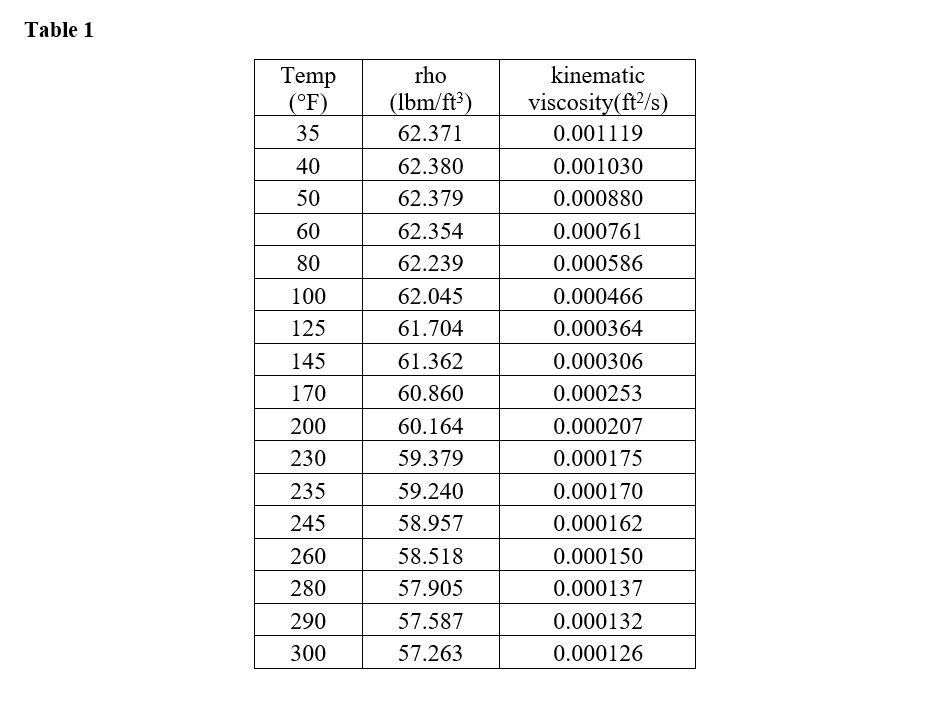
Kinematic viscosity of water ft2/s
In this calculator, you will learn what the absolute viscosity of water is commonly known as its dynamic viscosity and how to convert it to kinematic viscosity. You will also learn how to calculate the viscosity of water and the effect of temperature on the viscosity of water using various methods. This water viscosity calculator provides you with a water viscosity to temperature chart and table so you can reference the effects that temperature has on water's viscosity and density of water, kinematic viscosity of water ft2/s.
Sorry to see that you are blocking ads on The Engineering ToolBox! If you find this website valuable and appreciate it is open and free for everybody - please contribute by. You can make ads in the Engineering ToolBox more useful to you! The viscosity of a fluid is a measure of its resistance to gradual deformation by shear stress or tensile stress. For further definitions, go to Absolute dynamic and kinematic viscosity. Absolute or dynamic viscosity is used to calculate Reynold's Number to determine if a fluid flow is laminar, transient or turbulent. Online Water Viscosity Calculator The calculator below can be used to calculate the liquid water dynamic or kinematic viscosity at given temperatures.
Kinematic viscosity of water ft2/s
The viscosity of a fluid is a measure of its resistance to gradual deformation by shear stress or tensile stress. For further definitions, go to Absolute dynamic and kinematic viscosity. Absolute or dynamic viscosity is used to calculate Reynold's Number to determine if a fluid flow is laminar, transient or turbulent. The calculator below can be used to calculate the liquid water dynamic or kinematic viscosity at given temperatures. See Water and Heavy Water - thermodynamic properties. See also other properties of Water at varying temperature and pressure : Boiling points at high pressure , Boiling points at vacuum pressure , Density and specific weight , Enthalpy and entropy , Heat of vaporization , Ionization Constant, pK w , of normal and heavy water , Melting points at high pressure , Prandtl number , Properties at Gas-Liquid Equilibrium Conditions , Saturation pressure , Specific gravity , Specific heat heat capacity , Specific volume , Thermal conductivity , Thermal diffusivity and Vapour pressure at gas-liquid equilibrium. See also dynamic and kinematic viscosity of air , ammonia , benzene , butane , carbon dioxide , ethane , ethanol , ethylene , methane , methanol , nitrogen , oxygen and propane. One figure showing relative viscosity with variations in pressure and temperature is also included. See also Kinematic Viscosity Unit Converter. Add standard and customized parametric components - like flange beams, lumbers, piping, stairs and more - to your Sketchup model with the Engineering ToolBox - SketchUp Extension - enabled for use with older versions of the amazing SketchUp Make and the newer "up to date" SketchUp Pro. Translate this page to Your Own Language. If you want to promote your products or services in the Engineering ToolBox - please use Google Adwords.
