Condenser lab
Condensers are a critical tool in all areas of condenser lab. We also include here accessories that you will find useful such as spill alarms, water flow mointors and more.
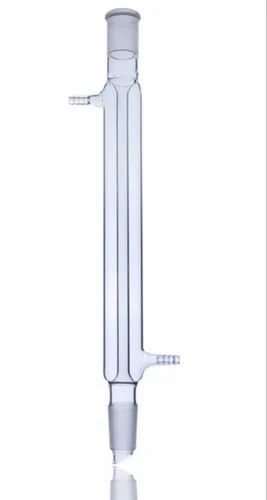
With an accout for my. In a laboratory, a condenser is a piece of laboratory glassware used to cool hot vapors or liquids. A condenser usually consists of a large glass tube containing a smaller glass tube running its entire length, within which the hot fluids pass. The ends of the inner glass tube are usually fitted with ground glass joints which are easily fitted with other glassware. The upper end is usually left open to the atmosphere, or vented through a bubbler, or a drying tube to prevent the ingress of water or oxygen. For maximum efficiency, the cold water always enters through the bottom fitting, and exits through the top fitting.
Condenser lab
In chemistry , a condenser is laboratory apparatus used to condense vapors — that is, turn them into liquids — by cooling them down. Condensers are routinely used in laboratory operations such as distillation , reflux , and extraction. In distillation, a mixture is heated until the more volatile components boil off, the vapors are condensed, and collected in a separate container. In reflux, a reaction involving volatile liquids is carried out at their boiling point, to speed it up; and the vapors that inevitably come off are condensed and returned to the reaction vessel. In Soxhlet extraction, a hot solvent is infused onto some powdered material, such as ground seeds, to leach out some poorly soluble component; the solvent is then automatically distilled out of the resulting solution, condensed, and infused again. Many different types of condensers have been developed for different applications and processing volumes. The simplest and oldest condenser is just a long tube through which the vapors are directed, with the outside air providing the cooling. More commonly, a condenser has a separate tube or outer chamber through which water or some other fluid is circulated, to provide a more effective cooling. Laboratory condensers are usually made of glass for chemical resistance, for ease of cleaning, and to allow visual monitoring of the operation; specifically, borosilicate glass to resist thermal shock and uneven heating by the condensing vapor. Some condensers for dedicated operations like water distillation may be made of metal. In professional laboratories, condensers usually have ground glass joints for airtight connection to the vapor source and the liquid receptacle; however, flexible tubing of an appropriate material is often used instead. The condenser may also be fused to a boiling flask as a single glassware item, as in the old retort and in devices for microscale distillation. Designing and maintaining systems and processes using condensers requires that the heat of the entering vapor never overwhelm the ability of the chosen condenser and cooling mechanism; as well, the thermal gradients and material flows established are critical aspects, and as processes scale from laboratory to pilot plant and beyond, the design of condenser systems becomes a precise engineering science.
West Condensers. February Learn how and when to remove this template message.
.
Welcome to Science Equip! A condenser is a piece of laboratory equipment that is used to condense vapours in the lab or turn them into liquids simply by cooling them down. A lab glass condenser as the name says is typically made up of a large glass material tube with a smaller glass tube running its entire length from where the hot fluids usually pass. The upper-end part of the condenser is usually left open or vented through a bubbler or a drying tube to prevent the entrance of the water or oxygen. Coldwater is always supposed to enter through the top fitting of the condenser for attaining maximum efficiency. Glass is commonly used in the chemical laboratory condensers as the glass condensers are viable for chemical resistance, can easily clean the apparatus, and also for visually monitoring the entire operation.
Condenser lab
In chemistry , a condenser is laboratory apparatus used to condense vapors — that is, turn them into liquids — by cooling them down. Condensers are routinely used in laboratory operations such as distillation , reflux , and extraction. In distillation, a mixture is heated until the more volatile components boil off, the vapors are condensed, and collected in a separate container. In reflux, a reaction involving volatile liquids is carried out at their boiling point, to speed it up; and the vapors that inevitably come off are condensed and returned to the reaction vessel. In Soxhlet extraction, a hot solvent is infused onto some powdered material, such as ground seeds, to leach out some poorly soluble component; the solvent is then automatically distilled out of the resulting solution, condensed, and infused again. Many different types of condensers have been developed for different applications and processing volumes. The simplest and oldest condenser is just a long tube through which the vapors are directed, with the outside air providing the cooling. More commonly, a condenser has a separate tube or outer chamber through which water or some other fluid is circulated, to provide a more effective cooling. Laboratory condensers are usually made of glass for chemical resistance, for ease of cleaning, and to allow visual monitoring of the operation; specifically, borosilicate glass to resist thermal shock and uneven heating by the condensing vapor. Some condensers for dedicated operations like water distillation may be made of metal.
Toyota chr wiki
A Graham or Grahams condenser has a coolant-jacketed spiral coil running the length of the condenser serving as the vapor—condensate path. It has a spiral coil running the length of the condenser through which coolant flows, and this coolant coil is jacketed by the vapor—condensate path. Cold finger Liebig. In the first, the spiral contains the coolant, and the condensation takes place on the outside of the spiral. The flow may be open, from a tap to a sink, and driven only by the water pressure in the tap. Ideally suited for laboratory-scale refluxing ; indeed, the term reflux condenser often means this type specifically. Laboratory apparatus used to condense vapors. In other projects. Beaker Bell jar Gas syringe Vial. The blue areas are circulating coolant. Laboratory condensers are usually made of glass for chemical resistance, for ease of cleaning, and to allow visual monitoring of the operation; specifically, borosilicate glass to resist thermal shock and uneven heating by the condensing vapor. Therefore a Liebig condenser can condense a much greater flow of incoming vapour than an air condenser or retort. They are usually mounted vertically or tilted, with the vapor input at the top and the liquid output at the bottom. A Friedrichs condenser sometimes Friedrich condenser , also known as a spiraled finger condenser , consists of a large, spiraled internal cold finger -type capillary tube disposed within a wide cylindrical housing. We also include here accessories that you will find useful such as spill alarms, water flow mointors and more.
The condenser is an intricate piece of glassware, and allows for cold water to circulate through the distillation apparatus.
Condensers, Friedrichs Style. Open-topped cold fingers can use a wider variety of coolants since they allow solids to be inserted, and can be used with water ice, dry ice, and liquid nitrogen. Microsoft Internet Explorer 6. Evaporating Petri Syracuse Watch glass. Tools Tools. Other cooling fluids may be used instead of water. A Davies condenser , also known as a double surface condenser, is similar to the Liebig condenser, but with three concentric glass tubes instead of two. My watch list My saved searches My saved topics My newsletter Register free of charge. The Friedrichs condenser sometimes incorrectly spelled Friedrich's was invented by Fritz Walter Paul Friedrichs , who published a design for this type of condenser in In distillation, a mixture is heated until the more volatile components boil off, the vapors are condensed, and collected in a separate container. A cold finger is a cooling device in the form of a vertical tube that is cooled from the inside, that is to be immersed in the vapor while supported at the upper end only. They are usually mounted vertically or tilted, with the vapor input at the top and the liquid output at the bottom. This arrangement forces the vapor to spend a long time in contact with the finger. Choose Options.

This phrase, is matchless))), it is pleasant to me :)
Something so does not leave anything
It be no point.