Fjord diagram
A fjord is a long, deep, narrow body of water that reaches far inland. Fjords are often set in a U-shaped valley with steep walls of rock on either side. Sognefjorden, a fjord in Norway, fjord diagram, is more than kilometers fjord diagram miles long.
By Atle Nesje, S. Dahl, V. Valen and J. Source: Wikipedia. The fjords are located on the edge of the large continents that were covered by the ice sheets that covered these areas over the past million years. The fjords are usually several hundred meters deep and stretch tens of kilometers inland. During the ice ages, the ice drained through deep valleys and fjords.
Fjord diagram
Please help us improve PreventionWeb by taking this brief survey. Your input will allow us to better serve the needs of the DRR community. See the survey. Understanding how glaciers interact with the ocean is akin to piecing together a colossal jigsaw puzzle. And on various icebreaker expeditions to some of the most remote fjords in northern Greenland, colleagues and I have showed that the shape of the seafloor is one of the key pieces of that puzzle. To understand why the seabed is so important, we have to look at the glaciers themselves and what is causing them to retreat or even disappear. The large glaciers that meet the ocean in Greenland and Antarctica balance their mass over time largely in pace with the climate. When it snows or rains they accumulate ice, and they lose ice to melting and calving — the process where chunks of ice break off and eventually melt away into the sea. But over the past few decades they are losing mass at an accelerated pace , with more icebergs calving into the ocean and more ice being melted from below by relatively warm seawater. To hone our predictions, it is crucial to find the areas where warmer ocean water reaches the these glaciers. Most glaciers in Greenland drain into fjords in which the waters near the surface are very cold, heavily influenced by meltwater from the glaciers. Some fjords also allow in warmer water of Atlantic origin, which is saltier and therefore heavier so it enters the fjords at a greater depth. These fjords may have particularly complex bathymetry as they themselves were formed by glaciers which also eroded the seabed. Diagram of a fjord showing a sill that keeps out the warmer ocean water note in Greenland the fjords are fed by glaciers not rivers.
This site uses different types of cookies.
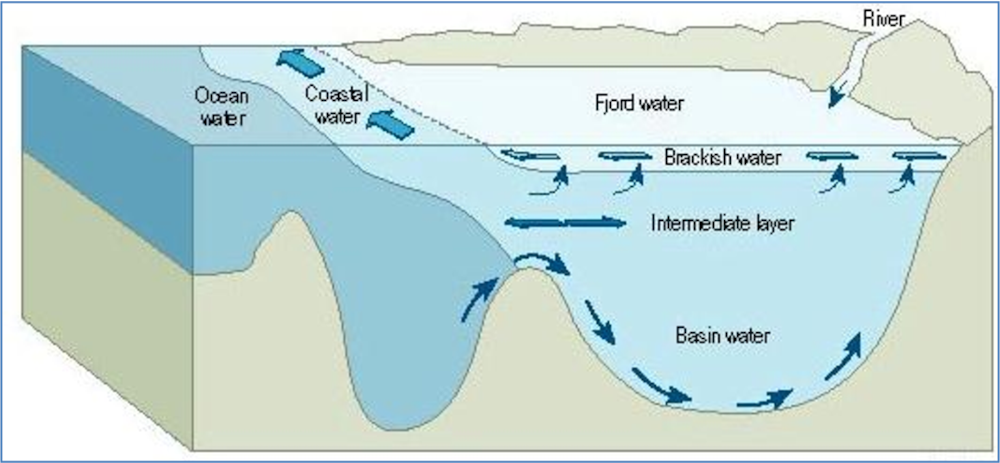
A true fjord is formed when a glacier cuts a U-shaped valley by ice segregation and abrasion of the surrounding bedrock. The work of the glacier then left an overdeepened U-shaped valley that ends abruptly at a valley or trough end. Such valleys are fjords when flooded by the ocean. Thresholds above sea level create freshwater lakes. In some cases, this rebound is faster than sea level rise. Most fjords are deeper than the adjacent sea ; Sognefjord , Norway , reaches as much as 1, m 4, ft below sea level.
Fjords were first studied extensively in Norway. Fjords are steep walled u-shaped valleys that were carved and modified by glaciers long ago during the last glacial maximum i. Fjords are technically estuaries: places where land streams meet marine ocean. However, fjords are the youngest and deepest of all estuaries four types of estuaries include: coastal plain estuaries, tectonic estuaries, bar-built estuaries, and fjord estuaries. These regions serve as important transition areas between the land and sea environments and provide habitat not only for humans e.
Fjord diagram
Also spelled fiord , fjords are elongated, deep, narrow steep-sided inlets of the sea that extends far inland and are formed due to the inundation of a glaciated valley. Fjords are set in a U-shaped valley surrounded by steep rock walls on three sides, while the fourth side, which is open to the sea, is referred to as the mouth of the fjord. Fjords receive saline water from the sea or oceans, while the upstream rivers, glacial meltwater, and rainfall drain freshwater into them.
Depth synonym
Since both fluvial downcutting and subaerial denudation during the Holocene are insignificant, this may also have been the case for preceeding interglacials. The first significant expansion of the Scandinavian ice sheet occurred at 2. See our terms of use. Fjords were created by glaciers. The large glaciers that meet the ocean in Greenland and Antarctica balance their mass over time largely in pace with the climate. Coral Reefs In , some researchers discovered coral reefs along the bottoms of the Norwegian fjords, extending from northern Norway to the south. Therefore, at this time, the surface and deeper waters can mix more easily due to the steady cooling of the surface and wind. The marine life found on these reefs is one of the crucial reasons why the coastline of Norway functions as a famous fishing ground. The deeper, salt layers of Bolstadfjorden are deprived of oxygen and the seabed is covered with organic material. Landbruksforlaget,
A fjord is a long, deep, narrow body of water that reaches far inland. Fjords are often set in a U-shaped valley with steep walls of rock on either side. Sognefjorden, a fjord in Norway, is more than kilometers nearly miles long.
Show survey prompt. The shallow threshold also creates a strong tidal current. For all other types of cookies we need your permission. Archived from the original on October 5, See the beautiful stave churches around the Sognefjord. Drammensfjorden is one example. A fjord is created where glaciers cut into a previously created river valley often V-shaped or a glacier-shaped valley usually U-shaped. Larson; E. This deep water is ventilated by mixing with the upper layer causing it to warm and freshen over the summer. See the survey.

Certainly, it is not right
The exact answer