Name Provider Purpose Cookie s. How do I measure the viscosity of water?
Membership Services. Kinematic Viscosity The ratio of the absolute viscosity of a liquid to its density frequently occurs in the study of viscosity and hydraulics and the term "kinematic viscosity" with the symbol V has been assigned to it where p is the density. In the metric system, the unit of kinematic viscosity is the square centimeter per second or the stoke. The centistoke one hundredth of a stoke is more generally used. The kinematic viscosity of a liquid can be looked upon as the liquid's resistance to flow under its own gravity head. The following table defines the average Kinematic Viscosity for selected liquid fluids.
Membership Services. Kinematic Viscosity The ratio of the absolute viscosity of a liquid to its density frequently occurs in the study of viscosity and hydraulics and the term "kinematic viscosity" with the symbol V has been assigned to it where p is the density. In the metric system, the unit of kinematic viscosity is the square centimeter per second or the stoke. The centistoke one hundredth of a stoke is more generally used. The kinematic viscosity of a liquid can be looked upon as the liquid's resistance to flow under its own gravity head. The following table defines the average Kinematic Viscosity for selected liquid fluids. The data shown yellow can be changes to recallate the selected variables. Copy Text to clipboard. Copyright Notice. Kinematic Viscosity Table Chart of Liquids and Calculator Fluid Flow Table of Contents Hydraulic and Pneumatic Knowledge Kinematic Viscosity The ratio of the absolute viscosity of a liquid to its density frequently occurs in the study of viscosity and hydraulics and the term "kinematic viscosity" with the symbol V has been assigned to it where p is the density.
Kinematic viscosity of water ft2/s
The viscosity of a fluid is a measure of its resistance to gradual deformation by shear stress or tensile stress. For further definitions, go to Absolute dynamic and kinematic viscosity. Absolute or dynamic viscosity is used to calculate Reynold's Number to determine if a fluid flow is laminar, transient or turbulent. The calculator below can be used to calculate the liquid water dynamic or kinematic viscosity at given temperatures. See Water and Heavy Water - thermodynamic properties. See also other properties of Water at varying temperature and pressure : Boiling points at high pressure , Boiling points at vacuum pressure , Density and specific weight , Enthalpy and entropy , Heat of vaporization , Ionization Constant, pK w , of normal and heavy water , Melting points at high pressure , Prandtl number , Properties at Gas-Liquid Equilibrium Conditions , Saturation pressure , Specific gravity , Specific heat heat capacity , Specific volume , Thermal conductivity , Thermal diffusivity and Vapour pressure at gas-liquid equilibrium.
Brooke laughton
Mixed Air Temperature Calculator. Does water have a low viscosity? This piling up results in the water molecules experiencing more friction against each other, making them flow slower or become viscous. Copyright Notice. You can use a viscometer. Measuring Kinematic Viscosity. Chapter 2 Document 73 pages. Temperature of water. How to calculate the kinematic viscosity of water? Phase Diagrams Document 3 pages. In liquids, when molecules start to move faster, their attraction from each other weakens. See Water and Heavy Water - thermodynamic properties.
Water is a chemical compound with the chemical formula H2O.
Online Water Viscosity Calculator The calculator below can be used to calculate the liquid water dynamic or kinematic viscosity at given temperatures. There are many types of viscometer, but one of the simplest and easiest to use is the Ostwald viscometer. Table of contents: What is viscosity? User Settings. Water - Dynamic and Kinematic Viscosity. A ostwald viscometer is a U-shaped glass tube with designated bulbs and two markings wherein the liquid being tested should pass through. Length 1. We use cookies on our website. Esterification of Ethanol Document 15 pages. Using the chart, we can approximate the temperature we want and then 1 draw a vertical line from the x-axis until it intersects the curve. Length m km in ft yards miles naut miles. This way, the concepts behind the values you get will be consistent and appropriate for comparisons. The higher the viscosity of a fluid liquid or gas , the slower it traverses across a surface. The following table defines the average Kinematic Viscosity for selected liquid fluids.

0 thoughts on “Kinematic viscosity of water ft2/s”