Lines of symmetry hexagon
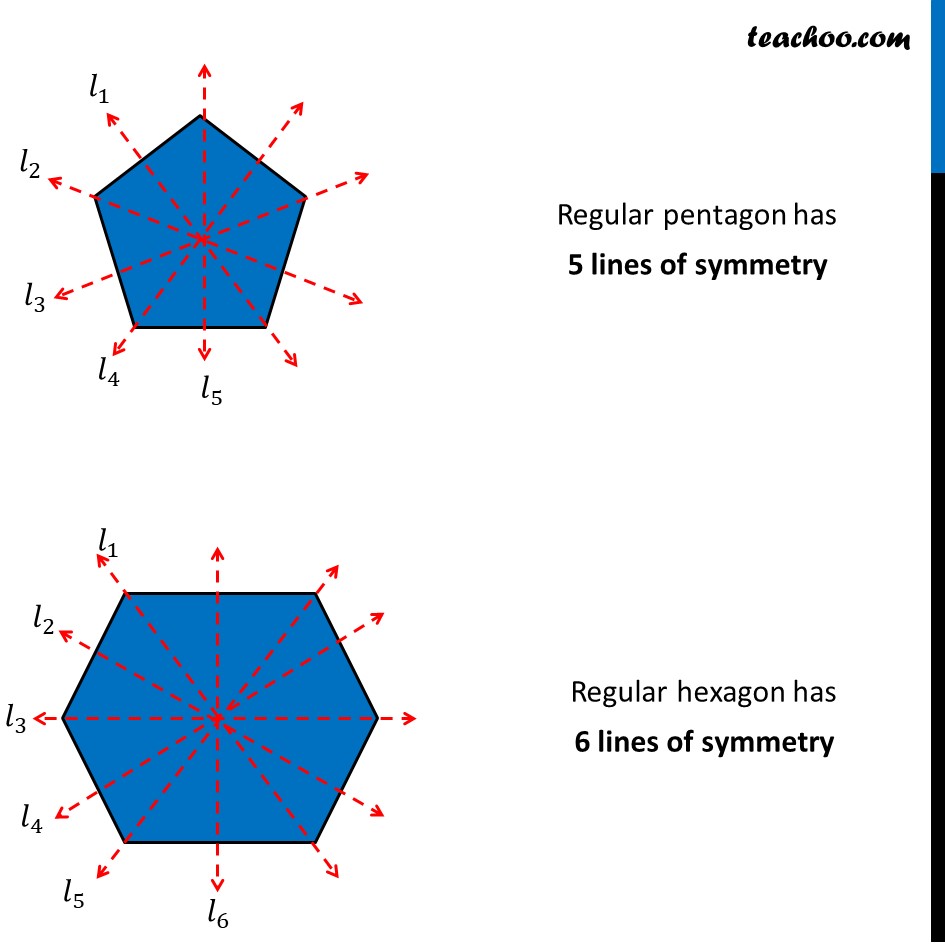
A regular hexagon is a polygon with 6 sides of equal measure. For all regular polygons, the number of lines of symmetry is equal to the number of sides. About Us. Already booked a tutor?
Always on the lookout for fun math games and activities in the classroom? Try our ready-to-go printable packs for students to complete independently or with a partner! Here you will learn about lines of symmetry, including symmetry properties within polygons, angle properties, and symmetry of different line graphs. Students first learn about line symmetry in grade 4 with their work with 2D shapes in geometry. Lines of symmetry are straight lines that divide a shape into two equal parts, where one part is an exact reflection or mirror image of the other. Regular polygons are polygons that have equal side lengths and equal angle measures.
Lines of symmetry hexagon
In geometry, a hexagon can be defined as a closed two-dimensional polygon with six sides. Hexagon has 6 vertices and 6 angles also. We can find the shape of a hexagon in a honeycomb, a football, face of pencil, and floor tiles. Hexagonal shape is classified into several types based on the measure of sides and angles. When the length of all the sides and measure of all the angles are equal, it is a regular hexagon. All interior angles of a regular hexagon are degrees each. A regular hexagon has 6 lines of symmetry and a rotational symmetry of order 6. In an irregular hexagon, the length of sides and measure of angles do not have the same measure. For convex hexagons, all of its interior angles must be less than degrees, and all the vertices are pointed outwards. Convex hexagons can be regular or irregular. In regular hexagons, all sides are equal in length. So, the perimeter of a regular hexagon is six times the length of one side. Example 1: Find the perimeter of a regular hexagon having each side measure 20 cm. Example 2: The perimeter of a regular hexagon is 36 cm.
The horizontal line is NOT a line of symmetry because it does not divide the parallelogram into two equal halves that are mirror images of each other.
A regular hexagon is defined as a hexagon that is both equilateral and equiangular. It is bicentric , meaning that it is both cyclic has a circumscribed circle and tangential has an inscribed circle. All internal angles are degrees. A regular hexagon has six rotational symmetries rotational symmetry of order six and six reflection symmetries six lines of symmetry , making up the dihedral group D 6. The longest diagonals of a regular hexagon, connecting diametrically opposite vertices, are twice the length of one side.
The shape will look the same on both sides of the line of symmetry. We can mark lines of symmetry using a dashed line drawn on the shape. We can find lines of symmetry using a mirror. We have a line of symmetry if the reflection of the shape in the mirror looks the same as the shape in front of the mirror. A line of symmetry can be found by folding the shape.
Lines of symmetry hexagon
A line of symmetry is a line that divides a figure into two identical parts. The figure below shows 3 line of symmetry examples. A line of symmetry is defined as an imaginary line that divides an object into two identical symmetrical halves. Another way to think about this is: if a figure can be folded over a line such that each half perfectly overlaps, the line is a line of symmetry. In the above figure, folding the left half of the square over the red dotted line results in the left half perfectly overlapping with the right half of the square. The dotted red line is therefore a line of symmetry.
R7800 firmware
In order to access this I need to be confident with: 2D shapes Regular polygons Irregular polygons Parallel lines Perpendicular lines. The interior of such a hexagon is not generally defined. Saudi Arabia. Always on the lookout for fun math games and activities in the classroom? For all regular polygons, the number of lines of symmetry is equal to the number of sides. Common Core State Standards How does this apply to 4th grade math? Chamfered dodecahedron. Isosceles triangles have only one line of symmetry. An equilateral triangle has 3 equal sides and 3 equal angles, so it will have 3 lines of symmetry. The cells of a beehive honeycomb are hexagonal for this reason and because the shape makes efficient use of space and building materials.
A regular hexagon is a polygon with 6 sides of equal measure. For all regular polygons, the number of lines of symmetry is equal to the number of sides.
So there will be 6 lines of symmetry for a regular hexagon. The Hexagon , a hexagonal theatre in Reading, Berkshire. The next lessons are Angles in polygons Congruence and similarity Transformations. You also have the option to opt-out of these cookies. Equilateral triangles are the only triangles that have 3 lines of symmetry because it is a regular triangle. In geometry, a hexagon can be defined as a closed two-dimensional polygon with six sides. They have line symmetry and rotational symmetry. Circles have an infinite amount of lines of symmetry. Marking the center, there are 6 lines that can be drawn through the center that cut the regular hexagon into equal halves that are mirror images of each other. Maths Formulas. Regular hexagon has all sides are equal in length. Related Worksheets. When the length of all the sides and measure of all the angles are equal, it is a regular hexagon.

Excuse for that I interfere � To me this situation is familiar. Is ready to help.