Glycocalyx
Glycocalyx n. The glycocalyx is a polysaccharide -based gel-like, glycocalyx, highly hydrous cellular thin layer, covering present outside the glycocalyx. It acts as an interface between the extracellular matrix and cellular membrane. Glycocalyx also acts as a medium for cell recognition, cell-cell glycocalyx cell signaling.
Critical Care volume 23 , Article number: 16 Cite this article. Metrics details. The glycocalyx is a gel-like layer covering the luminal surface of vascular endothelial cells. It is comprised of membrane-attached proteoglycans, glycosaminoglycan chains, glycoproteins, and adherent plasma proteins. The glycocalyx maintains homeostasis of the vasculature, including controlling vascular permeability and microvascular tone, preventing microvascular thrombosis, and regulating leukocyte adhesion. During sepsis, the glycocalyx is degraded via inflammatory mechanisms such as metalloproteinases, heparanase, and hyaluronidase. These sheddases are activated by reactive oxygen species and pro-inflammatory cytokines such as tumor necrosis factor alpha and interleukin-1beta.
Glycocalyx
Glycocalyx is a surface layer that covers the cell membrane of many bacteria, epithelial cells or other cells. It is made up of proteoglycans, glycoproteins and glycolipids. This acts as a barrier for a cell from its surroundings and provides protection. It helps in maintaining the integrity of cells. It is involved in cell-cell interactions such as signalling, adhesion, etc. The glycocalyx layer also provides mechanical strength to tissues. Glycocalyx consists of proteoglycans, glycosaminoglycans, and other glycoproteins. It is made up of polysaccharide side chains of membrane proteins and lipids. The transmembrane proteins associated with glycocalyx are often linked to the cytoskeleton, which facilitates cell signalling. Glycocalyx is the outermost layer of the three-layered cell envelope present in many bacterial and other prokaryotic cells. The composition and thickness of the glycocalyx layer differ in different bacteria. It may be present in the form of a slimy layer or as a thick capsule. Glycocalyx is followed by the cell wall and plasma membrane. It is a network of polysaccharides attached to the cell wall. In a capsule, the glycocalyx layer is thick and tough.
Cell Dev.
This changed in recent years. Latest research has shown that the glycocalyx is an organelle of vital significance, actively involved in and functionally relevant for various cellular processes, that can be directly targeted in therapeutic contexts. This review gives a brief introduction into glycocalyx biology and describes the specific challenges glycocalyx research faces. Then, the traditional view of the role of the glycocalyx is discussed before several recent breakthroughs in glycocalyx research are surveyed. These results exemplify a currently unfolding bigger picture about the role of the glycocalyx as a fundamental cellular agent.
If the glycocalyx appears unorganized and more loosely attached, it is referred to as a slime layer. The glycocalyx is usually a viscous polysaccharide or polypeptide slime. Actual production of a glycocalyx often depends on environmental conditions. Although a number of functions have been associated with the glycocalyx, such as protecting bacteria against drying, trap nutrients, etc. The glycocalyx enables certain bacteria to resist phagocytic engulfment by white blood cells in the body or protozoans in soil and water. The glycocalyx also enables some bacteria to adhere to environmental surfaces rocks, root hairs, teeth, etc. As will be seen in Unit 5, there are several steps involved in phagocytosis. First the surface of the microbe must be attached to the cytoplasmic membrane of the phagocyte.
Glycocalyx
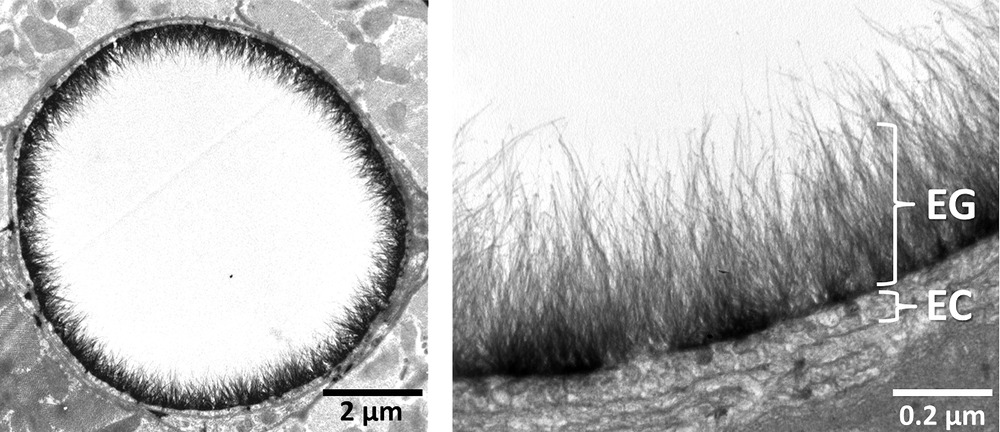
Federal government websites often end in. The site is secure. The vascular endothelial glycocalyx is a dense, bush-like structure that is synthesized and secreted by endothelial cells and evenly distributed on the surface of vascular endothelial cells.
Valentina y leo san juan
The second aspect that determines monosaccharide identity are chemical modifications such as oxidation of hydroxyl groups, N -acetylation, sulfation, and many more. For simplicity, the different sugars found within the glycocalyx are depicted with the same symbol blue hexagons. Quantification of septic glycocalyx degradation using circulating biomarkers Syndecan-1 Studies demonstrate that syndecan-1 shedding is associated with both sepsis presence and severity Table 1. Microorganisms They measured heparan sulfate levels in plasma collected upon ICU admission and found that patients with indirect lung injury had fold higher median levels of heparan sulfate compared to normal donors. Dick W. As a consequence, TPLSM offers good resolution and optical sectioning at reasonable acquisition speed, while bleaching and phototoxicity of the dyes is limited to the focal position. Cite this article Uchimido, R. This acts as a barrier for a cell from its surroundings and provides protection. In addition, sevoflurane has been shown to have a certain protective effect on the glycocalyx. B The antibody-sialidase conjugate T-Sia 2. This group of endothelial glycoproteins, characterized by relatively small 2—15 sugar residues and branched carbohydrate side chains, comprises a number of molecules that all have been studied intensively; major classes that will be discussed in more detail below are the endothelial cell adhesion molecules and components of the coagulation and fibrinolysis system.
Glycocalyx n. The glycocalyx is a polysaccharide -based gel-like, highly hydrous cellular thin layer, covering present outside the cell. It acts as an interface between the extracellular matrix and cellular membrane.
Circ Res. The endothelial glycocalyx and perioperative lung injury. Life Sci. C-reactive protein impairs the endothelial glycocalyx resulting in endothelial dysfunction. Recently, the glycocalyx has been added to the list of possible candidates. Therefore, glycocalyx can prevent negatively charged molecules such as albumin from passing through the BBB due to charge repulsion Deen et al. Fluid resuscitation is an essential therapeutic treatment for sepsis and septic shock [ 53 ]. Copy to clipboard. Shear stress and the endothelial transport barrier. Introduction The surface of the vascular endothelium is covered with a layer of villiform substance, which is called the glycocalyx. From this point onward, glucuronic acids and glucosamines are linked to the core protein. However, it is not clear whether the glycocalyx in the BBB is different from the glycocalyx in the general vascular structure. B Five examples for sugar conjugates found in the glycocalyx: GM4, a glycolipid; an extended core 4 O -glycosylation structure; the core structure of complex N -glycosylation; a side chain found in chondroitin sulfate; hyaluronan or hyaluronic acid.

0 thoughts on “Glycocalyx”