Lewis dot structure germanium
Ge, Sb, Se and Br have 4, 5, 4, 6 and 7 valence electrons respectively.
A chemical element is identified by the number of protons in its nucleus, and it must collect an equal number of electrons if it is to be electrically neutral. As electrons are added, they fill electron shells in an order determined by which configuration will give the lowest possible energy. In the periodic table, the elements are placed in "periods" and arranged left to right in the order of filling of electrons in the outer shell. So hydrogen and helium complete the first period. The number of electrons in a given shell can be predicted from the quantum numbers associated with that shell along with the Pauli exclusion principle. The third shell also has 8 electrons, but things get more complicated after than because the subshells spread out enough that there is overlap between them.
Lewis dot structure germanium
.
U2 - Prob. Ge, Sb, Se and Br bond with 4, 3, 2 and 1 hydrogen respectively to form the corresponding covalent hydrides.
.
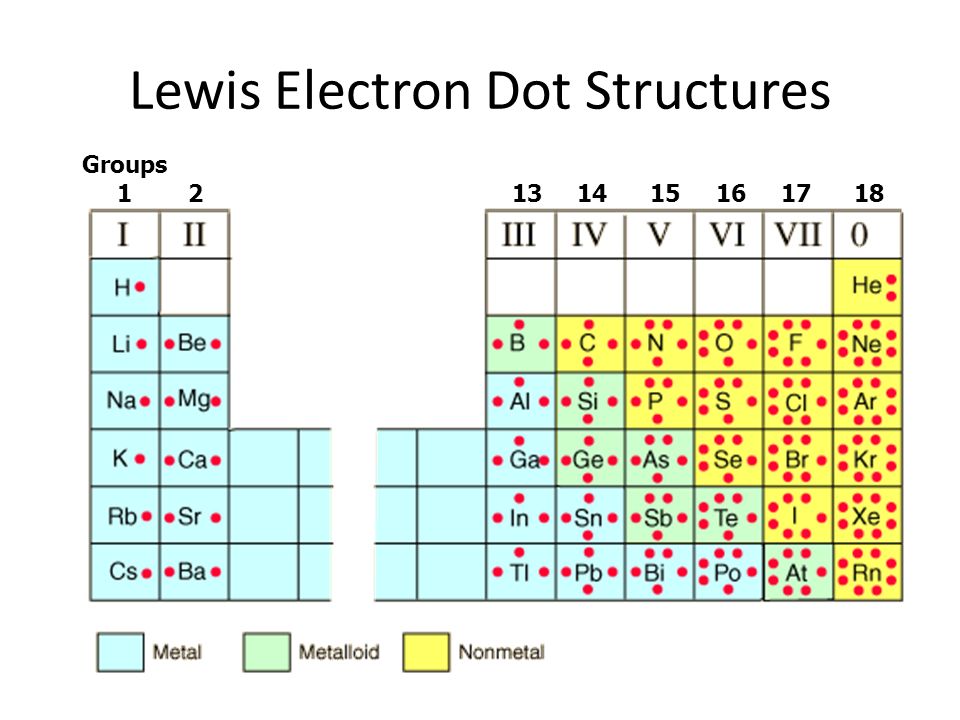
It is usually easier to figure out a problem if you can draw a picture, either mental or real, of what is happening. This is often done in physics and mathematics, and it is especially helpful when looking at the bonding, structure, physical properties, and reactivity of compounds. The most common picture, or model, of elements and compounds used is the Lewis Dot Structure. These pictures show you the type s of atom s involved, their position in the molecule, and where their valence electrons are situated. Dash each dash represents two electrons that are shared between two atoms as a covalent bond. The valence electron configurations of the constituent atoms of a covalent compound are important factors in determining its structure, stoichiometry, and properties. For example, chlorine, with seven valence electrons, is one electron short of an octet. If two chlorine atoms share their unpaired electrons by making a covalent bond and forming Cl 2 , they can each complete their valence shell:. Each chlorine atom now has an octet.
Lewis dot structure germanium
In all cases, these bonds involve the sharing or transfer of valence shell electrons between atoms. In this section, we will explore the typical method for depicting valence shell electrons and chemical bonds, namely Lewis symbols and Lewis structures. We use Lewis symbols to describe valence electron configurations of atoms and monatomic ions. A Lewis symbol consists of an elemental symbol surrounded by one dot for each of its valence electrons:.
Celebs with stoma bags
Electron Distributions Into Shells for the First Three Periods A chemical element is identified by the number of protons in its nucleus, and it must collect an equal number of electrons if it is to be electrically neutral. The attractive force which has the ability of holding various constituent elements like atoms, ions, molecules, etc. Types of Chemical Bonds. SI1RE Ch. Chemical compounds are dependent on the strength of chemical bonds b…. Publisher: Cengage Learning. Chemistry: Principles and Reactions. Zumdahl, Donald J. Author: William L. A coordinate covalent bond is also known as a dative bond, which is a type of covalent bond.
Allotropes Some elements exist in several different structural forms, called allotropes. Each allotrope has different physical properties.
There are one lone pair electrons on Sb atom. Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind Zumdahl, Susan A. U2 - Prob. Organic Chemistry. There is no lone pair of electrons. Lewis dot symbols for all the given elements are drawn below. Se has 6 valence electrons and bonds with 2 hydrogens. Publisher: McGraw-Hill Education. So hydrogen and helium complete the first period. Skoog, F. Ge, Sb, Se and Br bond with 4, 3, 2 and 1 hydrogen respectively to form the corresponding covalent hydrides. Types of Chemical Bonds.

I apologise, I can help nothing. I think, you will find the correct decision.