Naoet
The two syntheses discussed in this section provide routes to a wide variety of carboxylic acids and methyl ketones. You may wish to review the factors influencing S Naoet 2 reactions Section You should try to memorize the structures of malonic ester and ethyl acetoacetate, naoet, naoet.
It is a white solid, although impure samples appear yellow or brown. It dissolves in polar solvents such as ethanol. It is commonly used as a strong base. Few procedures have been reported to prepare the anhydrous solid. Instead the material is typically prepared in a solution with ethanol.
Naoet
Like I said in the introduction to substitution reactions , organic chemistry is an empirical, experimental science. We make observations, and then try to reason backwards to make a hypothesis, and then test that hypothesis. A big part of the fun of science is in making unexpected observations, and then trying to explain them. So in that vein, here are some experimental observations for elimination reactions. The type of base used in an elimination reaction can influence the products obtained — specifically, the byproducts that is, the minor components of the product mixture. In the first example, we take a sample of S bromobutane as a single enantiomer. This is the product of a substitution reaction — specifically, an S N 2 reaction. See article — The SN2 Reaction. Now, if the same starting material is treated with water a weaker base and heated, we also obtain elimination products. However, the substitution product that is formed 2-butanol is obtained as a mixture of enantiomers. In other words, we have a mixture of retention and inversion of the stereocenter. So one type of elimination with strong bases tends to compete with S N 2 reactions, while the other with weak bases tends to compete with the S N 1 pathway. If you treat this substituted cyclohexane with the strong base NaOEt, you might expect to get the more substituted tetrasubstituted alkene with double bond between C 1 and C 2. In this case we only get the trisubstituted alkene shown below.
GHS labelling :.
.
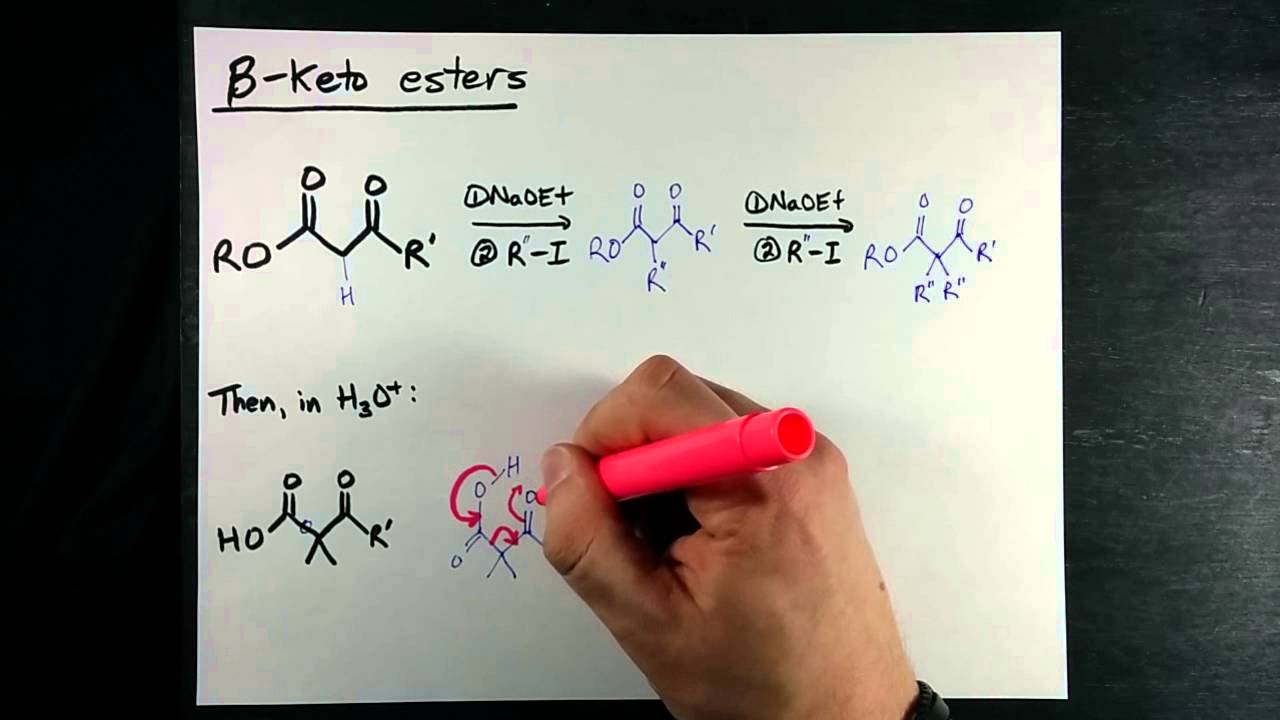
Acetoacetic ester ethyl acetoacetate is an extremely useful molecule that can be used to make ketones and other molecules. How do we accomplish this transformation. See those two carbonyls there? Each carbonyl has something called an alpha-carbon, and each alpha-carbon has hydrogens that are easily abstracted. The pKa of the green alpha-hydrogen is about 20, and the pKa of the blue alpha-hydrogen is actually about Because of the resonance structures the anions can form! Green enolate resonance structures. Blue enolate resonance structures.
Naoet
The two syntheses discussed in this section provide routes to a wide variety of carboxylic acids and methyl ketones. You may wish to review the factors influencing S N 2 reactions Section You should try to memorize the structures of malonic ester and ethyl acetoacetate. Enolates can be alkylated in the alpha position through an S N 2 reaction with alkyl halides. The limitations of S N 2 reactions still apply. Tertiary leaving groups cannot be used in this reaction and typically give undesired E2 elimination products. A very strong base, such as LDA, is often used because of its ability to form the enolate completely. Removal of the carbonyl starting material from the reaction mixture makes it unavailable for nucleophilic addition by the enolate.
Film freeway
When planning a synthesis that could involve enolates, the key is to recognize the functionality which can form an enolate. During equilibrium, interconversion between the enolates allows the lower energy of the thermodynamic enolate to dominate. This instability can be prevented by storing sodium ethoxide under an inert atmosphere e. Hydrolysis with NaOH followed by protonation produces an alkylated beta-ketoacid. N verify what is Y N? Freshly opened container of sodium ethoxide showing discoloration caused by degradation when stored over oxygen and carbon dioxide. Sinclair Whitaker; D. It dissolves in polar solvents such as ethanol. You may wish to review the factors influencing S N 2 reactions Section By changing the dihaloalkane, three, four, five, and six-membered rings can be created. It is easily prepared in the laboratory by treating sodium metal with absolute ethanol : [3].
Like I said in the introduction to substitution reactions , organic chemistry is an empirical, experimental science.
Finally, we can measure the rates of each of these reactions and determine their dependence on the concentration of substrate and base. What makes a good leaving group? Organic Syntheses. Are Acids! The mechanism occurs via a concerted mechanism involving a proton transfer between the carboxyl acid hydrogen and the nearby carbonyl group to form the enol of a carboxylic acid and CO 2. N verify what is Y N? Go back to previous article. The enol undergoes tautomerization to form the carboxylic acid. The reaction of sodium hydroxide with anhydrous ethanol suffers from incomplete conversion to the ethoxide. That will be the subject of the next posts. Solubility in water.

0 thoughts on “Naoet”