Cross section of a leaf gcse
Ms Armit: The leaf is a major organ in plants in which photosynthesis occurs.
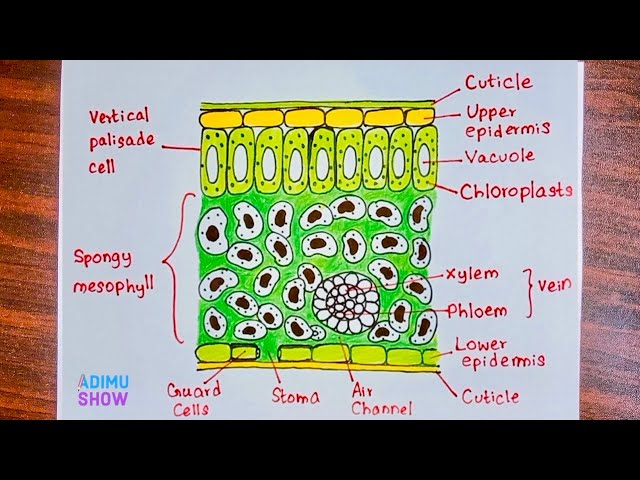
Learn Teach Quiz Login? The cuticle is transparent and very thin to allow maximum light penetration. The epidermis is is also transparent and very thin to allow maximum light penetration. These cells are located close to the leaf surface to maximise light absorption. They are upright, elongated and tightly packed together in order to increase the surface area for light absorption. They also contain chloroplasts, but not quite as many. These cells have large air spaces between them that allow carbon dioxide and oxygen to diffuse between them.
Cross section of a leaf gcse
The structure of a leaf has adaptations so that it can carry out photosynthesis close photosynthesis A chemical process used by plants to make glucose and oxygen from carbon dioxide and water, using light energy. Oxygen is produced as a by-product of photosynthesis. Algae subsumed within plants and some bacteria are also photosynthetic. Light absorption happens in the palisade mesophyll close palisade mesophyll Plant tissue containing closely packed cells in the upper layer of a leaf. Palisade cells are column-shaped and packed with many chloroplasts close chloroplast Contains the green pigment chlorophyll; the site of photosynthesis. They are arranged closely together so that a lot of light energy can be absorbed. The stomata close stomata Tiny holes in the epidermis skin of a leaf. They control gas exchange by opening and closing and are involved in loss of water from leaves. Singular is stoma. Each stoma can be open or closed, depending on how turgid close turgid Enlarged and swollen with water. Having turgor. Description of a plant cell in which the vacuole has swollen due to water gain by osmosis. Diffusion close diffusion The movement of molecules from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration.
Leaves and photosynthesis. Each hole is a single stoma. Without photosynthesis, there'd be very little life on Earth, because when plants photosynthesise, they take in carbon dioxide, and release oxygen as a by-product.
.
Leaves, stems and roots are organs consisting of different types of tissues Plant leaves are the main organ close organ A group of different tissues that work together to carry out a particular function, eg heart and lungs. Oxygen is produced as a by-product of photosynthesis. Algae subsumed within plants and some bacteria are also photosynthetic. The function of a leaf is photosynthesis. Leaves are the source of all of food on Earth. The internal structure of the leaf is also adapted to promote efficient photosynthesis:.
Cross section of a leaf gcse
Ms Armit: The leaf is a major organ in plants in which photosynthesis occurs. Without photosynthesis, there'd be very little life on Earth, because when plants photosynthesise, they take in carbon dioxide, and release oxygen as a by-product. Cal: I am liking plants a lot right now, so let's find out more on how the structures of leaves help plants to photosynthesise. The green of the leaf is the chlorophyll, the pigment that absorbs energy from the sun. Some plants have evolved with large leaves to maximise the amount of light they can absorb, often found under forest canopies where they struggle for exposure to light.
Oldandyoungxnxx
Another very important part of the leaf are the palisade cells. Plants get the carbon dioxide they need from the air through their leaves. Plant adaptation Function Broad leaves Provide a large surface area to absorb as much sunlight as possible. Cal: What, respire like us? Ms Armit: There's more. These are called stomata. Ms Armit: I'm so glad you've found a new passion. What are the four main features of a leaf which are mentioned in the video? The upper part of the leaf is where the light falls, and it contains a type of cell called a palisade cell. Leaf structure. Credit: Ben Himme. The air spaces also gives these cells a large surface area to maximise the diffusion of carbon dioxide into the cell and oxygen out of the cell. The stomata can open and close to:. Any idea why?
In angiosperm anatomy, a leaf can be identified by where it emerges from the node. In a node, a leaf emerges below the axillary bud. Leaves are generally composed of a few main parts: the blade and the petiole.
Ms Armit: There's more. Here's one I made earlier. Would you believe it? It moves by diffusion through small holes in the underside of the leaf called stomata. They also transport the sugar produced by photosynthesis away from these cells to the rest of the plant tissues to be used as an energy source or stored. Start activity. Cal: I am liking plants a lot right now, so let's find out more on how the structures of leaves help plants to photosynthesise. Cal: If they've got all those chloroplasts, then you'd need them to be near the top of the leaf to get that all-important sunshine. Leaves come in all different shapes and sizes. Put some on the other side, like that. These cells are located close to the leaf surface to maximise light absorption. Ms Armit: The leaf is a major organ in plants in which photosynthesis occurs. On the lower half of the leaf are spongy mesophyll cells. Knowledge of leaves is also important to horticulturists. Water The water needed for photosynthesis is absorbed through the roots and transported through tubes to the leaf.

The excellent and duly message.
Clearly, many thanks for the information.
I consider, that you are not right. I can prove it. Write to me in PM, we will discuss.