Caudate nucleus
Federal government websites often end in.
At the time the article was last revised Yoshi Yu had no financial relationships to ineligible companies to disclose. Caudate nuclei are paired nuclei which along with the globus pallidus and putamen are referred to as the corpus striatum , and collectively make up the basal ganglia. The caudate nuclei have both motor and behavioral functions, in particular maintaining body and limb posture, as well as controlling approach-attachment behaviors, respectively 3. The caudate nucleus is located lateral to the lateral ventricles, with the head lateral to the frontal horn, and body lateral to the body of the lateral ventricle. The tail of the caudate nucleus terminates immediately above the temporal horn of the ventricle. It is bound laterally by the anterior crus of the internal capsule.
Caudate nucleus
It plays a critical role in various higher neurological functions. Each caudate nucleus is composed of a large anterior head, a body, and a thin tail that wraps anteriorly such that the caudate nucleus head and tail can be visible in the same coronal cut. When combined with the putamen, the pair is referred to as the striatum and is often considered jointly in function. The striatum is the major input source for the basal ganglia, which also includes the globus pallidus, subthalamic nucleus, and substantia nigra. These deep brain structures together largely control voluntary skeletal movement. The caudate nucleus functions not only in planning the execution of movement, but also in learning, memory, reward, motivation, emotion, and romantic interaction. Input to the caudate nucleus travels from the cortex, mostly the ipsilateral frontal lobe. Efferent projections from the caudate nucleus travel to the hippocampus, globus pallidus, and thalamus. Research has implicated caudate nucleus dysfunction in several pathologies, including Huntington and Parkinson disease, various forms of dementia, ADHD, bipolar disorder, obsessive-compulsive disorder, and schizophrenia. Publication types Study Guide.
This fact leads to the hypothesis that diminished levels of caudate nucleus activity may play a role in migraine headache pain, caudate nucleus. Romantic love: a mammalian brain system for mate choice. A study draws a relationship between caudate asymmetry and symptoms related to ADHD.
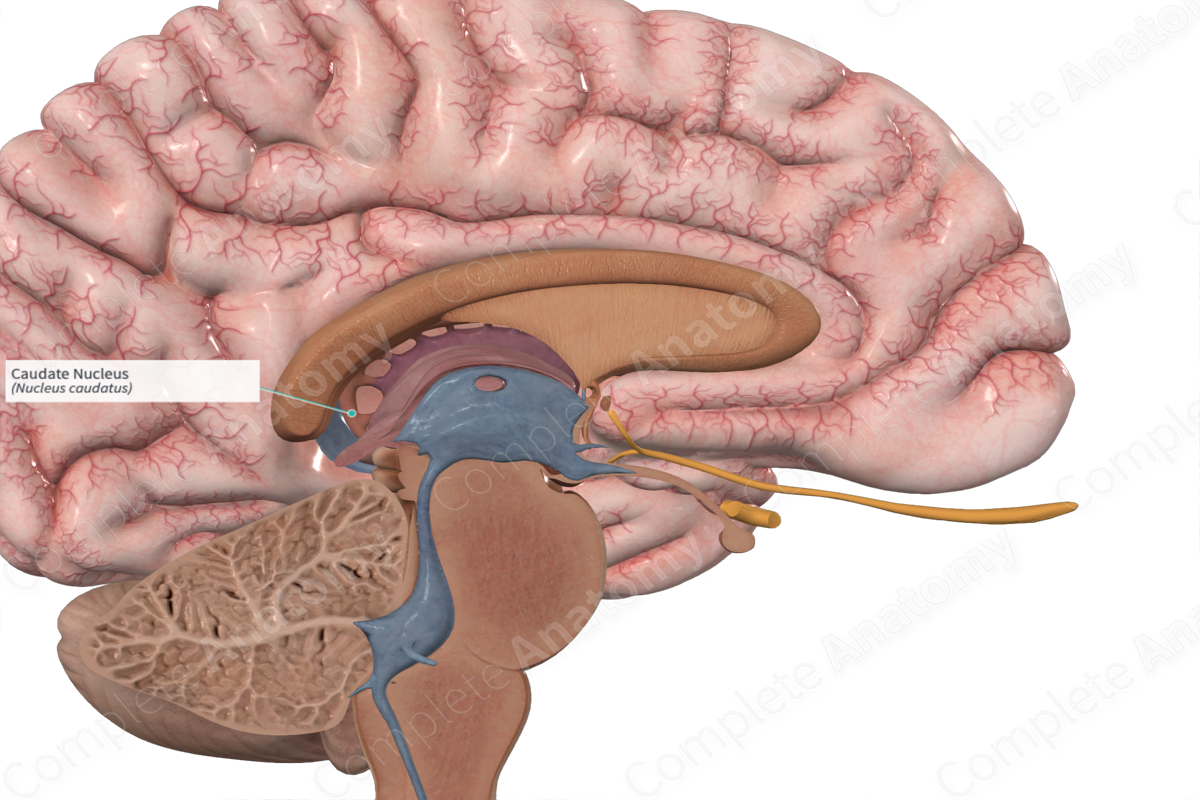
The caudate nuclei there are two—one on each side of the brain can be found below the cerebral cortex , situated next to the lateral ventricles. Like the lateral ventricles, the caudate is a C-shaped structure with a thick anterior portion called the head , which becomes narrower as it extends towards the back of the brain. The middle portion of the caudate is known as the body , and this tapers off into the tail of the caudate. The caudate nucleus is considered part of the basal ganglia. The basal ganglia are a group of subcortical nuclei that are involved in a variety of cognitive and emotional functions, but are best known for their role in movement. To read more about the basal ganglia and this purported function, see this article. To accomplish their movement-related functions, the basal ganglia need to receive information from the cortex about movements that you want to make.
