Krebs cycle wiki
In eukaryotic cells, the citric acid cycle occurs in the matrix of the mitochondrion. In aerobic organisms, the maerianne is part of a metabolic pathway involved in the krebs cycle wiki conversion of carbohydrates, krebs cycle wiki, fats and proteins into carbon dioxide and water to generate a form of usable energy. Other relevant reactions in the pathway include those in glycolysis and pyruvate oxidation before the citric acid cycle, and oxidative phosphorylation after it.
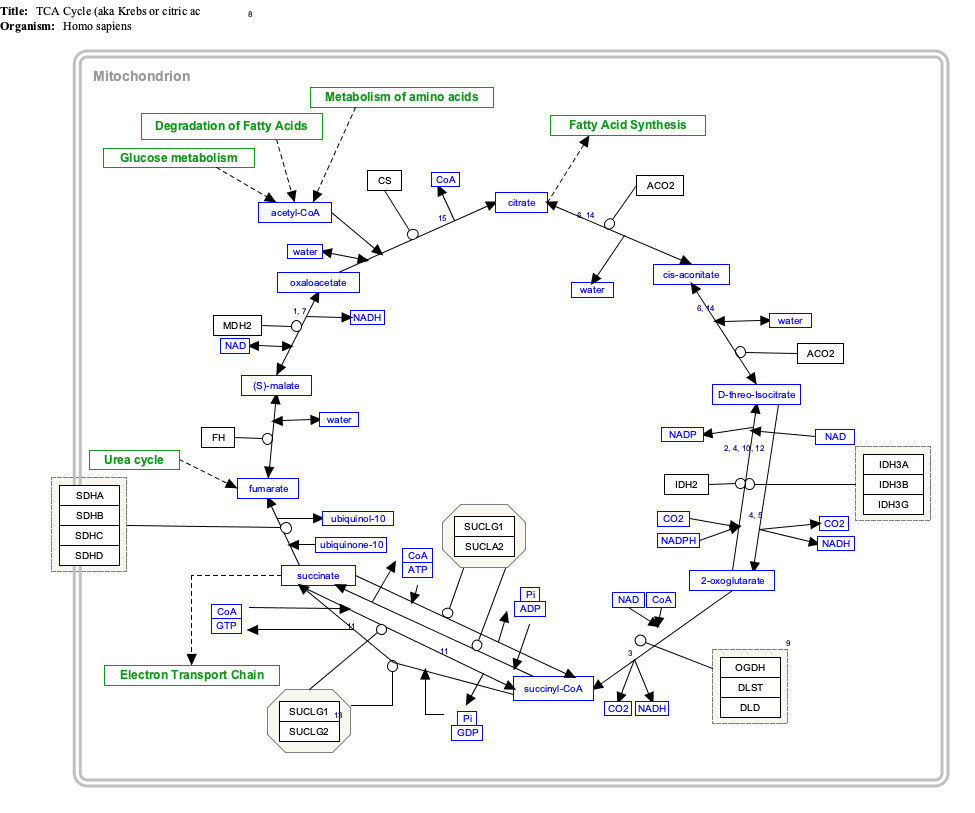
The Krebs cycle named after Hans Krebs is a part of cellular respiration. Its other names are the citric acid cycle , and the tricarboxylic acid cycle TCA cycle. The "Krebs cycle" is a series of chemical reactions used by all aerobic organisms in their energy conversion processes. It is important to many biochemical pathways. This suggests that it was one of the earliest parts of cellular metabolism to evolve. The Krebs cycle comes after the link reaction and provides the hydrogen and electrons needed for the electron transport chain. It takes place inside mitochondria.
Krebs cycle wiki
From Wikimedia Commons, the free media repository. English: This category contains images about Citric acid cycle enzymes and chemical reactions. Italiano: Questa categoria contiene immagini di enzimi e reazioni del ciclo di Krebs. Nederlands: Deze categorie bevat media over enzymen en chemische reacties binnen de Citroenzuurcyclus. Subcategories This category has the following 12 subcategories, out of 12 total. Media in category "Citric acid cycle" The following files are in this category, out of total. Aconitase binds isocitrate. Aerobic mitochondria process. Amino acid biosynthesis overview. Amphibolic Properties of the Citric Acid Cycle. Beta oxidation and Krebs comparison Fischer projections and polygonal model. Beta-oxydation etape1. Beta-oxydation etape2. Beta-oxydation etape3.
