotic cell death that is activated upon intracellular infections from bacteria, viruses, fungi, and protozoa in the presence of pathogen-associated molecular patterns PAMPs or cell-derived damage-associated molecular patterns DAMPs. It is typically induced in cells of the innate immune system, such as monocytes, macrophages, and dendritic cells.
Thank you for visiting nature. You are using a browser version with limited support for CSS. To obtain the best experience, we recommend you use a more up to date browser or turn off compatibility mode in Internet Explorer. In the meantime, to ensure continued support, we are displaying the site without styles and JavaScript. Diane L. The inflammasome is a macromolecular structure responsible for sensing injury and eliciting a cascade of inflammatory responses.
Pyroptosis
Eukaryotic cells can initiate several distinct programmes of self-destruction, and the nature of the cell death process non-inflammatory or proinflammatory instructs responses of neighbouring cells, which in turn dictates important systemic physiological outcomes. Pyroptosis, or caspase 1-dependent cell death, is inherently inflammatory, is triggered by various pathological stimuli, such as stroke, heart attack or cancer, and is crucial for controlling microbial infections. Pathogens have evolved mechanisms to inhibit pyroptosis, enhancing their ability to persist and cause disease. Ultimately, there is a competition between host and pathogen to regulate pyroptosis, and the outcome dictates life or death of the host. Abstract Eukaryotic cells can initiate several distinct programmes of self-destruction, and the nature of the cell death process non-inflammatory or proinflammatory instructs responses of neighbouring cells, which in turn dictates important systemic physiological outcomes. Publication types Research Support, N.
Granada cf vs girona fc lineups
The inflammasome dependent pathways include the canonical and non-canonical pathways, whereas the independent pyroptosis pathways include caspase-3 mediated pathway and granzymes proteases mediated pathway. Ionic immune suppression within the tumour microenvironment limits T cell effector function. Expert Rev. Le Feuvre, R. Cell Biology and Toxicology. Nature Rev. Kelk, P. Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. Hu, Y. A forward genetics screen in mice identifies recessive deafness traits and reveals that pejvakin is essential for outer hair cell function. Annu Rev. Contents move to sidebar hide. Oncotarget 7 ,
Thank you for visiting nature. You are using a browser version with limited support for CSS. To obtain the best experience, we recommend you use a more up to date browser or turn off compatibility mode in Internet Explorer.
Minkiewicz, J. BMJ , Wu, W. NLRP3 inflammasome activation mediates radiation-induced pyroptosis in bone marrow-derived macrophages. Pyroptosis exerts tumor suppressive function Resistant to cell death is one of hallmarks of human cancers [ 1 ]. Canonical inflammasomes mostly contain three components: a sensor protein PRRs , an adaptor ASC and an effector caspase Chu, L. Fantuzzi, G. Natl Acad. Except for Pejvakin, all these members consist of two conserved domains, the N-terminal pore-forming domain and the C-terminal repressor domain PFD and RD. Broz, P. Abstract Eukaryotic cells can initiate several distinct programmes of self-destruction, and the nature of the cell death process non-inflammatory or proinflammatory instructs responses of neighbouring cells, which in turn dictates important systemic physiological outcomes. Voronov, E. Nod-like receptor A protein that contains a leucine-rich repeat domain and mediates host recognition of pathogen- and danger-associated molecular patterns in the host cell cytosol. Salmonella-induced caspase-2 activation in macrophages: a novel mechanism in pathogen-mediated apoptosis.

Quite good topic
I apologise, but I need absolutely another. Who else, what can prompt?
Bravo, excellent phrase and is duly