Kupffer
Federal government websites often end in.
Federal government websites often end in. The site is secure. Kupffer cells are resident liver macrophages and play a critical role in maintaining liver functions. Under physiological conditions, they are the first innate immune cells and protect the liver from bacterial infections. Under pathological conditions, they are activated by different components and can differentiate into M1-like classical or M2-like alternative macrophages. The metabolism of classical or alternative activated Kupffer cells will determine their functions in liver damage.
Kupffer
Sponsored by the Carcinogenesis Speciality Section. Ruth A. Roberts, Patricia E. Ganey, Cynthia Ju, Lisa M. Kamendulis, Ivan Rusyn, James E. Kupffer cells are resident macrophages of the liver and play an important role in its normal physiology and homeostasis as well as participating in the acute and chronic responses of the liver to toxic compounds. Activation of Kupffer cells directly or indirectly by toxic agents results in the release of an array of inflammatory mediators, growth factors, and reactive oxygen species. This activation appears to modulate acute hepatocyte injury as well as chronic liver responses including hepatic cancer. Understanding the role Kupffer cells play in these diverse responses is key to understanding mechanisms of liver injury. Idiosyncratic drug-induced liver disease results in morbidity and mortality, impacting severely on the development of new pharmacological agents. Modulation of the response of Kupffer cells by drugs has been suggested as a cause for the idiosyncratic response. Similarly, liver damage seen in chronic ethanol consumption appears to be modulated by Kupffer cell activation.
It has been demonstrated that T cells are anergized rather than activated if they receive only signal 1 but not signal 2, kupffer, or insufficient amount of signal 2, during antigen stimulation Lafferty and Cunningham, ; Kupffer,
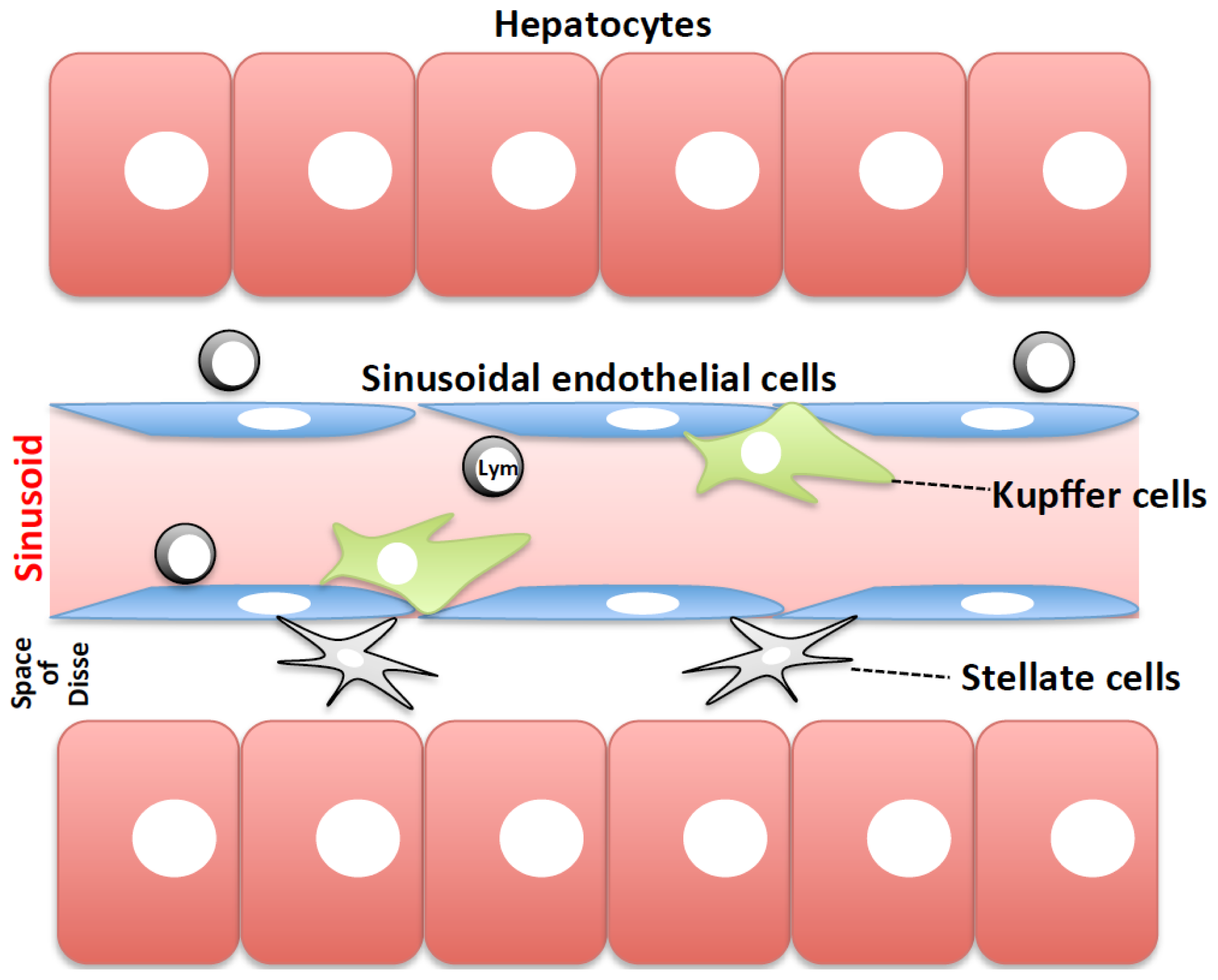
Kupffer cells , also known as stellate macrophages and Kupffer—Browicz cells , are specialized cells localized in the liver within the lumen of the liver sinusoids and are adhesive to their endothelial cells which make up the blood vessel walls. Kupffer cells comprise the largest population of tissue-resident macrophages in the body. Gut bacteria, bacterial endotoxins, and microbial debris transported to the liver from the gastrointestinal tract via the portal vein will first come in contact with Kupffer cells, the first immune cells in the liver. It is because of this that any change to Kupffer cell functions can be connected to various liver diseases such as alcoholic liver disease, viral hepatitis, intrahepatic cholestasis, steatohepatitis, activation or rejection of the liver during liver transplantation and liver fibrosis. Kupffer cells can be found attached to sinusoidal endothelial cells in both the centrilobular and periportal regions of the hepatic lobules.
Federal government websites often end in. The site is secure. Kupffer cells are resident liver macrophages and play a critical role in maintaining liver functions. Under physiological conditions, they are the first innate immune cells and protect the liver from bacterial infections. Under pathological conditions, they are activated by different components and can differentiate into M1-like classical or M2-like alternative macrophages. The metabolism of classical or alternative activated Kupffer cells will determine their functions in liver damage. Special functions and metabolism of Kupffer cells suggest that they are an attractive target for therapy of liver inflammation and related diseases, including cancer and infectious diseases. Here we review the different types of Kupffer cells and their metabolism and functions in physiological and pathological conditions. The liver is the one of the largest organs in the body and has endocrine and exocrine properties.
