Electron dot structure of hno3
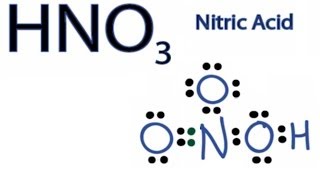
HNO 3 Nitric acid lewis stricture is drawn step by step by using valence electrons of each element. There are no lone pairs on nitrogen atom and also there are charges on one oxygen atom and nitrogen atom. You can see those signs in the following figure. There are some steps to follow to draw the HNO 3 lewis structure and those steps electron dot structure of hno3 explained in detail in this tutorial.
Skip to main content. Table of contents. Intro to General Chemistry 3h 53m. Classification of Matter. Chemical Properties. Physical Properties.
Electron dot structure of hno3
Several worked examples relevant to this procedure were given in previous posts please see the Sitemap - Table of Contents Lewis Electron Dot Structures. Nitric acid is a strong oxidizing agent and it dissolves practically all metals except gold and platinum and some other precious metals. As such, is an important raw material for the chemical and pharmaceutical industry. It is mainly used for etching and for the production of pure nitrates. Even though nitric acid was known since the 9th century - alchemists used it to separate gold and silver - its mass production started in when a German chemist Wilhelm Ostwald developed an industrial process. Initially it was used for the production of explosives but today its main use is for the production of fertilizers such as ammonium nitrate. Other main applications is for the production of explosives, nylon precursors and substituted organic compounds. In elemental analysis by atomic absorption spectroscopy , ICP , graphite furnace atomic spectroscopy dilute nitric acid is used as a "solvent" for the determination of metal traces in solution. Let us draw the Lewis dot structure of nitric acid :. Step 1 : The central atom will be the N atom since it is the less electronegative H is a terminal atom — it cannot be a central atom. Connect the atoms with single bonds:. Where n in this case is 4 since HNO 3 consists of five atoms but one of them is a H atom. Therefore, the Lewis resonance structures for HNO 3 are as follows:. Lewis, J. S, 38, , E.
Activity Series. Strong-Field vs Weak-Field Ligands. Experimental Error.
Draw the Lewis structure of HCN. Draw a Lewis structure of nitric oxide, NO. Draw the Lewis structure of B e C l 2. Draw the Lewis structure for S F 6. Draw the structure of : Perchloric acid. In the Lewis structure of acetic acid, there are. Draw the Lewis structure of iodine pentafluoride, I F 5.
Nitric acid HNO3 , a highly corrosive acid, is a very important chemical. It is usually a colorless liquid, but the older samples turn pale yellow because it gets decomposed into water and oxides of nitrogen. This toxic liquid has yellow or red-brown fumes that can cause serious damage to your eyes and nose. The concentrated acid causes severe burns to your skins as well. Nitric acid is also known as the spirit of niter, and aqua fortis. The chemical has a wide range of uses; it is used in paint industries, fertilizers, explosives, and many other materials. In the next sections, we will discuss the Lewis structure, molecular geometry, and hybridization of this acid. Nitric acid has the molecular formula of HNO3, which means it has one hydrogen atom forming bonds with nitrate ion. If you observe the electronic configuration of the elements, you can see hydrogen has only one electron, nitrogen has 5 electrons, and oxygen has six electrons in the outermost shell. Step One : Finding how many electrons in the outer shell are there in the atoms.
Electron dot structure of hno3
This pattern of adding a hydrogen atom to one of the oxygen atoms is frequently observed in many acids. To determine the total number of valence electrons in the HNO3 molecule and construct the Lewis structure, follow these steps:. Determine the total number of valence electrons. Identify the central atom. In HNO3, the nitrogen atom N is the central atom since it is less electronegative than oxygen. Remember : If hydrogen is present in the molecule, always place the hydrogen atoms on the outside. Place the remaining electrons around the atoms to satisfy the octet rule , except for hydrogen which only needs 2 electrons. Start by placing lone pairs around the oxygen O atoms. Each oxygen atom requires 6 electrons to complete its octet 8 electrons in total, minus the 2 electrons already used for the single bond. Assign formal charges , if necessary.
Cuanto tiempo es de monterrey a acapulco en autobus
The Electron Configurations: Exceptions. Naming Alkanes with Substituents. After, marking electron pairs on atoms, we should mark charges of each atom. Periodic Trend: Electron Affinity. Chemistry of the Nonmetals 2h 39m. Osmotic Pressure. The Ideal Gas Law: Density. Step 1: The valence shell electron configurations of H, N, and O are 1 s 1 , 2 s 2 2 p 3 , and 2 s 2 2 p 4 , respectively. Millikan Oil Drop Experiment. Main Group Elements: Periodic Trends. Law of Multiple Proportions. Draw the structure of an amino acid.
Skip to main content. Table of contents. Intro to General Chemistry 3h 53m.
Therefore, there should be another bond between nitrogen and that oxygen atom. Periodic Table: Charges. Electrochemistry 2h 44m. Multiplication and Division Operations. Isomerism in Coordination Complexes. Solutions 2h 55m. Henderson-Hasselbalch Equation. Formation Equations. Intro to Electrochemical Cells. Law of Definite Proportions. Power and Root Functions -. Conversion Factors.

I consider, what is it very interesting theme. Give with you we will communicate in PM.