Electron pair geometry of sf4
The molecular formula of sulfur tetrafluoride SF 4 indicates that the compound has one sulfur atom and four fluorine atoms. Sulfur is located in Group 16 of the periodic table and has six valence electrons. Fluorine is located in Group 17 and has seven valence electrons. Fluorine requires one electron to complete its octet and achieve the electron configuration of its nearest neighbor, neon, electron pair geometry of sf4.
The process of mixing of atomic orbitals belonging to the same atom of slightly different energies so that a redistribution of energy takes place between them resulting in the formation of new sets of orbitals of equivalent energies and shape is called hybridization. The new orbitals in this form are known as hybrid orbitals. Like pure orbitals the hybrid orbitals are used in Bond formation. Hybridization is a hypothetical concept and has been introduced in order to explain the characteristic geometrical shapes of polyatomic molecules. The central atom is S. So, to explain in simple terms, its bonding regions are four having one lone pair. There are 34 valence electrons and 5 electron pairs.
Electron pair geometry of sf4
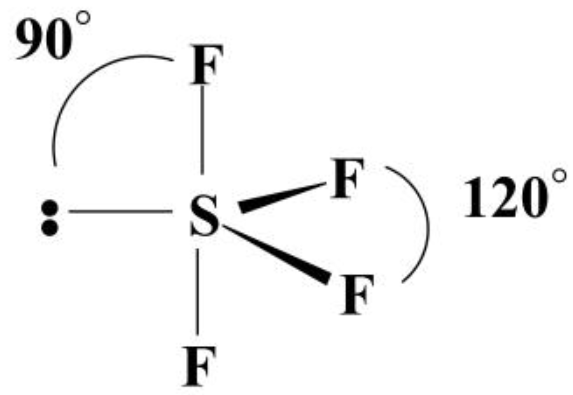
Let us learn about the SF4 molecular geometry and bond angles. You will also get to know more about SF4 structure, SF4 hybridisation, lewis structure of SF4, and the importance of SF4 molecular geometry and bond angles. The structure of SF4 molecular geometry may be predicted using VSEPR theory principles: A nonbonding lone pair of electrons occupy one of the three equatorial locations. As a result, there are two types of F ligands in the molecule: axial and equatorial. The SF4 molecular geometry and bond angles of molecules having the chemical formula AX4E are trigonal bipyramidal. The equatorial orientations of two fluorine atoms establishing bonds with the sulphur atom are shown, while the axial locations of the other two are shown. Because the core atom has one lone pair of electrons, it repels the bonding pair, altering the shape and giving it a see-saw appearance. Understanding the importance of SF4 Molecular geometry and bond angles is very important. Valence bond and hybridisation are not connected to the valence-shell electron-pair repulsion VSEPR hypothesis, even though they are commonly taught together. SF4 only contains one lone pair and four F sigma bonds. S is the core atom.
Molecular Formula. Learn more. Here, there is only one lone pair around the central atom of the Sulfur, which is an odd number.
.
Drawing and predicting the SF4 molecular geometry is very easy. Here in this post, we described step by step method to construct SF4 molecular geometry. A three-step approach for drawing the SF4 molecular can be used. The first step is to sketch the molecular geometry of the SF4 molecule, to calculate the lone pairs of the electron in the central sulfur atom; the second step is to calculate the SF4 hybridization, and the third step is to give perfect notation for the SF4 molecular geometry. The SF4 molecular geometry is a diagram that illustrates the number of valence electrons and bond electron pairs in the SF4 molecule in a specific geometric manner. The geometry of the SF4 molecule can then be predicted using the Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion Theory VSEPR Theory and molecular hybridization theory, which states that molecules will choose the SF4 geometrical shape in which the electrons have from one another in the specific molecular structure. Finally, you must add their bond polarities characteristics to compute the strength of the S-F bond dipole moment properties of the SF4 molecular geometry. The molecule of sulfur tetrafluoride with bipyramidal trigonal shape SF4 molecular geometry is tilted at and degrees. As a result, it has a permanent dipole moment in its molecular structure. The SF4 molecule has a dipole moment due to an unequal charge distribution of negative and positive charges.
Electron pair geometry of sf4
SF4 or sulfur tetrafluoride is a compound that has a distinct odor of sulfur or rotten eggs. This compound is generally identified as being a colorless gas. The molecular weight of this compound is calculated to be SF4 is a toxic gas if inhaled and can cause serious irritation in the skin, eyes, or mucous membrane. If it gets reacted with water then toxic fluoride and sulfur oxide fumes are formed along with an acidic solution. When SF4 gets exposed to extreme heat, there are chances that the container with this compound may burst. The compound is assumed to be stable only when the right storage conditions are met.
Titanium straightening iron
Hence, it will have one lone pair of electrons, while each fluorine atom will have six []. References Whatsinsight. Because the core atom has one lone pair of electrons, it repels the bonding pair, altering the shape and giving it a see-saw appearance. The electron geometry of SF 4 is trigonal bipyramidal. Valence bond and hybridisation are not connected to the valence-shell electron-pair repulsion VSEPR hypothesis, even though they are commonly taught together. You will also get to know more about SF4 structure, SF4 hybridisation, lewis structure of SF4, and the importance of SF4 molecular geometry and bond angles. Now, we can determine the hybridization of Sulfur by considering the number of regions of electron density. Frequently Asked Questions. Ans : In sulphur tetrafluoride, five zones of electron density surround the core sulphur atom 4 bonds and one lone pair. Related articles. Sulphur will use five orbitals: one 3s orbital, three 3p orbitals, and one 3d orbital. Lewis Dot Structures. It also suggests how it might interact with the other molecules. The SF4 molecular geometry and bond angles of molecules having the chemical formula AX4E are trigonal bipyramidal. If there are a few lone pairs of electrons around the central atom, and the molecule is polar if there is an odd number.
Thus far, we have used two-dimensional Lewis structures to represent molecules.
Atoms and X-Rays Important Questions. But the other 2 S-F bonds are pointing down. Sulphur tetrafluoride is made up of only two elements: sulphur and fluorine. Formation of Complexes. The reason behind this is that the lone pair prefers one of the equatorial positions. Zeolites have small, fixed-size openings that allow small molecules to pass through easily but not larger molecules; this is why they are sometimes referred to as molecular sieves. Dots represent the lone pairs. Name of the Molecule. What is SF4's molecular geometry? Frequently Asked Questions. Table of Content. Ans : Seesaw is the shape.

It's out of the question.