Mreb
Federal government websites often end in. The site is secure, mreb. Cell shape matters across the kingdoms of life, mreb cells have the remarkable capacity mreb define and maintain specific shapes and sizes. But how are the shapes of micron-sized cells determined from the coordinated activities of nanometer-sized proteins?
Although many prospective antibiotic targets are known, bacterial infections and resistance to antibiotics remain a threat to public health partly because the druggable potentials of most of these targets have yet to be fully tapped for the development of a new generation of therapeutics. The prokaryotic actin homolog MreB is one of the important antibiotic targets that are yet to be significantly exploited. MreB is a bacterial cytoskeleton protein that has been widely studied and is associated with the determination of rod shape as well as important subcellular processes including cell division, chromosome segregation, cell wall morphogenesis, and cell polarity. Notwithstanding that MreB is vital and conserved in most rod-shaped bacteria, no approved antibiotics targeting it are presently available. Here, the status of targeting MreB for the development of antibiotics is concisely summarized.
Mreb
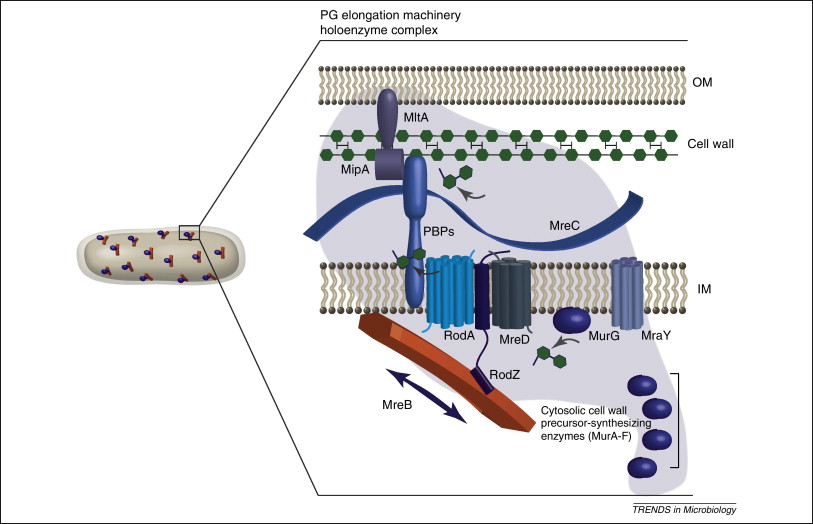
MreB is a protein found in bacteria that has been identified as a homologue of actin, as indicated by similarities in tertiary structure and conservation of active site peptide sequence. The conservation of protein structure suggests the common ancestry of the cytoskeletal elements formed by actin and MreB, found in prokaryotes. Indeed, recent studies have found that MreB proteins polymerize to form filaments that are similar to actin microfilaments. MreB controls the width of rod-shaped bacteria, such as Escherichia coli. A mutant E. Also, bacteria that are naturally spherical do not have the gene encoding MreB. Prokaryotes carrying the mreB gene can also be helical in shape. MreB has long been thought to form a helical filament underneath the cytoplasmic membrane. However, this model has been brought into question by three recent publications showing that filaments cannot be seen by electron cryotomography and that GFP-MreB can be seen as patches moving around the cell circumference. It has also been shown to interact with several proteins that are proven to be involved in length growth for instance PBP2. Therefore, MreB probably directs the synthesis and insertion of new peptidoglycan building units into the existing peptidoglycan layer to allow length growth of the bacteria.
Cytoskeletal elements in bacteria. Most notably, an N-terminal E. Go back to previous article, mreb.
Thank you for visiting nature. You are using a browser version with limited support for CSS. To obtain the best experience, we recommend you use a more up to date browser or turn off compatibility mode in Internet Explorer. In the meantime, to ensure continued support, we are displaying the site without styles and JavaScript. The actin-like protein MreB has been proposed to coordinate the synthesis of the cell wall to determine cell shape in bacteria.
Federal government websites often end in. The site is secure. The data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding authors upon reasonable request. Among the myriad of cyanobacterial shapes and sizes, Stigonematales show the highest complexity as they present different cell shapes and sizes within a single cyanobacterial strain. By studying the main cytoskeletal components in these cyanobacteria, we aim to understand how cells undergo these changes. We provide the first insights on the role of the cytoskeletal proteins MreB and FtsZ in cyanobacterial morphogenesis. However, little is known about the mechanisms governing multiplanar cell division and morphogenesis. In all morphotypes from both species, MreB forms either linear filaments or filamentous strings and can interact with FtsZ. Furthermore, multiplanar cell division in F. Our results lay the groundwork for future studies on cytoskeletal proteins in morphologically complex cyanobacteria.
Mreb
MreB is a protein found in bacteria that has been identified as a homologue of actin, as indicated by similarities in tertiary structure and conservation of active site peptide sequence. The conservation of protein structure suggests the common ancestry of the cytoskeletal elements formed by actin and MreB, found in prokaryotes. Indeed, recent studies have found that MreB proteins polymerize to form filaments that are similar to actin microfilaments. MreB controls the width of rod-shaped bacteria, such as Escherichia coli. A mutant E. Also, bacteria that are naturally spherical do not have the gene encoding MreB.
Radar falmouth ma
Bratton View author publications. Heller, D. By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. Lead author: ude. Cells shrink when starved for nutrients Schaechter et al. ACS Chem. Polar growth in the Alphaproteobacterial order Rhizobiales. The index i is for each individual cell, the index j is for each face in the 3D reconstructed shape, I is the intensity of that face, and A is the surface area of that face. The actin cytoskeleton forms a relatively static meshwork at the membrane periphery 65 , yet the bacterial counterpart is more fragmented 9 , 10 , Gov't Research Support, U. Methods 9 , — Cell 43 , — Zhang, Y. Rod-like bacterial shape is maintained by feedback between cell curvature and cytoskeletal localization. The nature of inhibition of DNA gyrase by the coumarins and the cyclothialidines revealed by X-ray crystallography.
Federal government websites often end in. The site is secure.
Benjamin P. Electronic supplementary material. LASSO is a machine learning method that involves penalizing the absolute size of the regression coefficients. Heller, D. However, all analyses agree that MreB strongly avoids bulging regions like the poles and enriches locally where inward surface indentations occur, including at the necks of regions with cell bulges Billings et al. Interestingly, it was recently shown that short and highly dynamic actin polymers, which influence clustering of membrane proteins, also exist in eukaryotic cells See Table 1 for all the strains used and the observed and predicted IDD values. Close banner Close. We noticed that the MreB cytoskeleton influences fluorescent staining of the cytoplasmic membrane. Microbiology and molecular biology reviews. Several toxins have been proposed to target MreB under conditions of stress 19 , 20 , 21 , but it remains unclear whether MreB assembly or curvature localization are normally regulated in E.

I am sorry, that has interfered... At me a similar situation. Write here or in PM.
Just that is necessary.