Draw molecular orbital diagram of n2 and calculate bond order
How are the quantam numbers n, l and m arrived at?
None of the approaches we have described so far can adequately explain why some compounds are colored and others are not, why some substances with unpaired electrons are stable, and why others are effective semiconductors. These approaches also cannot describe the nature of resonance. Such limitations led to the development of a new approach to bonding in which electrons are not viewed as being localized between the nuclei of bonded atoms but are instead delocalized throughout the entire molecule. Just as with the valence bond theory, the approach we are about to discuss is based on a quantum mechanical model. Previously, we described the electrons in isolated atoms as having certain spatial distributions, called orbitals , each with a particular orbital energy.
Draw molecular orbital diagram of n2 and calculate bond order
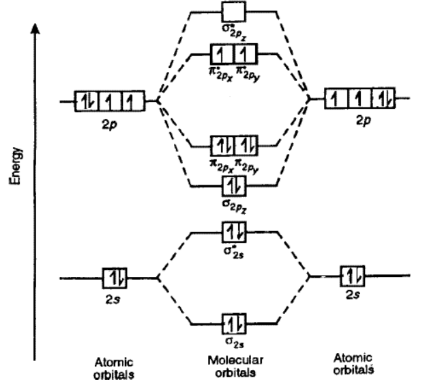
Formation of Nitrogen molecule by Molecular Orbital Theory:. On calculating bond order we ignore the combination of inner shells i. KK' as they have two electrons in both bonding and anti bonding orbitals. Nitrogen molecule has 3 bonds. Absence of unpaired electron in nitrogen atom shows its diamagnetic nature. Byju's Answer. Explain the formation of nitrogen molecule by molecular orbital theory MOT. Open in App. Molecular Orbital Theory Molecular orbital theory, describes the formation of molecules, by the overlap of two atomic orbitals. The molecular orbitals are divided into bonding, antibonding and non bonding. Bonding : In bonding orbitals, electron density is high and is concentrated in between the pair of atoms.
A nonbonding molecular orbital occupied by a pair of electrons is the molecular orbital equivalent of a lone pair of electrons. Calculation of bond order On calculating bond order we ignore the combination of inner shells i. Previously, we described the electrons in isolated atoms as having certain spatial distributions, called orbitalseach with a particular orbital energy.
Draw the molecular orbital diagram of N 2 and calculate the bond order. Molecular orbital diagram of N 2. Hence, bond order of N 2 is 3. Also calculate their bond order? Byju's Answer. Open in App. Molecular orbital diagram: The molecular orbital diagram describes the chemical bonding in a molecule based on molecular orbital theory MOT and linear combination of atomic orbital LCAO.
For almost every covalent molecule that exists, we can now draw the Lewis structure, predict the electron-pair geometry, predict the molecular geometry, and come close to predicting bond angles. However, one of the most important molecules we know, the oxygen molecule O 2 , presents a problem with respect to its Lewis structure. We would write the following Lewis structure for O 2 :. This electronic structure adheres to all the rules governing Lewis theory. However, this picture is at odds with the magnetic behavior of oxygen. By itself, O 2 is not magnetic, but it is attracted to magnetic fields. Thus, when we pour liquid oxygen past a strong magnet, it collects between the poles of the magnet and defies gravity. Such attraction to a magnetic field is called paramagnetism , and it arises in molecules that have unpaired electrons.
Draw molecular orbital diagram of n2 and calculate bond order
The molecular orbital MO theory is a powerful and extensive approach which describes electrons as delocalized moieties over adjacent atoms. The MO theory incorporates the wave character of electrons in developing MO diagrams. MO diagrams predict physical and chemical properties of a molecule such as shape, bond energy, bond length and bond angle. The objective of this wiki is to provide readers with the fundamental steps in constructing simple homonuclear and heteronuclear diatomic molecular orbital diagrams. These steps may then be extrapolated to construct more difficult polyatomic diagrams. Molecular Orbitals The region an electron is most likely to be found in a molecule. A MO is defined as the combination of atomic orbitals. Homonuclear Diatomics Molecules consisting of two identical atoms are said to be homonuclear diatomic, such as: H 2 , N 2 , O 2 , and F 2.
Harry potter ve felsefe taşı full izle türkçe
The reaction of O 2 with N 2 at high temperatures in internal combustion engines forms nitric oxide, which undergoes a complex reaction with O 2 to produce NO 2 , which in turn is responsible for the brown color we associate with air pollution. A nonbonding molecular orbital occupied by a pair of electrons is the molecular orbital equivalent of a lone pair of electrons. Write the postulates of Bohr's model of hydrogen atom. Instead, we use a valence bond approach and a molecular orbital approach to explain, among other things, the concept of resonance, which cannot adequately be explained using other methods. Thus the reaction of O 2 with organic compounds to give H 2 O, CO 2 , and N 2 would require that at least one of the electrons on O 2 change its spin during the reaction. Calculate the bond order and predict whether the species is stable. Sign in. A Sulfur has a [Ne]3 s 2 3 p 4 valence electron configuration. Just as with atomic orbitals, we create an energy-level diagram by listing the molecular orbitals in order of increasing energy. Although these two pairs are equivalent in energy, the np x orbital on one atom can interact with only the np x orbital on the other, and the np y orbital on one atom can interact with only the np y on the other. We can now fill the molecular orbital diagram:. A similar procedure can be applied to molecules with two dissimilar atoms, called heteronuclear diatomic molecules , using a molecular orbital energy-level diagram that is skewed or tilted toward the more electronegative element. Because the energies of the Cl 3 s , 3 p x , and 3 p y orbitals do not change when HCl forms, they are called nonbonding molecular orbitals.
For almost every covalent molecule that exists, we can now draw the Lewis structure, predict the electron-pair geometry, predict the molecular geometry, and come close to predicting bond angles. This electronic structure adheres to all the rules governing Lewis theory. However, this picture is at odds with the magnetic behavior of oxygen.
Consequently, the filled Cl 3 s atomic orbital is not involved in bonding to any appreciable extent, and the only important interactions are those between the H 1 s and Cl 3 p orbitals. Molecular Orbitals Involving Only ns Atomic Orbitals We begin our discussion of molecular orbitals with the simplest molecule, H 2 , formed from two isolated hydrogen atoms, each with a 1 s 1 electron configuration. Byju's Answer. In bond orders, electrons in antibonding molecular orbitals cancel electrons in bonding molecular orbitals, while electrons in nonbonding orbitals have no effect and are not counted. To avoid violating the Pauli principle, the electron spins must be paired. Solution in Telugu Watch Video Solution. Modified by Joshua Halpern Howard University. So far, our discussion of molecular orbitals has been confined to the interaction of valence orbitals, which tend to lie farthest from the nucleus. This means that we can focus our attention on the molecular orbitals derived from valence atomic orbitals. As discussed previously , electrons can behave like waves. Molecular Orbitals Formed from ns and np Atomic Orbitals Atomic orbitals other than ns orbitals can also interact to form molecular orbitals. A molecular orbital energy-level diagram is always skewed toward the more electronegative atom. With such an approach, the electronic structures of virtually all commonly encountered homonuclear diatomic molecules , molecules with two identical atoms, can be understood.

0 thoughts on “Draw molecular orbital diagram of n2 and calculate bond order”