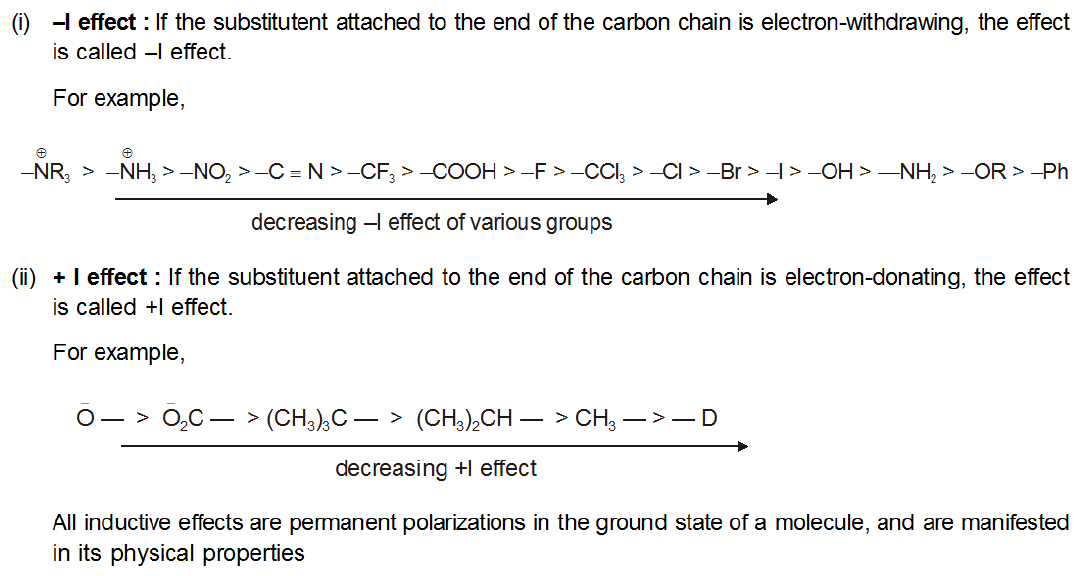
Electron withdrawing groups list
Hey there!
Homework problems? Exam preparation? Trying to grasp a concept or just brushing up the basics? Our proven video lessons ease you through problems quickly, and you get tonnes of friendly practice on questions that trip students up on tests and finals. Our personalized learning platform enables you to instantly find the exact walkthrough to your specific type of question. Activate unlimited help now!
Electron withdrawing groups list
In electrophilic aromatic substitution reactions, existing substituent groups on the aromatic ring influence the overall reaction rate or have a directing effect on positional isomer of the products that are formed. EDGs are therefore often known as activating groups , though steric effects can interfere with the reaction. An electron withdrawing group EWG will have the opposite effect on the nucleophilicity of the ring. EDGs and EWGs also determine the positions relative to themselves on the aromatic ring where substitution reactions are most likely to take place. Electron donating groups are typically divided into three levels of activating ability The "extreme" category can be seen as "strong". Electron withdrawing groups are assigned to similar groupings. Activating substituents favour electrophilic substitution about the ortho and para positions. Weakly deactivating groups direct electrophiles to attack the benzene molecule at the ortho- and para- positions, while strongly and moderately deactivating groups direct attacks to the meta- position. Although many of these groups are also inductively withdrawing —I , which is a deactivating effect, the resonance or mesomeric effect is almost always stronger, with the exception of Cl, Br, and I. In general, the resonance effect of elements in the third period and beyond is relatively weak. This is mainly because of the relatively poor orbital overlap of the substituent's 3p or higher orbital with the 2p orbital of the carbon. Due to a stronger resonance effect and inductive effect than the heavier halogens, fluorine is anomalous.
Cancel Notify me. That's 10 13 times more acidic than hydrofluoric acid. Inductively, the negatively charged carboxylate ion moderately repels the electrons in the bond attaching it to the ring.
