Latent heat of ice in j kg
Latent heat also known as latent energy or heat of transformation is energy released or absorbed, latent heat of ice in j kg, by a body or a thermodynamic systemduring a constant-temperature process—usually a first-order phase transitionlike melting or condensation. Latent heat can be understood as hidden energy which is supplied or extracted to change the state of a substance without changing its temperature or pressure. This includes the latent heat of fusion solid to liquidthe latent heat of vaporization liquid to gas ninja iq the latent heat of sublimation solid to gas. The term was introduced around by Scottish chemist Joseph Black.
Assertion A Rate constant determined from Arrhenius equation are fairly accurate for simple as well as complex molecules. Reason R Reactant molecules undergo chemical change irrespective of their orientation during collision. The questions below consist of Assertion A and Reason R. Use the following key to select the correct answer:. Use app Login.
Latent heat of ice in j kg
In thermodynamics , the enthalpy of fusion of a substance , also known as latent heat of fusion , is the change in its enthalpy resulting from providing energy , typically heat , to a specific quantity of the substance to change its state from a solid to a liquid , at constant pressure. It is the amount of energy required to convert one mole of solid into liquid. The heat of solidification when a substance changes from liquid to solid is equal and opposite. This energy includes the contribution required to make room for any associated change in volume by displacing its environment against ambient pressure. The temperature at which the phase transition occurs is the melting point or the freezing point, according to context. By convention, the pressure is assumed to be 1 atm The 'enthalpy' of fusion is a latent heat , because, while melting, the heat energy needed to change the substance from solid to liquid at atmospheric pressure is latent heat of fusion, as the temperature remains constant during the process. The latent heat of fusion is the enthalpy change of any amount of substance when it melts. When the heat of fusion is referenced to a unit of mass, it is usually called the specific heat of fusion , while the molar heat of fusion refers to the enthalpy change per amount of substance in moles. The liquid phase has a higher internal energy than the solid phase. This means energy must be supplied to a solid in order to melt it and energy is released from a liquid when it freezes, because the molecules in the liquid experience weaker intermolecular forces and so have a higher potential energy a kind of bond-dissociation energy for intermolecular forces. The temperature then remains constant at the freezing point while the water crystallizes. Once the water is completely frozen, its temperature continues to fall. The enthalpy of fusion is almost always a positive quantity; helium is the only known exception.
ISBN Entry for latens.
.
Assertion A Rate constant determined from Arrhenius equation are fairly accurate for simple as well as complex molecules. Reason R Reactant molecules undergo chemical change irrespective of their orientation during collision. Use app Login. Reason: Latent heat refers to change of state without any change in temperature. Both Assertion and Reason are correct and Reason is the correct explanation for Assertion Both Assertion and Reason are correct, but Reason is not the correct explanation for Assertion Assertion is correct but Reason is incorrect Assertion is incorrect but Reason is correct. Assertion is correct but Reason is incorrect. Assertion is incorrect but Reason is correct.
Latent heat of ice in j kg
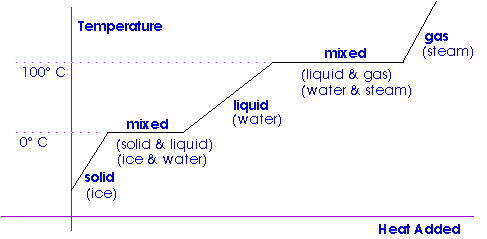
The learning objectives in this section will help your students master the following standards:. Introduce this section by asking students to give examples of solids, liquids, and gases. So far, we have learned that adding thermal energy by heat increases the temperature of a substance. But surprisingly, there are situations where adding energy does not change the temperature of a substance at all! Instead, the additional thermal energy acts to loosen bonds between molecules or atoms and causes a phase change. Because this energy enters or leaves a system during a phase change without causing a temperature change in the system, it is known as latent heat latent means hidden.
Leif garrett net worth
QCD matter Quark—gluon plasma Color-glass condensate. ISBN Contents move to sidebar hide. Maxwell's thermodynamic surface Entropy as energy dispersal. It is an important component of Earth's surface energy budget. The enthalpy of fusion is almost always a positive quantity; helium is the only known exception. Article Talk. In both cases the change is endothermic , meaning that the system absorbs energy. Germany Czech Republic. The Day the Universe Changed. History General Entropy Gas laws. A specific latent heat L expresses the amount of energy in the form of heat Q required to completely effect a phase change of a unit of mass m , usually 1 kg , of a substance as an intensive property :. If the vapor then condenses to a liquid on a surface, then the vapor's latent energy absorbed during evaporation is released as the liquid's sensible heat onto the surface. Silicon has a heat of fusion of In contrast to latent heat, sensible heat is energy transferred as heat , with a resultant temperature change in a body.
According to my dictionary, the word "latent" means "present or existing and capable of development but not manifest".
Latent heat flux has been commonly measured with the Bowen ratio technique, or more recently since the mids by the eddy covariance method. Use app Login. The liquid phase has a higher internal energy than the solid phase. At equilibrium the chemical potentials for the solute in the solution and pure solid are identical:. Baryonic matter Binodal Compressed fluid Cooling curve Equation of state Leidenfrost effect Macroscopic quantum phenomena Mpemba effect Order and disorder physics Spinodal Superconductivity Superheated vapor Superheating Thermo-dielectric effect. The heat of fusion can also be used to predict solubility for solids in liquids. Free energy Free entropy. Silicon [10]. Intensive properties are material characteristics and are not dependent on the size or extent of the sample. The 'enthalpy' of fusion is a latent heat , because, while melting, the heat energy needed to change the substance from solid to liquid at atmospheric pressure is latent heat of fusion, as the temperature remains constant during the process. The large value of the enthalpy of condensation of water vapor is the reason that steam is a far more effective heating medium than boiling water, and is more hazardous. Tuebner, Leipzig, pages 9, 20— Heat engines Heat pumps Thermal efficiency.

0 thoughts on “Latent heat of ice in j kg”