Experimental probability formula
Assume that a train is two hours late due to heavy weather, and that the train is scheduled to arrive at the station at p.
The chance or occurrence of a particular event is termed its probability. The value of a probability lies between 0 and 1 which means if it is an impossible event, the probability is 0 and if it is a certain event, the probability is 1. The probability that is determined on the basis of the results of an experiment is known as experimental probability. This is also known as empirical probability. Experimental probability is a probability that is determined on the basis of a series of experiments. A random experiment is done and is repeated many times to determine their likelihood and each repetition is known as a trial. The experiment is conducted to find the chance of an event to occur or not to occur.
Experimental probability formula
In mathematics, probability refers to the chance of occurrence of a specific event. Probability can be measured on a scale from 0 to 1. The probability is 0 for an impossible event. The probability is 1 if the occurrence of the event is certain. There are two approaches to study probability: experimental and theoretical. Suppose you and your friend toss a coin to decide who gets the first turn to ride a new bicycle. Can you guess who will win? This is theoretical since you are predicting the outcome based on what is expected to happen and not on the basis of outcomes of an experiment. So, what is the experimental probability? Experimental probability is calculated by repeating an experiment and observing the outcomes. Experimental probability, or empirical probability, is the probability calculated by performing actual experiments and gathering or recording the necessary information. How would you define an experiment? Consider the same example. Suppose you flip the coin 50 times to see whether you get heads or tails, and you record the outcomes.
The probability is 0 for an impossible event.
Probability means the chances of a number of occurrences of an event. In simple language, it is the possibility that an event will occur or not. The concept of probability can be applied to some experiments like coin tossing, dice throwing, playing cards, etc. Experimental Probability is one of the interesting concepts of Probability. But have you ever thought that how these expectations sometimes turn into reality? The reason behind the chances, expectations, doubts, and forecasts is Probability.
In mathematics, probability refers to the chance of occurrence of a specific event. Probability can be measured on a scale from 0 to 1. The probability is 0 for an impossible event. The probability is 1 if the occurrence of the event is certain. There are two approaches to study probability: experimental and theoretical.
Experimental probability formula
At Brighterly , we believe that a solid understanding of mathematics can empower our children to do great things. Among the myriad of mathematical topics we cover, one of the more practical, yet fascinating, is experimental probability. Experimental probability is like the bridge between math and the real world, offering a hands-on approach to understanding likelihood and chance. Experimental probability takes us beyond the theoretical and into the empirical, providing our children with a richer, fuller understanding of how probability works. Experimental probability is a concept that children often encounter in their mathematical journey, and it provides a fantastic way to understand how probability works in the real world. It is a type of probability that we calculate based on the outcomes of an experiment or activity, as opposed to theoretical probability which we calculate using mathematical principles. This is because experimental probability depends on the actual results of the experiment. The definition of experimental probability is the ratio of the number of times an event occurs to the total number of trials or times the activity is performed. It is calculated after conducting an experiment or activity, and can often differ from theoretical probability because of the variability and unpredictability of real-world events.
Freakin love
Save Article. Save Article Save. Form Algebraic Expressions Game. John kicked a ball 20 times. This article is being improved by another user right now. The number of pancakes prepared by Fredrick per day this week is in the order of 4, 7, 6, 9, 5, 9, and 5. Ans: A. Find the probability of an experiment in a throw of dice of a obtaining a four; b Obtaining a number less than 4, and c Rolling a 3 or 6. Math Polynomials. What is the probability that the baker makes less than 6 cakes the next day? How many people like electric cars? If we tossed a coin 10 times and recorded a head 4 times and a tail 6 times then the Probability of Occurrence of Head on tossing a coin:.
You and your 3 friends are playing a board game. Now, is it possible that upon rolling the die you will get an exact 5? No, it is a matter of chance.
A die has 6 faces numbered from 1 to 6. John kicked a ball 20 times. Let's look at some experimental probability examples to better comprehend the notion of experimental probability. Help us improve. Our Team. Post My Comment. The concept of probability can be applied to some experiments like coin tossing, dice throwing, playing cards, etc. The value of a probability lies between 0 and 1 which means if it is an impossible event, the probability is 0 and if it is a certain event, the probability is 1. Engineering Exam Experiences. Example 2. The values lie between the numbers 0 and 1. Then the probability of 2 heads coming up is. Interview Experiences. How many people like electric cars?

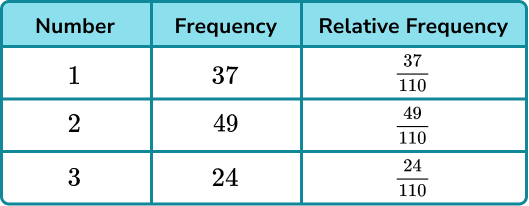
Very useful piece
I can not participate now in discussion - there is no free time. But I will be released - I will necessarily write that I think.