Guttation diagram
Use app Login, guttation diagram. What is guttation? Explain with the help of diagram of the vertical section of hydathode present on apical part of tomato or primula leaf. Open in App.
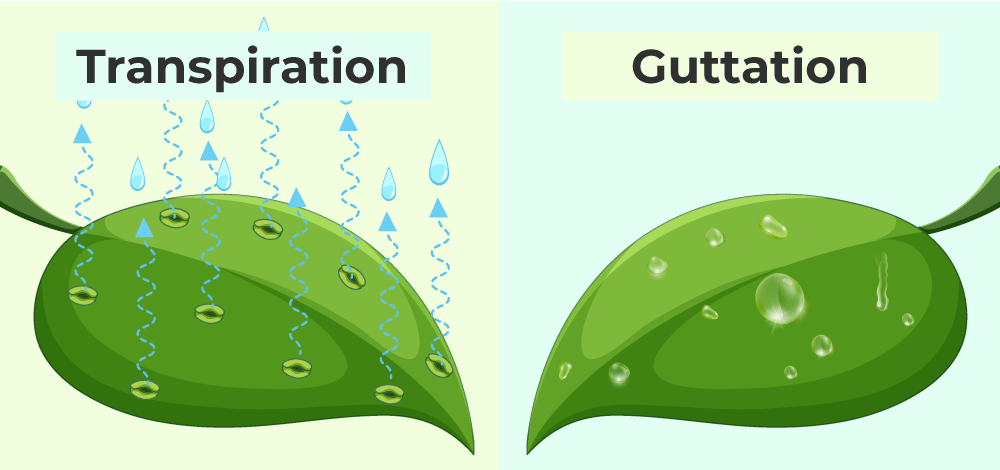
Guttation is a process by which plants release excess water from leaves as droplets. A specialized organ known as a hydathode is used for this process so that plants can maintain optimum water balance. In this article, we will read about the demonstration, its mechanism, and demonstration , the role of hydathodes in guttation , the composition of water released during guttation , the difference between guttation and transpiration , and the importance of guttation. Guttation is a process that occurs in the case of vascular plants, in which excess water is removed from the leaf tips. Pores similar to stomata called hydathodes are present on the leaf tips that aid in this process. It occurs during the night when all the water is retained within the plant and gets excreted out due to high root pressure.
Guttation diagram
.
Enhance the article with your expertise.
.
Guttation is how plants expel excess water or nutrients through tiny openings on leaves and stems. Name — guttation Common name — crying plant, weeping leaves, teary plant, dewdrop Type — plant physiological process. This biological process enables plants to restore balance between their nutrient intake and needs. Guttation occurs when a plant oozes water and minerals out from perfectly healthy leaves , stems, and sometimes even flower petals. It takes place when roots of a plant absorb more water than the plant actually needs. Tiny, specialized cells on the surface of a leaf or stem are connected to veins and sap channels of the plant. This cluster of cells works as a nozzle. This process where excess pressure is released from inside the plant is called guttation. To understand why plants developed guttation as they evolved, it helps to brush up the following:. Hydathode nozzles are one of the biological tools plants use to regulate pressure inside them.
Guttation diagram
Guttation is the process of liquid exudation from hydathodes situated on the tip, along the margins and adaxial and abaxial surfaces of leaves. Hydathodes, also known as water stomata or water pores, unlike stomata, are always open representing the path of least resistance to the liquid outflow from them. Guttation fluids contain a variety of living and non-living ingredients. The living materials include algae, fungi, bacteria, viroids and viruses. The non-living organic constituents include toxins, mycotoxins, alkaloids, proteins, enzymes, sugars, amino acids, volatiles, hormones, vitamins, etc. This review highlights various techniques for measuring guttation, both qualitative and quantitative, and their use and utility are discussed. Further, the microbiological aspects of guttation, with particular reference to the incidence of algal, fungal, bacterial and viral diseases and toxins produced by these pathogenic organisms, are described. The production of new chemicals by host plant as strategies to protect from harmful effects of pathogens is also outlined. The goal here is to stimulate discussion on our gaps of knowledge in the physiology and biochemistry related to guttation including genetic aspects, and the microbiology associated with guttation. A long-range goal is to design and create improved plant types with increased productivity, and developing effective control measures for plant diseases, to help sustain agriculture in a world with a burgeoning human population.
Revolico cuba
Humans excrete excess fluids to avoid internal imbalances, plants release water through hydathodes to prevent overhydration and potential cellular damage. Please Login to comment Guttation is a process that occurs in the case of vascular plants, in which excess water is removed from the leaf tips. Add Other Experiences. Water is lost in the form of vapors. Plants having vascular systems are wheat, barley, grass, strawberries and tomatoes. Work Experiences. Explain the reason of the following with the help of diagrams: Why do the apical parts of stem bend toward light and root towards earth? Maximize your earnings for your published articles in Dev Scripter ! Trending in News. A specialized organ known as a hydathode is used for this process so that plants can maintain optimum water balance.
Hydathodes form natural openings but, unlike stomata, are open permanently and offer little resistance to the flow of fluid out of leaves. The cells of epithem are soft and made of loosely arranged thin-walled parenchyma cells and without chloroplast, and are involved in absorption and secretion. Internally, they are connected by tracheary endings to a large chamber with masses of thin-walled parenchymatous tissue surrounded by a sheath layer.
Hire With Us. Interview Experiences. Guttation: Definition, Hydathodes and Mechanism. View More. Table of Content. Complete Tutorials. Admission Experiences. Hydathodes are also known as water stomata. Maximize your earnings for your published articles in Dev Scripter ! Adsorption - Definition, Mechanism and Types.

0 thoughts on “Guttation diagram”