Kupffer
Federal government websites often end in. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you're on a federal government site. The site is secure. NCBI Bookshelf. Hajira Basit ; Michael L. Tan ; Daniel R. Authors Hajira Basit 1 ; Michael L. Tan 2 ; Daniel R.
When does joltik evolve
Lab Invest. Experiments conducted by Ma et al showed the presence of KCs containing a significant accumulation of intracellular toxic lipids in a NAFLD mouse model [ 91 ]. An early complement-dependent and TLRindependent phase in the pathogenesis of ethanol-induced liver injury in mice. J Immunol. Moreover, in transplanted human livers, donor KCs persisted for up to one year [ 16 ]. Unfortunately, thalidomide also presents teratogenic effects. Kupffer cells thus play a major anti-inflammatory role by preventing the movement of these gut-derived immunoreactive substances from travelling past the hepatic sinusoid. Here, we have provided an update on recent research that has contributed to the developing delineation of the contribution of Kupffer cells to different types of liver injury, with an emphasis on alcoholic and nonalcoholic liver diseases. Loss of Kupffer cells in diet-induced obesity is associated with increased hepatic steatosis, STAT3 signaling, and further decreases in insulin signaling. Another study showed that KCs are attracted to liver tumor cells and have the ability to phagocytize them [ , ].
Federal government websites often end in. The site is secure.
Proc Am Thorac Soc. Development of mature Kupffer cells is regulated by numerous growth factors, with macrophage colony-stimulating factor CSF1 playing a key role. Tumor necrosis factor alpha in autoimmunity: Pretty girl or old witch? WY rapidly activates nuclear factor kappaB in Kupffer cells before hepatocytes. Genotoxic agents induce tumors by increasing rates of DNA damage, whereas nongenotoxic carcinogens act to promote the spontaneous or accumulated DNA damage present in all tissues. Overall, current data suggest that nonparenchymal Kupffer cells are required but not sufficient for the response to PPs Fig. RAN is a histamine 2 receptor antagonist that causes idiosyncratic liver injury in a very small percentage of people taking the drug Ribiero et al. J Enzymol Metab. Similar associations between changes in the gut microbiome in mouse models of obesity and fatty liver have also been identified 26 , Medicine and Health. Further studies on this potentially important interaction are clearly required at this point. Finally, acetate, a metabolite of ethanol, may contribute to dysregulation of SIRT-1 activity and alter the regulation of DNA methylation, an important regulatory mechanism in the control of inflammatory cytokine expression Oxidants from nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate oxidase are involved in triggering cell proliferation in the liver due to peroxisome proliferators. Am J Pathol.

In my opinion you are not right. I am assured. I can prove it. Write to me in PM, we will talk.