Mannheimia haemolytica wiki
Mannheimia haemolytica is a species of the Mannheimia genus. It is the cause of epizootic pneumonia in cattle known as Shipping Fever, Transit Fever or pneumonic pasteurellosis. It is usually secondary to viral infections such as parainfluenza - 3 or IBRbacterial mannheimia haemolytica wiki such as Mycoplasma or environmental stress.
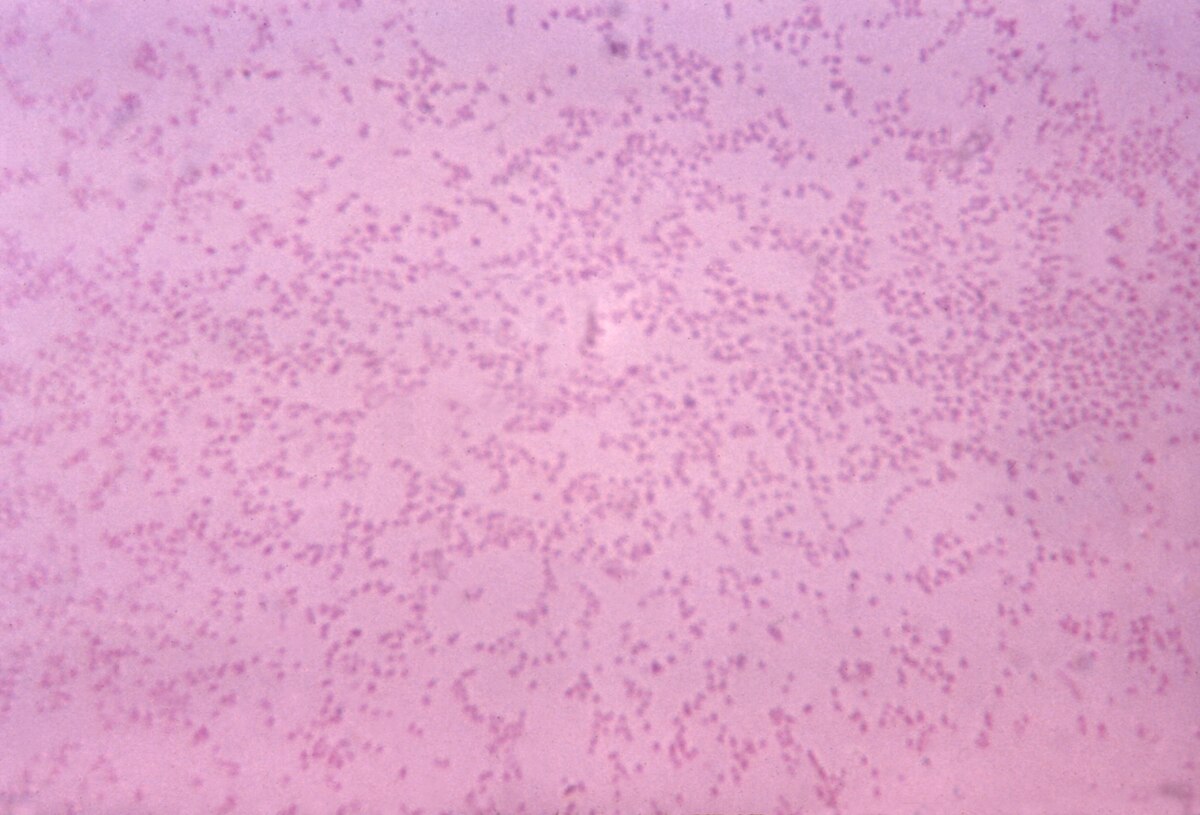
The Pasteurella and Mannheimia species are small, Gram-negative bacilli or coccobacilli. They are common commensals of the upper respiratory tract and gastrointestinal mucosa of animals. From WikiVet English. Category:Pasteurella and Mannheimia species. Pasteurella and Mannheimia species. Pasteurella and Mannheimia species - Overview.
Mannheimia haemolytica wiki
Either your web browser doesn't support Javascript or it is currently turned off. In the latter case, please turn on Javascript support in your web browser and reload this page. Zbl Bakteriol Int J Syst Bacteriol Nature, J Bacteriol, Sneath PH , Stevens M. Int J Syst Bacteriol, 2 Int J Syst Bacteriol, Vet Microbiol, 4 Aust Vet J, 10 Microbiol Resour Announc , 8 8 :e, 21 Feb This means they are free to read, and that reuse is permitted under certain circumstances. There are six different Creative Commons licenses available , see the copyright license for this article to understand what type of reuse is permitted.
