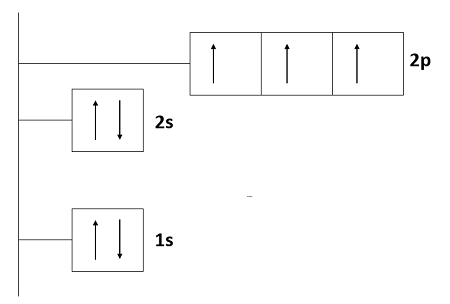
Orbital diagram for nitrogen
Note: The review of general chemistry in sections 1. The electron configuration of an atom is the representation of the arrangement of electrons distributed among the orbital shells and subshells.
Draw the molecular orbital diagram of N 2 and calculate the bond order. Molecular orbital diagram of N 2. Hence, bond order of N 2 is 3. Also calculate their bond order? Byju's Answer. Open in App. Molecular orbital diagram: The molecular orbital diagram describes the chemical bonding in a molecule based on molecular orbital theory MOT and linear combination of atomic orbital LCAO.
Orbital diagram for nitrogen
The nitrogen orbital diagram is a graphical representation of the electron configuration of the nitrogen atom. This diagram shows how the electrons in the nitrogen atom are arranged in different orbitals. Orbital is the region of space around the nucleus of an atom where electrons are found. The electrons of the atom revolve around the nucleus in a certain circular path. These circular paths are called orbit shell. Again, atomic energy shells are subdivided into sub-energy levels. These sub-energy levels are also called orbital. The most probable region of electron rotation around the nucleus is called the orbital. The sub-energy levels depend on the azimuthal quantum number. The sub-energy levels are known as s, p, d, and f. The orbital number of the s-subshell is one, three in the p-subshell, five in the d-subshell, and seven in the f-subshell. Each orbital can have a maximum of two electrons. The nitrogen orbital notation is a shorthand system designed to represent the exact positions of the electrons in the nitrogen atom.
Molecular Orbital Theory. The second electron will also enter the p y orbital in the clockwise direction and the third electron will also enter the p z orbital in the clockwise direction.
.
The nitrogen orbital diagram is a graphical representation of the electron configuration of the nitrogen atom. This diagram shows how the electrons in the nitrogen atom are arranged in different orbitals. Orbital is the region of space around the nucleus of an atom where electrons are found. The electrons of the atom revolve around the nucleus in a certain circular path. These circular paths are called orbit shell. Again, atomic energy shells are subdivided into sub-energy levels. These sub-energy levels are also called orbital.
Orbital diagram for nitrogen
The electron configuration of an atom is the representation of the arrangement of electrons distributed among the orbital shells and subshells. Commonly, the electron configuration is used to describe the orbitals of an atom in its ground state, but it can also be used to represent an atom that has ionized into a cation or anion by compensating with the loss of or gain of electrons in their subsequent orbitals. Many of the physical and chemical properties of elements can be correlated to their unique electron configurations. The valence electrons, electrons in the outermost shell, are the determining factor for the unique chemistry of the element. Before assigning the electrons of an atom into orbitals, one must become familiar with the basic concepts of electron configurations. Every element on the Periodic Table consists of atoms, which are composed of protons, neutrons, and electrons. The four different types of orbitals s,p,d, and f have different shapes, and one orbital can hold a maximum of two electrons. The p, d, and f orbitals have different sublevels, thus can hold more electrons.
Labrador puppy weight chart kg
A single orbital can hold a maximum of two electrons, which must have opposing spins; otherwise they would have the same four quantum numbers, which is forbidden. Bond Order by MOT. As a full-time chemistry writer on Valenceelectrons. It shows electrons in both bonding and anti-bonding molecular orbital. Now, when the fourth electron wants to enter the p-subshell, then it will enter the p x orbital in the anti-clockwise direction. This diagram shows how the electrons in the cerium atom are arranged in different orbitals. This diagram shows how the electrons in the oganesson atom are arranged in different orbitals. The sub-energy levels depend on the azimuthal quantum number. For more information on how electron configurations and the periodic table are linked, visit the Connecting Electrons to the Periodic Table module. To write the orbital diagram of nitrogen, you have to write the orbital notation of nitrogen. The nitrogen orbital diagram is a graphical representation of the electron configuration of the nitrogen atom. Calculate the respective bond order. Go back to previous article. Before assigning the electrons of an atom into orbitals, one must become familiar with the basic concepts of electron configurations. Commonly, the electron configuration is used to describe the orbitals of an atom in its ground state, but it can also be used to represent an atom that has ionized into a cation or anion by compensating with the loss of or gain of electrons in their subsequent orbitals.
This is the first example so far that has more than two pendant atoms and the first example in which the molecule has atoms that lie in three dimensions i. Ammonia is a trigonal pyramidal molecule, with three pendant hydrogen atoms.
The nitrogen orbital notation is a shorthand system designed to represent the exact positions of the electrons in the nitrogen atom. Introduction Before assigning the electrons of an atom into orbitals, one must become familiar with the basic concepts of electron configurations. Each orbital can be represented by specific blocks on the periodic table. The order of levels filled looks like this: 1s, 2s, 2p, 3s, 3p, 4s, 3d, 4p, 5s, 4d, 5p, 6s, 4f, 5d, 6p, 7s, 5f, 6d, and 7p One way to remember this pattern, probably the easiest, is to refer to the periodic table and remember where each orbital block falls to logically deduce this pattern. Again, atomic energy shells are subdivided into sub-energy levels. The electron configuration for sulfur is 1s 2 2s 2 2p 6 3 s 2 3p 4 and can be represented using the orbital diagram below. Leave a Reply Cancel reply Your email address will not be published. The Aufbau principle is that the electrons present in the atom will first complete the lowest energy orbital and then gradually continue to complete the higher energy orbital. The valence electrons, electrons in the outermost shell, are the determining factor for the unique chemistry of the element. The cerium orbital diagram is a graphical representation of the electron configuration of the cerium atom. So the remaining three electrons will enter the 2p orbital in the clockwise direction. The 2s orbital is now full. The sub-energy levels depend on the azimuthal quantum number. The fifth electron will also enter the p y orbital in the anti-clockwise direction and the sixth electron will also enter the p z orbital in the anti-clockwise direction. The nitrogen orbital diagram is a graphical representation of the electron configuration of the nitrogen atom.

Moscow was under construction not at once.
In my opinion you commit an error. I can defend the position. Write to me in PM, we will talk.
Excuse, it is removed