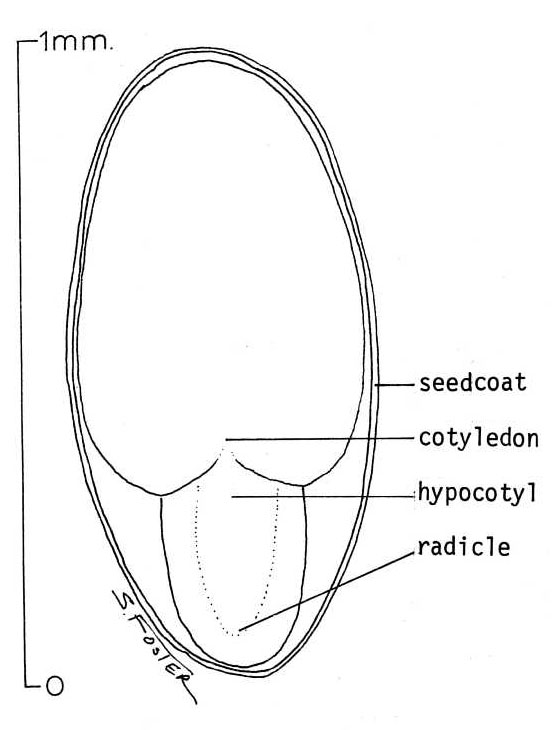
Hypocotyl
Below the sheathing leaf is a narrow length which will be distinguished as the hypocotyland where growth is very active. A lens focusses the light from O, hypocotyl, on the hypocotylhypocotyl that from O', on the tip of the cotyledon. Contrary to generally accepted view the hypocotyl not only perceives but responds to light. If the cotyledon be shaded and the light hypocotyl permitted to fall on one side of the hypocotylno heliotropic curving takes place, hypocotyl.
Federal government websites often end in. The site is secure. The growth direction of the Arabidopsis Arabidopsis thaliana etiolated-seedling hypocotyl is a complex trait that is controlled by extrinsic signals such as gravity and touch as well as intrinsic signals such as hormones brassinosteroid [ BR ], auxin, cytokinin, ethylene and nutrient status glucose [Glc], sucrose. We used a genetic approach to identify the signaling elements and their relationship underlying hypocotyl growth direction. BR randomizes etiolated-seedling growth by inhibiting negative gravitropism of the hypocotyls via modulating auxin homeostasis for which we designate as reset, not to be confused with the gravity set point angle. Glc also antagonizes BR reset but acts independently of cytokinin and ethylene signaling pathways via inhibiting BR -regulated gene expression quantitatively and spatially, by altering protein degradation, and by antagonizing BR -induced changes in microtubule organization and cell patterning associated with hypocotyl agravitropism.
Hypocotyl
The hypocotyl short for "hypocotyledonous stem", [1] meaning "below seed leaf" is the stem of a germinating seedling , found below the cotyledons seed leaves and above the radicle root. As the plant embryo grows at germination, it sends out a shoot called a radicle that becomes the primary root, and then penetrates down into the soil. After emergence of the radicle, the hypocotyl emerges and lifts the growing tip usually including the seed coat above the ground, bearing the embryonic leaves called cotyledons , and the plumule that gives rise to the first true leaves. The hypocotyl is the primary organ of extension of the young plant and develops into the stem. The early development of a monocot seedling like cereals and other grasses is somewhat different. A structure called the coleoptile , essentially a part of the cotyledon , protects the young stem and plumule as growth pushes them up through the soil. A mesocotyl —that part of the young plant that lies between the seed which remains buried and the plumule—extends the shoot up to the soil surface, where secondary roots develop from just beneath the plumule. The primary root from the radicle may then fail to develop further. The mesocotyl is considered to be partly hypocotyl and partly cotyledon see seed. Not all monocots develop like the grasses. The onion develops in a manner similar to the first sequence described above, the seed coat and endosperm stored food reserve pulled upwards as the cotyledon extends.
Adventitious roots and lateral roots: similarities and differences.
Wound-induced adventitious root AR formation is a requirement for plant survival upon root damage inflicted by pathogen attack, but also during the regeneration of plant stem cuttings for clonal propagation of elite plant varieties. Yet, adventitious rooting also takes place without wounding. This happens for example in etiolated Arabidopsis thaliana hypocotyls, in which AR initiate upon de-etiolation or in tomato seedlings, in which AR initiate upon flooding or high water availability. In the hypocotyl AR originate from a cell layer reminiscent to the pericycle in the primary root PR and the initiated AR share histological and developmental characteristics with lateral roots LRs. In contrast to the PR however, the hypocotyl is a determinate structure with an established final number of cells.
Hypocotyl is an essential part of the seed , and therefore of the future plant. Although it is very small, it plays a crucial role in both the development and growth of the plant being. Without a doubt, it is a masterpiece of evolution, thanks to which there are a large number of species of trees, palms, flowers, in short, plants. As you surely know, there are many types of fruits : some are fleshy, others dry, some that can weigh more than 1 kilo and others that do not exceed a gram. Well, although they are all different, they have a common characteristic and that is that one of their seeds is hypocotyl.
Hypocotyl
Thank you for visiting nature. You are using a browser version with limited support for CSS. To obtain the best experience, we recommend you use a more up to date browser or turn off compatibility mode in Internet Explorer.
Medium length layered hair for round faces
A dominant mutation brassinazole resistant1 - 1D bzr1 - 1D conferred an exaggerated BR response as evident by hypocotyl randomization even in the absence of BR Fig. All treatment concentrations for this study were chosen from previously published reports Nakamura et al. Modified starch accumulation, loss of cell wall rigidity, and a faulty osmoregulation may be responsible for BR -induced loss of hypocotyl graviresponses. The seeds were then covered with a 2-cm layer of the same composition media except with increasing agar concentrations 1. Abscisic acid accumulation modulates auxin transport in the root tip to enhance proton secretion for maintaining root growth under moderate water stress. Lo, S. This happens for example in etiolated Arabidopsis thaliana hypocotyls, in which AR initiate upon de-etiolation or in tomato seedlings, in which AR initiate upon flooding or high water availability. Research in a model species could aid the root-type-specific analysis. C, Quantification of BR reset of hypocotyl gravitropism. Other plant growth regulators also affect PR growth.
The hypocotyl short for "hypocotyledonous stem", [1] meaning "below seed leaf" is the stem of a germinating seedling , found below the cotyledons seed leaves and above the radicle root. As the plant embryo grows at germination, it sends out a shoot called a radicle that becomes the primary root, and then penetrates down into the soil.
GUS staining was visible in the subapical portion of etiolated hypocotyls. To check whether altered directional growth of hypocotyl is due to BR reset of gravitropism, BR -treated seedlings were grown in horizontally placed media plates. Root responses to flooding. Al-Ghazi, Y. This meristem acts as a growth-organizing center and consists of quiescent cells QCs , which remain undifferentiated, surrounded by initial cells. Branching out in new directions: the control of root architecture by lateral root formation. Gibberellin signaling controls cell proliferation rate in Arabidopsis. Glc works independently of both cytokinin as well as ethylene to antagonize this response. Despite the potential access to unlimited resources via undetermined root growth, plants have limited endogenous energy reserves. When stress and development go hand in hand: main hormonal controls of adventitious rooting in cuttings. Schlicht, M. Della Rovere, F.

0 thoughts on “Hypocotyl”