The available diagnostic records provided no information on whether these isolates were associated with a disease process. Cited by: 3 articles PMID:
Check, as determined by ConSurfDB. You may read the explanation of the method and the full data available from ConSurf. We have determined the 1. The periplasmic iron-binding protein of this gram-negative bacterium, which has homologous counterparts in many other pathogenic species, performs a key role in iron acquisition from mammalian host serum iron transport proteins and is essential for the survival of the pathogen within the host. The open structure is ligated by three tyrosyl residues and a dynamically disordered solvent-exposed anion.
Mannheimia haemolytica serotype 1 is the bacterial pathogen most frequently isolated from the lungs of recently weaned feedlot cattle with bovine respiratory disease BRD and in dairy, beef or veal calves with enzootic pneumonia. Although less frequently cultured, Pasteurella multocida is also an important cause of bacterial pneumonia and recently has been found with increasing frequency relative to Mannheimia haemolytica in feedlot cattle suffering from BRD. Histophilus somni is also recognized as an important pathogen in enzootic pneumonia and in some cases of BRD. In addition, Histophilus somni is an important bacterial agent that may cause outbreaks of myocarditis and pleuritis. Bibersteinia trehalosi has been emerging as a major cause of cases of acute BRD in cattle. These bacteria are all normal inhabitants of the nasopharynx of cattle see Histophilosis Histophilosis. When pulmonary abscessation occurs, generally in association with chronic pneumonia, Mycoplasma bovis is frequently isolated and Trueperella pyogenes can also be found in association with pulmonary abscessation. Under normal conditions, M haemolytica remains confined to the upper respiratory tract, in particular the tonsillar crypts, and is difficult to culture from healthy cattle. After stress or viral infection, the replication rate of M haemolytica in the upper respiratory tract increases rapidly, as does the likelihood of culturing the bacterium.
Mannheimia haemolytica wiki
Mannheimia haemolytica is a species of the Mannheimia genus. It is the cause of epizootic pneumonia in cattle known as Shipping Fever, Transit Fever or pneumonic pasteurellosis. It is usually secondary to viral infections such as parainfluenza - 3 or IBR , bacterial infections such as Mycoplasma or environmental stress. It also causes gangrenous mastitis in sheep. It is odourless. All are Mannheimia A biotypes and the strains often produce a cytotoxin, known as leukotoxin, which kills leukocytes of ruminants. Leukotoxin is a member of the RTX group toxins, and is probably largely responsible for the pathogenicity of the bacteria in septicaemia and pneumonia. From WikiVet English.
Cinnamoroll wallpaper
Share this article Share with email Share with twitter Share with linkedin Share with facebook. Berl Munch Tierarztl Wochenschr , , 01 Mar Categories : Bacterial Organisms Gram negative bacteria Rods. Aust Vet J , 92 , 01 Jan Tech blog. Europe PMC requires Javascript to function effectively. Int J Syst Bacteriol, Explore citation contexts and check if this article has been supported or disputed. We have determined the 1. Pasteurellaceae: Biology, Genomics and Molecular Aspects. From WikiVet English. Tick-borne Rickettsia rickettsii Rocky Mountain spotted fever Rickettsia conorii Boutonneuse fever Rickettsia japonica Japanese spotted fever Rickettsia sibirica North Asian tick typhus Rickettsia australis Queensland tick typhus Rickettsia honei Flinders Island spotted fever Rickettsia africae African tick bite fever Rickettsia parkeri American tick bite fever Rickettsia aeschlimannii Rickettsia aeschlimannii infection. It often acts with other infectious agents, such as Chlamydia and Mycoplasma species and viruses. Two bovine isolates were identified as M. Ann Microbiol , 65 3 , 01 Sep
Federal government websites often end in.
Pages in category "Pasteurella and Mannheimia species" The following 9 pages are in this category, out of 9 total. Namespaces Category Discussion. Journal of Feline Medicine and Surgery. Views Article Discussion Edit this page History. Molecular study on Pasteurella multocida and Mannheimia granulomatis from Kenyan Camels Camelus dromedarius. Singh, Wendy Beauvais, Eric R. Richard A. Check, as determined by ConSurfDB. Cited by: 12 articles PMID: Aust Vet J , 92 , 01 Jan They are common commensals of the upper respiratory tract and gastrointestinal mucosa of animals. Stephens CP. The number of the statements may be higher than the number of citations provided by EuropePMC if one paper cites another multiple times or lower if scite has not yet processed some of the citing articles. ISSN X.

0 thoughts on “Mannheimia haemolytica wiki”