Cell progenitors
Thank you for visiting nature. You are using a browser version with limited support for CSS. To obtain the best experience, we recommend you use a more up to date browser or turn off compatibility mode in Internet Explorer, cell progenitors.
Federal government websites often end in. The site is secure. It is well evident that the embryonic stem cells ESCs are pluripotent, can differentiate into all the three germ layers namely ectoderm, mesoderm and endoderm and into odd cell types present in the body, are immortal, can expand in large numbers in vitro , and are genetically stable over long periods in culture. However, hES cells have the associated issues of immune-rejection and risk of teratoma formation. The situation is alarming as it is not clear whether these therapies would benefit the public. Are mesenchymal cells true stem cells or just stromal cells?
Cell progenitors
They have the potential to increase healing and for potentially regenerating an entire organ from a few cells. They are investigated in treatment of:. Stem Cells are reserve cells that have the ability to change into many different types of cells and grow indefinitely. Stem cells also have the potential to create new tissue and even whole organs from just a few stem cells. Progenitor cell are very similar to stem cells. They are biological cells and like stem cells, they too have the ability to differentiate into a specific type of cell. However, they are already more specific than stem cells and can only be pushed to differentiate into its "target" cell. Four main types of stem cells: 1 Adult or somatic stem cells 2 Fetal stem cells 3 Embryonic stem cells 4 Induced stem cells. Many, as each "target" cell has its own progenitor cell. Some of the types include: 1 Satellite cells found in muscles.
Toggle limited content width. Bioinformatics 28— Giordano, M.
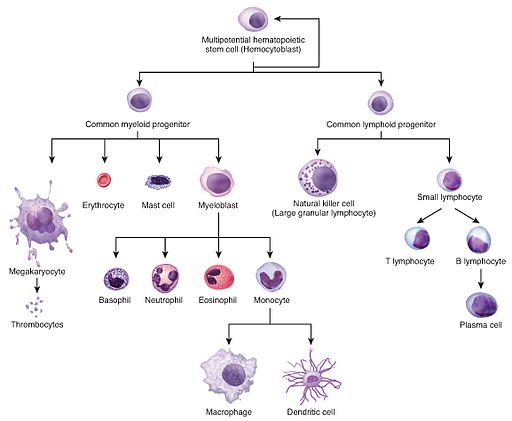
A progenitor cell is a biological cell that can differentiate into a specific cell type. Stem cells and progenitor cells have this ability in common. However, stem cells are less specified than progenitor cells. Progenitor cells can only differentiate into their "target" cell type. Controversy about the exact definition remains and the concept is still evolving. The terms "progenitor cell" and "stem cell" are sometimes equated. Most progenitors are identified as oligopotent.
In cell biology , precursor cells —also called blast cells —are partially differentiated, or intermediate, and are sometimes referred to as progenitor cells. A precursor cell is a stem cell with the capacity to differentiate into only one cell type, meaning they are unipotent stem cells. In embryology , precursor cells are a group of cells that later differentiate into one organ. However, progenitor cells are considered multipotent. Due to their contribution to the development of various organs and cancers, precursor and progenitor cells have many potential uses in medicine. There is ongoing research on using these cells to build heart valves, blood vessels, and other tissues by using blood and muscle precursor cells. The prospect of regenerative medicine has become increasingly more popular in recent years. Stem cell research has been gaining traction as a possible method of treatment for various human diseases. One large subcategory of progenitor cells are neural precursor cells NPCs , which consist of oligodendrocyte, astrocyte, and neuronal precursor cells.
Cell progenitors
We've updated our Privacy Policy to make it clearer how we use your personal data. We use cookies to provide you with a better experience. You can read our Cookie Policy here. Types of progenitor cells - Neural progenitor cells. Every cell in the human body, and that of other mammals, originates from stem cell precursors. Progenitor cells are descendants of stem cells that then further differentiate to create specialized cell types. There are many types of progenitor cells throughout the human body. Each progenitor cell is only capable of differentiating into cells that belong to the same tissue or organ. Some progenitor cells have one final target cell that they differentiate to, while others have the potential to terminate in more than one cell type. Stem cells share two qualifying characteristics.
Mystic cruises careers
Elucidation of the phenotypic, functional, and molecular topography of a myeloerythroid progenitor cell hierarchy. Liao, Y. Yang, L. Here the author discusses the existing confusion as to what are the true stem cells in the body, how these are different from the tissue-specific progenitors and whether these may be implicated in initiating cancers. The nature of telomere fusion and a definition of the critical telomere length in human cells. They replenish special cells, but also maintain the blood, skin and intestinal tissues. Skip to main content Thank you for visiting nature. Moreover, the present article suggests that pluripotent stem cells exist in adult body organs and the need to bank cord blood as a source of stem cells may be a futile exercise. There are two broad categories of stem cells found in all mammals. Reporting Summary. Autologous bone marrow derived stem cell therapy in heart disease: discrepancies and contradictions.
Federal government websites often end in. The site is secure.
Supplementary Table 7 Mass cytometry reagents. Stem Cell Rev. All other codes are available on request. Role of naive-derived T memory stem cells in T-cell reconstitution following allogeneic transplantation. Yang, L. Advancing regenerative medicine. What are progenitor cells? Onai, N. Neutrophils deficient in PU. Chudakov Authors Giovanni Galletti View author publications. Differentiation of human embryonic stem cells occurs through symmetric cell division. Cell Culture. Roychoudhuri University of Cambridge and M. The epigenetic landscape of T cell exhaustion.

0 thoughts on “Cell progenitors”