Lines of symmetry in a pentagon
Here we will learn about lines of symmetryincluding symmetry properties within polygons, angle properties, and symmetry of different line graphs. Lines of symmetry are straight lines of symmetry in a pentagon that divide a shape into two equal parts where one part is an exact reflection of the other. A rectangle has two lines of symmetry LoS shown below using a dashed line.
A line of symmetry is a line that splits a design in half so that both of the halves are symmetrical look the same on both sides. To create a line of symmetry, you need an anchor point. This is the point where the two halves of the design meet. Want to learn even more about symmetry? Have a go at an interactive example question! There are lots of reasons why symmetry is helpful.
Lines of symmetry in a pentagon
A shape can be folded to see if it has a line of symmetry close symmetry Symmetry occurs when half a 2D shape can be reflected in the mirror line known as the line of symmetry to form the whole shape. A shape has a line of symmetry when the folded part sits perfectly on top with all edges matching. The folded part does not sit perfectly on top of the other part. Only the fourth shape has a line of symmetry. A square is a regular polygon close polygon A polygon is a 2-dimensional closed shape with straight sides, eg triangle, hexagon, etc. It has four lines of symmetry and four sides. A regular pentagon close pentagon A polygon with five sides. The order of rotational symmetry of a shape is the number of times it can be rotated around a full circle and still look the same. It only has one order of rotational symmetry, the starting position. In this guide. Types of angle Angles at a point and on a straight line Angles in parallel lines Triangles Quadrilaterals Polygons Symmetry. Lines of symmetry.
Exam prep information pack. The technical storage or access is necessary for the legitimate purpose of storing preferences that are not requested by the subscriber or user. Example 1: the equilateral triangle Example 2: the regular pentagon Example 3: using angles Example 4: angle facts Example 5: quadratic graph Example 6: reciprocal graph.
.
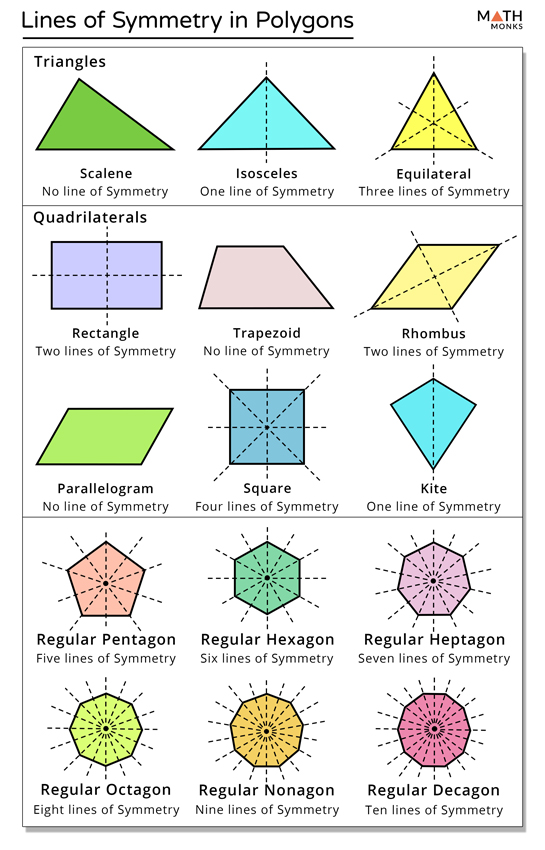
Always on the lookout for fun math games and activities in the classroom? Try our ready-to-go printable packs for students to complete independently or with a partner! Here you will learn about lines of symmetry, including symmetry properties within polygons, angle properties, and symmetry of different line graphs. Students first learn about line symmetry in grade 4 with their work with 2D shapes in geometry. Lines of symmetry are straight lines that divide a shape into two equal parts, where one part is an exact reflection or mirror image of the other. Regular polygons are polygons that have equal side lengths and equal angle measures. Notice how the number of lines of symmetry in these regular polygons is equal to the number of sides and angles the polygons have. All regular polygons share the property that the number of sides is equal to the number of lines of symmetry. Irregular polygons are polygons that do not have all equal angles and all equal side lengths.
Lines of symmetry in a pentagon
A shape can be folded to see if it has a line of symmetry close symmetry Symmetry occurs when half a 2D shape can be reflected in the mirror line known as the line of symmetry to form the whole shape. A shape has a line of symmetry when the folded part sits perfectly on top with all edges matching. The folded part does not sit perfectly on top of the other part.
Katerina kyriazi
Practice lines of symmetry questions. But opting out of some of these cookies may affect your browsing experience. A shape has rotational symmetry when it can be rotated and it still looks the same. Cookie settings Cookie settings. Lines of symmetry in regular shapes Lines of symmetry in irregular shapes Lines of symmetry in graphs Lines of symmetry in circles. If we constructed a line of symmetry at the origin, the line would be perpendicular at 90 degrees to the original line. How to draw lines of symmetry In order to draw lines of symmetry: Locate the centre of the 2D shape. Types of angle Angles at a point and on a straight line Angles in parallel lines Triangles Quadrilaterals Polygons Symmetry. Get started for free! Download apps. Facebook-f Twitter Instagram Youtube. This topic is relevant for:. You may find it helpful to start with the main symmetry lesson for a summary of what to expect, or use the step by step guides below for further detail on individual topics. The equilateral triangle has 3 lines of symmetry.
.
The minimum order of rotational symmetry a shape can have is 1. Continue to rotate the ruler around degrees over the centre point to cover all sides and vertices. As the shape has an even number of vertices, we need to pass through opposite vertices and then pass through opposing sides. Quick links. Maths information pack. Cookie settings Cookie settings. First name. On the other hand, some shapes have no lines of symmetry. We tend to find symmetrical objects attractive and harmonious. Show answer. It has rotational symmetry of order two. Our brains really like symmetrical things and are automatically drawn to it. Book a chat with our team.

I am sorry, that has interfered... This situation is familiar To me. I invite to discussion. Write here or in PM.
What about it will tell?