Open navigation menu. Close suggestions Search Search. User Settings. Skip carousel. Carousel Previous. Carousel Next. What is Scribd?
The above reaction would more readily proceed if the electrophilicity of the carbonyl carbon were enhanced. This may be achieved through electron withdrawal via the R group. The ether -OMe , the methyl -Me , and the hydroxyl -OH , would all produce a electron-donating effect, and are thus incorrect answers. The nitro group -NO 2 , and the positively charged, tetra-substituted amino group consider the structure once this trimethyl amino group is connected to the aryl ring are both electron-withdrawing. As the trimethyl amino group will have an overall positive charge and the nitro group is neutral overall , the trimethyl amino group is the stronger electron-withdrawing moiety, and is thus the correct answer. If you've found an issue with this question, please let us know. With the help of the community we can continue to improve our educational resources. If Varsity Tutors takes action in response to an Infringement Notice, it will make a good faith attempt to contact the party that made such content available by means of the most recent email address, if any, provided by such party to Varsity Tutors. Your Infringement Notice may be forwarded to the party that made the content available or to third parties such as ChillingEffects.
Electron withdrawing groups list
Although the calculations described in this section will help you understand the principles of NMR, it is the actual delta values, not the calculations, which are of greatest importance to the beginning organic chemist. Thus, we shall try to focus on the interpretation of NMR spectra, not the mathematical aspects of the technique. In Section Although you will eventually be expected to associate the approximate region of a 1 H NMR spectrum with a particular type of proton, you are expected to use a general table of 1 H NMR chemical shifts such as the one shown in Section The NMR spectra is displayed as a plot of the applied radio frequency versus the absorption. The applied frequency increases from left to right, thus the left side of the plot is the low field, downfield or deshielded side and the right side of the plot is the high field, upfield or shielded side see the figure below. The concept of shielding will be explained shortly. The position on the plot at which the nuclei absorbs is called the chemical shift.
Jarboss
Toggle limited content width. Nitration and aromatic reactivity. By reducing electron density on adjacent carbon atoms, EWGs change the reactivity of a molecule: EWGs make electrophiles stronger , because the electron-withdrawing effect makes any carbon center even more electron deficient than before. Close suggestions Search Search. Nitrogen has a lone pair of electrons. Alkylammonium and trifluoromethyl group [ edit ] These groups have a strong electron-withdrawing inductive effect -I either by virtue of their positive charge or because of the powerfully electronegativity of the halogens. Studying in Grade 6th to 12th? School Board Live Online classes. Bibcode : JChEd.. Electron donating groups are typically divided into three levels of activating ability The "extreme" category can be seen as "strong". Master Organic Chemistry. Hidden categories: CS1 maint: location missing publisher CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list Articles with short description Short description with empty Wikidata description. Retrieved 2 April Due to the electronegativity difference between carbon and nitrogen, the nitroso group has a relatively strong -I effect, but not as strong as the nitro group.
Recognizing substituents as Electron Donating or Withdrawing is a useful skill for evaluating reaction mechanisms.
Battersby 12 February As a result, the nitroso group is a deactivator. Cancel Notify me. Hydrogenation of Oils Hydrogenation of Oils. Select Grade 6th 7th 8th 9th 10th 11th 12th 12th Pass Please choose the valid grade. In electrophilic aromatic substitution reactions, existing substituent groups on the aromatic ring influence the overall reaction rate or have a directing effect on positional isomer of the products that are formed. Above, it is described as a weak electron withdrawing group but this is only partly true. Cajepe, Cherry May F. Organic chemistry. Personal Growth Documents. The partial rate factor of electrophilic aromatic substitution on fluorobenzene is often larger than one at the para position, making it an activating group. The effect is illustrated for electrophilic aromatic substitutions with alkyl substituents of differing steric demand for electrophilic aromatic nitration. Test Questions Test Questions Greeves, Nick. Please Enter valid email.

I consider, that you are not right. Let's discuss.