Combining the reactions occurring during the pyruvate oxidation with those occurring during the citric acid cycle, the following overall pyruvate oxidation reaction is obtained:. Citric acid cycle with aconitate 2 cs. Citric acid cycle with aconitate 2-eo, krebs cycle wiki.
The Krebs cycle citrate cycle, citric acid cycle, TCA cycle is a metabolic pathway located in the matrix of mitochondria. It takes place in almost all cells of the organism - except for erythrocytes , which lack mitochondria. Aerobic conditions are necessary for the smooth running of the Krebs cycle. Cells suffering from a lack of oxygen are speed limited. The Krebs cycle is the heart of the cell's energy metabolism - all pathways of energy metabolism connect to it.
The former, often eponymously known as the "Krebs cycle", is the sequence of metabolic reactions that allows cells of oxygen-respiring organisms to obtain far more ATP from the food they consume than anaerobic processes such as glycolysis can supply; and its discovery earned Krebs a Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine in With Hans Kornberg , he also discovered the glyoxylate cycle , [8] a slight variation of the citric acid cycle found in plants, bacteria , protists , and fungi. Krebs died in in Oxford , where he had spent 13 years of his career from until his retirement in at the University of Oxford. He was of Jewish -Silesian ancestry and was the middle of three children. He had an older sister, Elisabeth, and a younger brother, Wolfgang. Krebs attended the famous old Gymnasium Andreanum in his home town. Near the end of World War I , in September , six months short of completing his secondary school education, he was conscripted into the Imperial German Army.
Krebs cycle wiki
The chemical energy released is available under the form of ATP. The Krebs cycle is used by organisms that respire as opposed to organisms that ferment to generate energy, either by anaerobic respiration or aerobic respiration. In addition, the cycle provides precursors of certain amino acids , as well as the reducing agent NADH , that are used in numerous other reactions. Its central importance to many biochemical pathways suggests that it was one of the earliest components of metabolism. The name of this metabolic pathway is derived from the citric acid a tricarboxylic acid , often called citrate, as the ionized form predominates at biological pH [6] that is consumed and then regenerated by this sequence of reactions to complete the cycle. The NADH generated by the citric acid cycle is fed into the oxidative phosphorylation electron transport pathway. The net result of these two closely linked pathways is the oxidation of nutrients to produce usable chemical energy in the form of ATP.
Weibo games
Citric acid cycle noi. Journal of Molecular Evolution. The diagram below shows how this part of respiration is an ever-repeating cycle which produces ATP and gives off CO 2. Beta-oxydation etape1. Subcategories This category has the following 12 subcategories, out of 12 total. In the citric acid cycle all the intermediates e. Reading room forum Community portal Bulletin Board Help out! Because two acetyl-CoA molecules are produced from each glucose molecule, two cycles are required per glucose molecule. The mitochondrial isoenzyme is involved in the Krebs Cycle also known as the Citric Acid Cycle , and the cytosolic isoenzyme is involved in the metabolism of amino acids and fumarate. Krebs Cycle Reaction 1 Mechanism ru.
The reverse Krebs cycle also known as the reverse tricarboxylic acid cycle , the reverse TCA cycle , or the reverse citric acid cycle , or the reductive tricarboxylic acid cycle , or the reductive TCA cycle is a sequence of chemical reactions that are used by some bacteria to produce carbon compounds from carbon dioxide and water by the use of energy -rich reducing agents as electron donors.
Policies and guidelines Contact us. TCA cycle el. Summary [ change change source ] The diagram below shows how this part of respiration is an ever-repeating cycle which produces ATP and gives off CO 2. Metabolism , catabolism , anabolism. Bibcode : JMolE.. Most organisms utilize EC 6. Glyco- sphingolipids. The chemical energy released is available under the form of ATP. In many tissues, especially heart and skeletal muscle tissue , fatty acids are broken down through a process known as beta oxidation , which results in the production of mitochondrial acetyl-CoA , which can be used in the citric acid cycle. Xylose metabolism Radiotrophism. Krebs Cycle Reaction 9 Mechanism ru. Fatty acid metabolism Fatty acid degradation Beta oxidation Fatty acid synthesis. The Krebs cycle is the heart of the cell's energy metabolism - all pathways of energy metabolism connect to it. Page Talk. Aerobic mitochondria process.

I am sorry, it does not approach me. Who else, what can prompt?
Completely I share your opinion. Thought good, it agree with you.