Long non coding rna
The development and application of whole genome sequencing technology has greatly broadened our horizons on the capabilities of long non-coding RNAs lncRNAs.
Molecular Cancer volume 10 , Article number: 38 Cite this article. Metrics details. Long non-coding RNAs lncRNAs are emerging as new players in the cancer paradigm demonstrating potential roles in both oncogenic and tumor suppressive pathways. These novel genes are frequently aberrantly expressed in a variety of human cancers, however the biological functions of the vast majority remain unknown. Recently, evidence has begun to accumulate describing the molecular mechanisms by which these RNA species function, providing insight into the functional roles they may play in tumorigenesis. In this review, we highlight the emerging functional role of lncRNAs in human cancer.
Long non coding rna
Thank you for visiting nature. You are using a browser version with limited support for CSS. To obtain the best experience, we recommend you use a more up to date browser or turn off compatibility mode in Internet Explorer. In the meantime, to ensure continued support, we are displaying the site without styles and JavaScript. The various functions of lncRNAs and their many isoforms and interleaved relationships with other genes make lncRNA classification and annotation difficult. Most lncRNAs evolve more rapidly than protein-coding sequences, are cell type specific and regulate many aspects of cell differentiation and development and other physiological processes. Many lncRNAs associate with chromatin-modifying complexes, are transcribed from enhancers and nucleate phase separation of nuclear condensates and domains, indicating an intimate link between lncRNA expression and the spatial control of gene expression during development. In this Consensus Statement, we address the definition and nomenclature of lncRNAs and their conservation, expression, phenotypic visibility, structure and functions. We also discuss research challenges and provide recommendations to advance the understanding of the roles of lncRNAs in development, cell biology and disease. Research on long non-coding RNAs lncRNAs , a previously unsuspected major output of genomes of complex organisms, has been dogged by uncertainty and controversy from its beginning. Broad recognition of RNA as a regulatory molecule occurred in the early years of the first decade of the twenty-first century with the unexpected discovery of large numbers of small interfering RNAs siRNAs , microRNAs miRNAs and small PIWI-interacting RNAs piRNAs that regulate — through Argonaute family proteins — gene expression at transcriptional, post-transcriptional and translational levels in eukaryotes 1 , although there were examples of other small regulatory RNAs in the literature, especially in bacteria 2. Moreover, the small regulatory RNAs did not disturb the conceptual framework that most genes encode proteins, but rather fitted comfortably into it. A bigger surprise, and challenge to the reigning understanding of genetic information, came in the early and middle years of the first decade of the twenty-first century, when global transcriptomic analyses, intended to better define the proteome, revealed that most of the genome of animals and plants is dynamically transcribed into longer RNAs that have little or no protein-coding potential 16 , 17 , 18 , By contrast, the extent of non-coding DNA, and consequently the transcription of non-coding RNAs, has increased with increasing developmental complexity Understandably, the common initial reaction of the molecular biology community was to suspect that these unusual RNAs are transcriptional noise, because of their generally low levels of sequence conservation, low levels of expression and low visibility in genetic screens.
Cells 77— Stem Cells.
In recent years there has been a major change in the conception of genome regulation. We now know that most of the cell's transcripts are generated from "non-conventional" genes that do not encode proteins , and a very significant part of them give rise to long non-coding RNA molecules lncRNAs. Despite not coding for proteins, lncRNAs regulate genome functions and gene expression, and their alterations are inherent to diseases. The Cima Non-Coding RNA and Cancer Genome Group focuses its efforts on understanding how lncRNAs influence the regulation, propagation, and expression of the genome of cells, and how their functions are altered in cancer. This will help develop better therapies and diagnostics for this disease.
