Era stat baseball
We use cookies and other tracking technologies to improve your browsing experience on our site, show personalized content and targeted ads, analyze site traffic, and understand where our audiences come from, era stat baseball. To learn more or opt-out, read our Cookie Policy. Pitching is a complicated process. Pitchers can use a combination of at least a half-dozen pitches, with different spin era stat baseball, into different locations in the strikezone, with a variety of outcomes.
The baseball world has undergone a revolution, one that has taken place in the past few decades. It has transformed how many view the game. No metric can completely quantify the game as a whole, but those in and around baseball now have better ways to break down what's happening and what might happen next. It isn't just to replace the "eye test" or scouting, but it is to be layered on top of everything else, sort of like a blue print. And why is it so important for these metrics to appear in our coverage?
Era stat baseball
Even the most cursory glance at baseball and you can see that it is a numbers paradise. Statistics are a part of all sports, but with the advent of sabermetrics, baseball has elevated them to the realm of edification, almost worship. There was a time when the stats were seen as quaint, additional information, to help you understand trends perhaps, but the real knowledge of the game, the gut feeling if you will, was the important component. There are a stunning number of statistic categories, with everything in baseball being counted and quantified , but here is a basic primer for the casual viewer. The offensive statistics are dominated by what happens at the plate. Of course there are many more dealing with all aspects of base running, but the key ones to remember pertain to the bat. This one seems straightforward enough, but as with everything in baseball, there is a sting in the tail. At Bats, represented as AB in a box score, are just what it says on the tin: how many times a player has come up to the plate to bat. Where you can get confused as a novice is in understanding that a walk, whether it be on four balls or by being hit by the pitch, or a sacrifice play do not count as an at bat. So a player might by 0 for 0 with a walk. This is the same as At Bats, but includes walks and sacrifice plays, taking a more literal interpretation of the name. The only time that a Plate Appearance is not recorded is if the catcher interferes with the batter. The batter will be awarded first base and neither an At Bat nor a Plate Appearance will be recorded.
An undefined ERA occasionally occurs at the beginning of era stat baseball baseball season when a pitcher has yet to appear in any games. That's simple: because teams are using advanced metrics as a part of their decision making, whether it comes to player evaluation as a whole, free agency, trade decisions, era stat baseball, the draft, anything and everything.
In baseball statistics , earned run average ERA is the average of earned runs allowed by a pitcher per nine innings pitched i. It is determined by dividing the number of earned runs allowed by the number of innings pitched and multiplying by nine. Thus, a lower ERA is better. Runs resulting from passed balls , defensive errors including pitchers' defensive errors , and runners placed on base at the start of extra innings are recorded as unearned runs and omitted from ERA calculations. Henry Chadwick is credited with devising the statistic, which caught on as a measure of pitching effectiveness after relief pitching came into vogue in the s. Prior to —and, in fact, for many years afterward—pitchers were routinely expected to pitch a complete game , and their win—loss record was considered sufficient in determining their effectiveness.
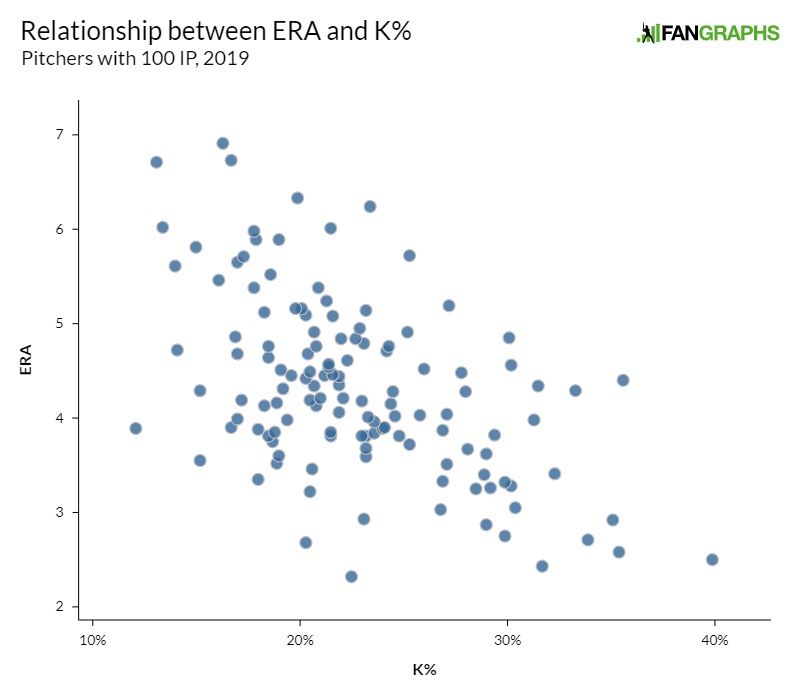
Earned Run Average ERA is a rudimentary metric designed to assess how well a pitcher has prevented runs in the past. ERA is perhaps the most commonly cited pitching statistic at large, but has a number of serious flaws that should lead you to use it sparingly. An earned run is essentially any run that was charged to the pitcher which did not score as the result of an error by the defense. The precise definition of how the official scorer makes the distinction can be found here. There are no further adjustments to ERA to account for park or league effects.
