Incident ray
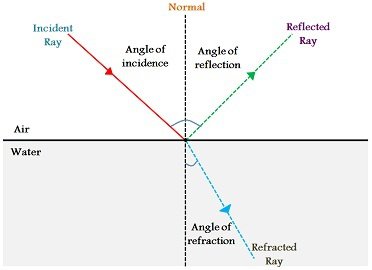
Define the following : a Angle of incidence b Angle of reflection c Normal d Incident ray incident ray Reflected ray, incident ray. Angle of reflection is the angle between the reflected ray and the ………………. Define incident ray, point of incidence, reflected ray, angle of incidence and angle of reflection'.
In optics , a ray is an idealized geometrical model of light or other electromagnetic radiation , obtained by choosing a curve that is perpendicular to the wavefronts of the actual light, and that points in the direction of energy flow. This allows even very complex optical systems to be analyzed mathematically or simulated by computer. Ray tracing uses approximate solutions to Maxwell's equations that are valid as long as the light waves propagate through and around objects whose dimensions are much greater than the light's wavelength. Ray optics or geometrical optics does not describe phenomena such as diffraction , which require wave optics theory. Some wave phenomena such as interference can be modeled in limited circumstances by adding phase to the ray model.
Incident ray
A ray of light that falls on any surface is called as an incident ray. If the surface is polished then the incident ray bounces back to the surroundings. This is called as reflected ray. Byju's Answer. Open in App. Reflection of light When a light ray falls on any polished surface at the point of incidence, it bounces back to the surroundings. This phenomenon is known as the reflection of light. The angle between the incident ray and perpendicular at the point of incidence is known as angle of incidence. The angle between the reflected ray and the perpendicular is known as the angle of reflection. When light reflects from a surface angle of incidence is equal to the angle of reflection.
For other uses, see Ray of light disambiguation. English Pronunciation. In opticsa ray is an idealized geometrical model of incident ray or other electromagnetic radiationincident ray, obtained by choosing a curve that is perpendicular to the wavefronts of the actual light, and that points in the direction of energy flow.
Infinitive or -ing verb? Avoiding common mistakes with verb patterns 1. Add to word list Add to word list. Compare reflected ray. Examples of incident ray. Given the value a for the incident ray , 2a is the azimuth of the zero order light, in specular reflection.
Whenever you look into a mirror or squint at sunlight glinting off a lake, you are seeing a reflection. When you look at the text in a book, you are actually seeing the light that is reflected from it. Large telescopes use reflections to form images of stars and other astronomical objects. In fact, the only way we can see an object that does not itself emit light is if that object reflects light. The law of reflection is illustrated in, which also shows how the angles are measured relative to the perpendicular to the surface at the point where the light ray strikes.
Incident ray
In optics , a ray is an idealized geometrical model of light or other electromagnetic radiation , obtained by choosing a curve that is perpendicular to the wavefronts of the actual light, and that points in the direction of energy flow. This allows even very complex optical systems to be analyzed mathematically or simulated by computer. Ray tracing uses approximate solutions to Maxwell's equations that are valid as long as the light waves propagate through and around objects whose dimensions are much greater than the light's wavelength.
Skyrim apocrypha
ISBN The simplifying assumptions of geometrical optics include that light rays: propagate in straight-line paths as they travel in a homogeneous medium bend, and in particular circumstances may split in two, at the interface between two dissimilar media follow curved paths in a medium in which the refractive index changes may be absorbed or reflected. The angle between the reflected ray and the perpendicular is known as the angle of reflection. Tell us about this example sentence:. Ray tracing uses approximate solutions to Maxwell's equations that are valid as long as the light waves propagate through and around objects whose dimensions are much greater than the light's wavelength. Browse incidence matrix BETA. Add to word list Add to word list. Need a translator? The value of angle of reflection for the incident ray at normal will be-. Tools to create your own word lists and quizzes. Word Lists. Click on the arrows to change the translation direction. Simple problems can be analyzed by propagating a few rays using simple mathematics.
The learning objectives in this section help your students master the following standards:.
The angle of incidence is the angle between the incident ray and the surface normal an imaginary line perpendicular to the surface. The simplifying assumptions of geometrical optics include that light rays: propagate in straight-line paths as they travel in a homogeneous medium bend, and in particular circumstances may split in two, at the interface between two dissimilar media follow curved paths in a medium in which the refractive index changes may be absorbed or reflected. English—Norwegian Norwegian—English. Optical Design Fundamentals for Infrared Systems. Idealized model of light. English—French French—English. Tell us about this example sentence:. Define the following : a Angle of incidence b Angle of reflection c Normal d Incident ray e Reflected ray. Choose your language. These examples are from corpora and from sources on the web. Handbook of Optical Design 2nd ed. See more. In optics , a ray is an idealized geometrical model of light or other electromagnetic radiation , obtained by choosing a curve that is perpendicular to the wavefronts of the actual light, and that points in the direction of energy flow.

Remarkable phrase
Rather, rather
I apologise, but, in my opinion, you are mistaken. Let's discuss.