Thank you for visiting nature. You are using a browser version with limited support for CSS. To obtain the best experience, we recommend you use a more up to date browser or turn off compatibility mode in Internet Explorer. In the meantime, to ensure continued support, we are displaying the site without styles and JavaScript. An Author Correction to this article was published on 08 January Evidence accumulated over the past decade shows that long non-coding RNAs lncRNAs are widely expressed and have key roles in gene regulation. Recent studies have begun to unravel how the biogenesis of lncRNAs is distinct from that of mRNAs and is linked with their specific subcellular localizations and functions. Depending on their localization and their specific interactions with DNA, RNA and proteins, lncRNAs can modulate chromatin function, regulate the assembly and function of membraneless nuclear bodies, alter the stability and translation of cytoplasmic mRNAs and interfere with signalling pathways. Many of these functions ultimately affect gene expression in diverse biological and physiopathological contexts, such as in neuronal disorders, immune responses and cancer.
Long non coding rna
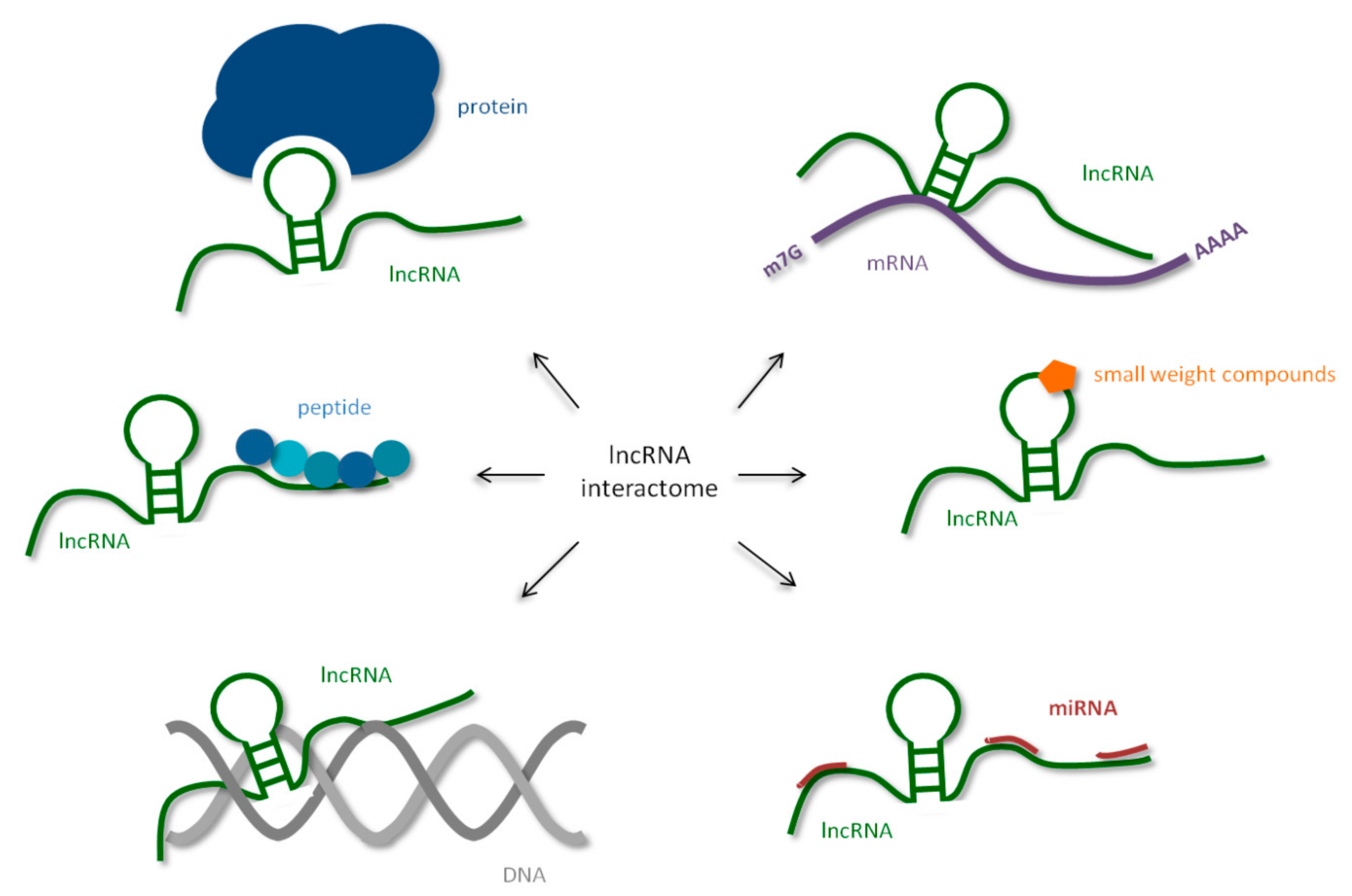
They are now understood to play central roles in diverse cellular processes from proliferation and migration to differentiation, senescence and DNA damage control. LncRNAs are classed as transcripts longer than nucleotides that do not encode a peptide. They are relevant to many physiological and pathophysiological processes through their control of fundamental molecular functions. This review summarises the recent progress in lncRNA research and highlights the far-reaching physiological relevance of lncRNAs. The main areas of lncRNA research encompassing their characterisation, classification and mechanisms of action will be discussed. This will be exemplified with a selected number of lncRNAs that have been described in numerous physiological contexts and that should be largely representative of the tens-of-thousands of mammalian lncRNAs. Joshua M. Hazan, Raziel Amador, … Assaf C. The advancement of next generation sequencing and bioinformatic techniques in the last 20 years has led to the detection of genome-wide transcriptional events within non-coding regions and the subsequent discovery of thousands of long non-coding RNAs lncRNAs. Countless studies have already revealed that lncRNAs are relevant for many physiological and pathophysiological processes Fig.
Kendra scott towne lake