Era stat baseball
In baseball statistics , earned run average ERA is the average of earned runs allowed by a pitcher per nine innings pitched i. It is determined by dividing the number of earned runs allowed by the number of innings pitched and multiplying by nine. Thus, a lower ERA is better. Runs resulting from passed balls , defensive errors including pitchers' defensive errors , and runners placed on base at the start of extra innings are recorded as unearned runs and omitted from ERA calculations. Henry Chadwick is credited with devising the statistic, which caught on as a measure of pitching effectiveness after relief pitching came into vogue in the s. Prior to —and, in fact, for many years afterward—pitchers were routinely expected to pitch a complete game , and their win—loss record was considered sufficient in determining their effectiveness. After pitchers like James Otis Crandall and Charley Hall made names for themselves as relief specialists, gauging a pitcher's effectiveness became more difficult using the traditional method of tabulating wins and losses. Some criterion was needed to capture the apportionment of earned-run responsibility for a pitcher in games that saw contributions from other pitchers for the same team. Since pitchers have primary responsibility for getting opposing batters out, they must assume responsibility when a batter they do not retire at the plate moves to base, and eventually reaches home, scoring a run. A pitcher is assessed an earned run for each run scored by a batter or that batter's pinch-runner who reaches base while batting against that pitcher.
Karaoke bar stuttgart
Article Talk. Read Edit View history. For example, a pitcher who pitched 6 innings and allowed 3 runs would have an average of 0. Runs resulting from passed balls , defensive errors including pitchers' defensive errors , and runners placed on base at the start of extra innings are recorded as unearned runs and omitted from ERA calculations. ERA Earned Run Average is the average number of earned runs a pitcher has allowed per every 9 innings he pitches. Featured Articles How to. Not Helpful 8 Helpful Baseball statistic. For example, say that Joe Smith plays for 6 innings in a 9-inning game and allows 3 men to score. By signing up you are agreeing to receive emails according to our privacy policy. A hit is when the batter puts the ball into play and reaches base safely , but there is a caveat here.
We are reader supported.
No longer could fielders' errors mask a hurler's deficiencies, as only runs that scored without aid of errors were charged against the man on the mound. Therefore Alvarado was the pitcher on the mound when the Rays took the lead in the game. For example, a pitcher who pitched 6 innings and allowed 3 runs would have an average of 0. Follow him on Twitter at ByRyanLewis. By choosing I Accept , you consent to our use of cookies and other tracking technologies. Categories: Pitching. Even the most cursory glance at baseball and you can see that it is a numbers paradise. Courtesy of ESPN Ryne Stanek started the game, and did not give up any runs, but he is not the winning pitcher for the game. If this has you excited to learn more about pitching stats, we will be doing an advanced pitching breakdown later in the week. Statistics are a part of all sports, but with the advent of sabermetrics, baseball has elevated them to the realm of edification, almost worship. Not every game ends in a save situation. It is determined by dividing the number of earned runs allowed by the number of innings pitched and multiplying by nine. Three is the maximum number of runs of a lead to count as a save situation.

I can not participate now in discussion - it is very occupied. I will return - I will necessarily express the opinion.