The caudate nuclei there are two—one on each side of the brain can be found below the cerebral cortex , situated next to the lateral ventricles. Like the lateral ventricles, the caudate is a C-shaped structure with a thick anterior portion called the head , which becomes narrower as it extends towards the back of the brain. The middle portion of the caudate is known as the body , and this tapers off into the tail of the caudate. The caudate nucleus is considered part of the basal ganglia. The basal ganglia are a group of subcortical nuclei that are involved in a variety of cognitive and emotional functions, but are best known for their role in movement. To read more about the basal ganglia and this purported function, see this article. To accomplish their movement-related functions, the basal ganglia need to receive information from the cortex about movements that you want to make.
Caudate nucleus
Our decisions often balance what we observe and what we desire. A prime candidate for implementing this complex balancing act is the basal ganglia pathway, but its roles have not yet been examined experimentally in detail. Here, we show that a major input station of the basal ganglia, the caudate nucleus, plays a causal role in integrating uncertain visual evidence and reward context to guide adaptive decision-making. In monkeys making saccadic decisions based on motion cues and asymmetric reward-choice associations, single caudate neurons encoded both sources of information. These results imply that the caudate nucleus plays causal roles in coordinating decision processes that balance external evidence and internal preferences. Effective decision-making often requires deliberation over uncertain evidence for and against different alternatives, as well as over the expected outcome associated with those alternatives. The final choice depends on how these two types of information are combined in the deliberation process.
Faux hawk male
Transverse Cut of Brain Horizontal Section , basal ganglia is blue. Figure 2: brainstem nuclei and their connections Figure 2: brainstem nuclei and their connections. The activity of the caudate nucleus increases in the left head during manic states in bipolar disorder. The differences in performance between the two types of patients in a test that, in short, requires subjects to select appropriate intermediate goals with a larger goal in mind draws a link between the caudate and goal-directed action. These results indicate that the caudate nucleus could be involved in coding a motor response. Review Perspective on basal ganglia connections as described by Nauta and Mehler in Where we were and how this paper effected where we are now. It is located on the inside of the brain's fornix, which is the…. These neurons may be involved with the inhibition of unwanted movements, and their degeneration may cause involuntary movement to be more difficult to suppress. OCLC Neurosci Biobehav Rev. Frontiers of Neurology and Neuroscience. The caudate nuclei have both motor and behavioral functions, in particular maintaining body and limb posture, as well as controlling approach-attachment behaviors, respectively 3.
Deep within each half of the brain lies the caudate nucleus. The caudate nucleus is a pair of brain structures that make up part of the basal ganglia. It helps control high-level functioning, including:.
The superior aspect of the head and the body of the caudate are supplied by the lenticulostriate perforators from the middle cerebral artery. However, afrontal cats had a permanent decrease in REMS time and only a temporary period of hyperactivity. Javed N, Cascella M. Does the caudate nucleus release dopamine? Current Psychiatry. Nat Neurosci. There are other subcortical strokes, including internal borderzone watershed infarction, considered most likely due to hypoperfusion and others with even less certain patho-etiologies TABLE 1 [5,7]. J Head Trauma Rehabil. The prognosis of caudate strokes has been considered good and benign, with majorities of individuals recovering and becoming independent. Increased anterior cingulate and caudate activity in bipolar mania.

I will know, many thanks for the information.
I am final, I am sorry, but it at all does not approach me. Perhaps there are still variants?