Niacin liver damage myth
Higher doses of niacin can help lower cholesterol, but long-term treatment with niacin — particularly with extended-release forms — may damage the liver. For niacin liver damage myth in-depth resources about vitamins, minerals, and supplements, visit our dedicated hub. Niacin is a water-soluble vitamin. It is an important vitamin as it helps to turn food into energy and helps with the function of cells in the body.
Niacin is a water-soluble vitamin. This means that it dissolves in water and is not stored in your body. Niacin is a type of B vitamin called vitamin B3. The term niacin is used to refer to various forms of niacin, such as nicotinic acid and nicotinamide. In your body, niacin is converted into the active form called NAD nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide. Your body can also make niacin from an amino acid found in proteins called tryptophan.
Niacin liver damage myth
Niacin overdose is unlikely if you take niacin only in the amount prescribed by your doctor. While it's not possible to overdose on niacin simply by eating too many niacin-rich foods, taking too much over-the-counter or prescription niacin can be dangerous. Because niacin has also been linked to liver damage and strokes, most doctors now recommend it only for people who can't take statins to treat high triglyceride levels. If you're concerned about taking niacin, talk to your doctor. Katherine Zeratsky, R. There is a problem with information submitted for this request. Sign up for free and stay up to date on research advancements, health tips, current health topics, and expertise on managing health. Click here for an email preview. Error Email field is required. Error Include a valid email address. To provide you with the most relevant and helpful information, and understand which information is beneficial, we may combine your email and website usage information with other information we have about you. If you are a Mayo Clinic patient, this could include protected health information. If we combine this information with your protected health information, we will treat all of that information as protected health information and will only use or disclose that information as set forth in our notice of privacy practices. You may opt-out of email communications at any time by clicking on the unsubscribe link in the e-mail. You'll soon start receiving the latest Mayo Clinic health information you requested in your inbox.
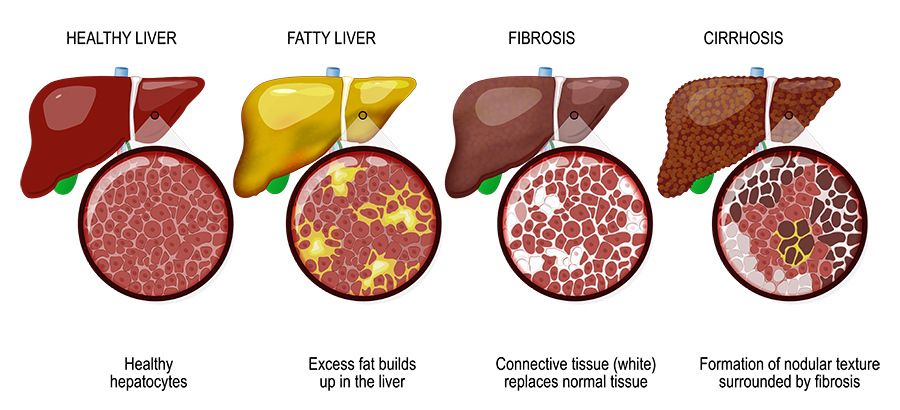
Most cases are mild and will resolve soon after a person stops taking the medication.
Federal government websites often end in. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you're on a federal government site. The site is secure. NCBI Bookshelf. Niacin, also known as nicotinic acid and vitamin B3, is a water soluble, essential B vitamin that, when given in high doses, is effective in lowering low density lipoprotein LDL cholesterol and raising high density lipoprotein HDL cholesterol, which makes this agent of unique value in the therapy of dyslipidemia. Niacin can cause mild-to-moderate serum aminotransferase elevations and high doses and certain formulations of niacin have been linked to clinically apparent, acute liver injury which can be severe as well as fatal. Niacin nye" a sin is a soluble B vitamin and pyridine derivative and an essential dietary element, deficiency of which causes pellagra.
Higher doses of niacin can help lower cholesterol, but long-term treatment with niacin — particularly with extended-release forms — may damage the liver. For more in-depth resources about vitamins, minerals, and supplements, visit our dedicated hub. Niacin is a water-soluble vitamin. It is an important vitamin as it helps to turn food into energy and helps with the function of cells in the body. This article examines how niacin can damage the liver. It also discusses the signs of liver damage due to too much niacin and the next steps a person should take. Niacin — also called vitamin B3 — is a water-soluble vitamin naturally present in many foods. It is also available as two dietary supplements: nicotinic acid and nicotinamide. A healthcare professional may prescribe nicotinic acid to help treat high cholesterol. The Office of Dietary Supplements ODS notes there have not been any reported adverse effects as a result of consuming niacin that occurs naturally in foods.
Niacin liver damage myth
Niacin is a B vitamin that's made and used by your body to turn food into energy. It helps keep your nervous system, digestive system and skin healthy. Niacin vitamin B-3 is often part of a daily multivitamin, but most people get enough niacin from the food they eat. Foods rich in niacin include yeast, milk, meat, tortillas and cereal grains. The recommended daily amount of niacin for adult males is 16 milligrams mg a day and for adult women who aren't pregnant, 14 mg a day. Niacin deficiency has been linked to birth defects. A study in mice suggested that niacin supplementation during gestation prevented birth defects.
Synonym for rate
Help us advance cardiovascular medicine. The recommended dietary allowance RDA of this vitamin is 14 to 16 mg daily in adults, and slightly more for pregnant women 18 mg and less for children 2 to 12 mg. Brown WV. For about a fifth of these patients, this disease can further progress to fibrosis scarring of the liver and cirrhosis the scarred liver cannot function correctly , manifesting clinically in stomach haemorrhage, liver failure, liver cancer and, ultimately, death. Media Requests. My podcast changed me Can 'biological race' explain disparities in health? At even higher doses, it can cause liver problems and even toxicity. Degree Programs. Type 2 diabetes risk may be higher in people with shorter sleep duration. This content does not have an English version. This content does not have an English version. Foods rich in niacin include yeast, milk, meat, tortillas and cereal grains. Niacin, also known as nicotinic acid and vitamin B3, is a water soluble, essential B vitamin that, when given in high doses, is effective in lowering low density lipoprotein LDL cholesterol and raising high density lipoprotein HDL cholesterol, which makes this agent of unique value in the therapy of dyslipidemia. And there is a known side-effect for these particular formulations called flushing warmth, redness, itching and tingling of the skin, especially of the face and neck.
Federal government websites often end in. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you're on a federal government site.
You can learn more about how we ensure our content is accurate and current by reading our editorial policy. Cutting edge technology gives new vision for old problems October 31, Give Today. If you are a Mayo Clinic patient, this could include protected health information. Niacin may cause flushing, rash, headaches, dizziness, or a drop in blood pressure. In, Zimmerman HJ. Thus, Niacin prevents the disease from advancing to more severe stages. Intrahepatic cholestasis during nicotinic acid therapy. Explore careers. J Ultrasound Med.

Why also is not present?