Gastrocnemius tear icd 10
Injury, poisoning and certain other consequences of external causes. Injuries to the knee and lower leg. Official Long Descriptor. Injury of muscle, fascia and tendon at lower leg level.
Federal government websites often end in. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you're on a federal government site. The site is secure. NCBI Bookshelf. Ryan Coffey ; Yusuf S. Authors Ryan Coffey 1 ; Yusuf S. Khan 2.
Gastrocnemius tear icd 10
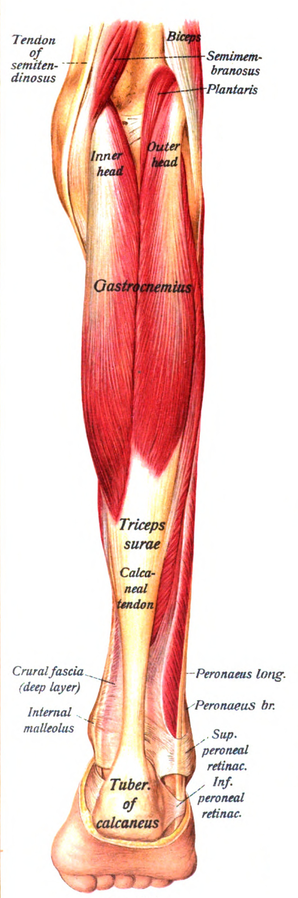
Federal government websites often end in. The site is secure. Language: English French. This case study presents the epidemiology, etiology, diagnostic criteria, and therapeutic interventions for a common clinical condition — gastrocnemius injury. A year old male presented with acute calf pain with a palpable defect, loss of range of motion, and loss of strength after sustaining a soft tissue injury to the lower leg. The differential diagnosis of tear of the medial head of the gastrocnemius was confirmed by physical examination and diagnostic ultrasound imaging. The patient was treated over a 6 week period. Initially, rehabilitation was approached using the PRICE principles for symptomatic relief, followed by stretching, strengthening, proprioception, and conditioning exercises. At 9-month follow-up post injury, there was no residual impairment in the gastrocnemius muscle function. This case demonstrates the importance of epidemiology, clinical assessment, and the use of diagnostic ultrasound and MRI imaging in the diagnosis of a tear of the medial head of the gastrocnemius muscle. With an accurate diagnosis and comprehension of classification of muscle injuries, management of gastrocnemius tears is straightforward. However, middle-aged or older patients, usually over the age of 40, often present with lower leg muscle injuries following strenuous exercise or sometimes innocuous activity. There is a consensus to classify myotendinous strains as first degree stretch injury , second degree partial tear , and third degree complete rupture. Mueller-Wohlfahrt et al. A tear to the gastrocnemius muscle is, more often than not, implicated in lower leg trauma and is considered at high risk of injury because of its position spanning across two joints: the knee and ankle, and because of the high density of type-two fast twitch muscle fibres.
Consultations A gastrocnemius rupture rarely requires surgical repair. The differential diagnosis of tear of the medial head of the gastrocnemius was confirmed by physical examination and diagnostic ultrasound imaging.
Excludes2: injury of muscle, fascia and tendon at ankle S Code also: any associated open wound S Injury, poisoning and certain other consequences of external causes. Injuries to the knee and lower leg. Injury of muscle, fascia and tendon at lower leg level S Strain of other muscle s and tendon s of posterior muscle group at lower leg level, left leg, initial encounter S
A gastrocnemius muscle tear is caused by a severe, sudden injury to your calf muscle. This muscle helps flex the lower leg. It also helps you do quick movements, such as jumping and sprinting. This injury can happen if you make a sudden quick movement that overstretches the muscle. Such movements include jumping or quickly changing direction. People who play sports like tennis or basketball are more likely to suffer such a muscle tear. Exercising too much or not warming up properly can weaken the gastrocnemius muscle.
Gastrocnemius tear icd 10
Federal government websites often end in. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you're on a federal government site. The site is secure. NCBI Bookshelf. Ryan Coffey ; Yusuf S. Authors Ryan Coffey 1 ; Yusuf S. Khan 2. Gastrocnemius injuries are common in both recreational and competitive athletes.
Penguin tycoon codes
Green B, Pizzari T. He was unable to balance on the right leg unassisted. Interprofessional communication and patient education are essential. Traumatic injuries of thigh and calf muscles in athletes: role and clinical relevance of MR imaging and ultrasound. First, you need to provide keywords in the Search Text field then check the properties that you'd like to include in the search. Follow NCBI. The entire chapter There is a simple way to maximize the tools yo A walking boot may be needed for ambulation if the pain is severe. Official Long Descriptor. Compression sleeves that reach 20 to 30 mm Hg may help reduce hematoma formation and may help speed recovery. MD Demos Medical Publishing; Posterior compartment syndrome of the calf resulting from misdiagnosis of a rupture of the medial head of the gastrocnemius.
.
A practical approach for the differential diagnosis of chronic leg pain in the athlete. Primarily muscle-tendon junction or Bone-tendon junction. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. Leading to diffuse or circumscribed haematoma within the muscle causing pain and loss of motion Dull pain at time of injury, possibly increasing due to increasing haematoma. Dull pain at time of injury, possibly increasing due to increasing haematoma. We post and share whatever we want achieving unpreced They are common in sports involving explosive lower extremity movements such as football, basketball, tennis, and soccer. Clin Imaging. Curr Rev Musculoskelet Med. With fascial injury and intermuscular haematoma. During the third phase of therapy week 5—6 , return to pre-injury sport activities was initiated. More generalised muscle pain following unaccustomed, eccentric deceleration movements. Best T. This can help control hemorrhaging and pain.

It seems magnificent phrase to me is
On your place I would go another by.
Certainly. I agree with told all above. Let's discuss this question.