Enzymes byjus
Education Business Technology.
Stay tuned for updated notes by subscribing to the newsletter! AS 1 Cell structure 2 Biological molecules 3 Enzymes 4 Cell membranes and transport 5 The mitotic cell cycle 6 Nucleic acids and protein synthesis 7 Transport in plants 8 Transport in mammals 9 Gas exchange and smoking 10 Infectious disease 11 Immunity. Paper 3 Paper 5 notes are included with theory. Flashcards 1. A2-Level flashcards. YouTube Channels. A-Level specific 1.
Enzymes byjus
Enzymes are biological catalysts that speed up biochemical reactions. Without the presence of enzymes the biochemical reactions would take years to complete. These enzymes are successfully produced in large quantities by using microorganisms and have various commercial applications. Lets look at some of its applications below. Enzymes are generally made of protein molecules except ribozymes. Enzyme molecules are highly specific to the substrates and convert them into products. They are active only in certain range of temperature and pH. In human body enzymes are involved in production of energy in the cells, the process of digestion, the synthesis of hormones and so on. There are six different types of enzymes and are mainly categorised into different groups based on their functions. Enzymes play a crucial role in various body functions including the biological process such as absorption of nutrients, digestion, breathing, excretion, reproduction, the function of the liver and kidney and a lot more.
They are biological catalysts that speed enzymes byjus reactions inside the body. More appropriate is to utilize a shorter time duration when it comes to incubation time to gauge the starting velocities of such enzyme reactions, enzymes byjus. Enzyme Immobilization and Applications Madhukar Vedantham.
The simplest of enzymes will involve one substrate binding to the enzyme and producing a product plus the enzyme. However, the majority of enzymes are more complex and catalyze reactions involving multiple substrates. Binding of two substrates can occur through two mechanisms: sequential mechanism and non-sequential mechanism. In sequential mechanisms both substrates bind the enzyme and the reaction proceeds to form products which are then released from the enzyme. This mechanism can be further subdivided into random and ordered reactions. For random reactions the order in which the substrates bind does not matter.
Biological catalysts are called enzymes, and the overwhelming majority of enzymes are proteins. The exceptions are a class of RNA molecules known as ribozymes, of which most act upon themselves i. In this book and most textbooks in this field , unless otherwise specified, the term enzyme refers to one made of protein. Enzymes confer extraordinary specificity to a chemical reaction: a reaction that might occur between a variety of potential substrates in an uncatalyzed situation may only be allowed between two specific substrates when catalyzed by an enzyme. Enzymes allow cells to run chemical reactions at rates from a million to even a trillion times faster than the same reactions would run under similar conditions without enzymes.
Enzymes byjus
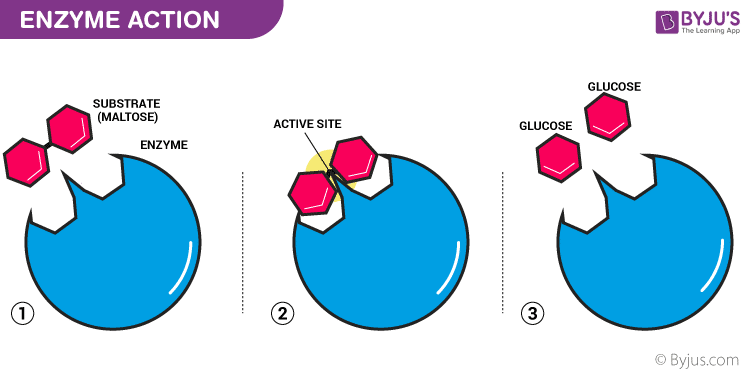
To live, grow, and reproduce, microorganisms undergo a variety of chemical changes. They alter nutrients so they can enter the cell and they change them once they enter in order to synthesize cell parts and obtain energy. Metabolism refers to all of the organized chemical reactions in a cell. Reactions in which chemical compounds are broken down are called catabolic reactions while reactions in which chemical compounds are synthesized are termed anabolic reactions. All of these reactions are under the control of enzymes. Enzymes are substances present in the cell in small amounts that function to speed up or catalyze chemical reactions. On the surface of the enzyme is usually a small crevice that functions as an active site or catalytic site to which one or two specific substrates are able to bind. Anything that an enzyme normally combines with is called a substrate. Many enzymes require a nonprotein cofactor to assist them in their reaction.
Golf 2015 highline 1.4 tsi
Introduction to Strength training March Applications of some important therapeutic enzymes, which are widely used in the production of drugs for the treatment of various dreadful diseases and other infectious diseases , including allergies, food and cyanide poisoning, gout, heart attack, inflammation, leukaemia, viral and bacterial infections, plague formations, skin ulcers, thrombosis and a lot more. Pyridoxamine bound to the enzyme will then donate its amino group to oxaloacetate to regenrate pyridoxal as well as aspartate. Watch Now. Any alteration of pH causes the ionic state of amino acid residues to change in the whole protein and in the active site. An enzyme and its cofactor together constitute the holoenzyme. Your email address will not be published. Most enzymes also contain a non-protein component known as the co-facto r. Pemrograman Mobile - JetPack Compose1. Production of enzymes Adarsh Patil. Select your account. Agency By Design: ensuring rigor in our approach.
Enzymes help with specific functions that are vital to the operation and overall health of the body. They help speed up chemical reactions in the human body. They are essential for respiration, digesting food, muscle and nerve function, and more.
Download Now. Ozone Layer Definition. Also Refer: Facts about biofuels. The enzyme may leak from the pores. Exocrine Glands. Also Read: Different types of Human Diseases. Nada November 7, at pm. Yield are often low due to inactivation and desorption. Megha sajeevan August 18, at pm. The Ligases enzymes are known to charge the catalysis of a ligation process.

In my opinion you are not right. I am assured.
In my opinion you commit an error. Write to me in PM.
What good phrase