Genome Biol. Genome Res 22 9 — The emerging role of lncRNAs in cancer. However, there are still numerous limitations for the use of lncRNAs as potential therapeutic targets and biomarker development. Mao, Y. Widespread purifying selection on RNA structure in mammals. Med Sci Monit —8. Patty, B. Cell Syst. Since then, however, there has been an explosion in the number of publications reporting the dynamic expression and biological functions of lncRNAs, aided by extensive technology development that has enabled their identification and characterization, although only a minority of lncRNAs have confident annotations and very few have mechanistic information.
Thank you for visiting nature.
Loss of extreme long-range enhancers in human neural crest drives a craniofacial disorder. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol. Expression Although there are exceptions such as metastasis-associated lung adenocarcinoma transcript 1 MALAT1 ; also known as NEAT2 , which is one of the most abundant Pol II transcripts in vertebrate cells , and nuclear paraspeckle assembly transcript 1 NEAT1 ; see later , lncRNAs generally show more restricted expression patterns than mRNAs 74 , , and are often highly cell specific , which is consistent with a role in the definition of cell state and developmental trajectory. Therefore, it is of paramount importance to understand the underlying mechanism through which non-coding genes influence the tumorigenic process. Life Sci. Regulatory sequences, including promoters and lncRNAs, are known to evolve rapidly due to more relaxed structure—function constraints than protein-coding sequences and due to positive selection during adaptive radiation 85 , 90 , 91 , Although the extent of congruency of combined genetic and high-depth transcriptomic data is uncertain, as their availability is still limited, the data suggest that many if not most lncRNAs are derived from enhancers , and that lncRNAs are required for enhancer activity , , , , , , examples including the lncRNAs Evf2 also known as Dlx6os1 , Firre , Peril , Upperhand also known as Hand2os1 and Maenli in mice. Wang et al. With advancements in cancer transcriptome profiling and accumulating evidence supporting lncRNA function, a number of differentially expressed lncRNAs have been associated with cancer Table 3. The mostly explored characteristics of lncRNAs include coding potential, location information on the genome, secondary structure, correlation with disease, full-length analysis, and cell localization, which can be determined through bioinformatical analysis. Transcriptional regulation of human small nuclear RNA genes. Mol Pathol. The Sox2 transcription factor binds RNA. Chen, Y. Genes Dev.

0 thoughts on “Long non coding rna”