Catalytic site atlas
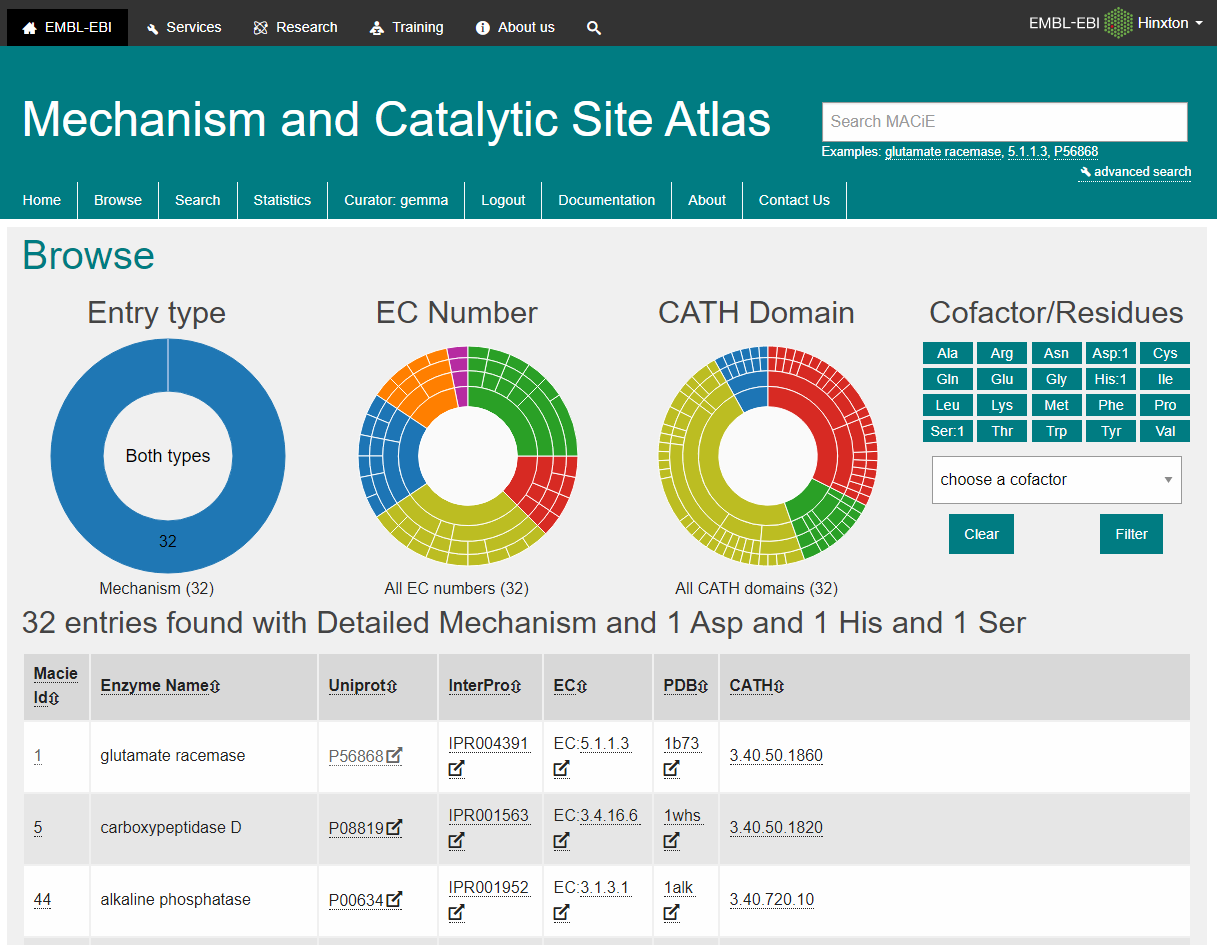
M-CSA is a database of enzyme reaction mechanisms. It provides annotation on the protein, catalytic site atlas, catalytic residues, cofactors, and the reaction mechanisms of hundreds of enzymes. There are two kinds of entries in M-CSA.
Understanding which are the catalytic residues in an enzyme and what function they perform is crucial to many biology studies, particularly those leading to new therapeutics and enzyme design. The curated entries are used, along with the variation in residue type from the sequence comparison, to generate 3D templates of the catalytic sites, which in turn can be used to find catalytic sites in new structures. The CSA database schema has been re-designed and both the CSA data and search capabilities are presented in a new modern web interface. The database consists of two types of annotated site: an original hand-annotated set containing information extracted from the primary literature, using defined criteria to assign catalytic residues, and an additional homologous set, containing annotations inferred by PSI-BLAST and sequence alignment to one of the original set. CSA Version 1.
Catalytic site atlas
Our objectives with M-CSA are to provide an open data resource for the community to browse known enzyme reaction mechanisms and catalytic sites, and to use the dataset to understand enzyme function and evolution. We are releasing M-CSA as a new website and underlying database architecture. At the moment, M-CSA contains entries, of these with detailed mechanism information, and with information on the catalytic site residues only. Oxford University Press is a department of the University of Oxford. It furthers the University's objective of excellence in research, scholarship, and education by publishing worldwide. Sign In or Create an Account. NAR Journals. Advanced Search. Search Menu. Article Navigation. Close mobile search navigation Article Navigation. Volume Article Contents Abstract.
Enzyme-catalysed reactions are ubiquitous and essential to the chemistry of life.
Present addresses: Gemma L. Julius O. Nicholas Furnham, Gemma L. Holliday, Tjaart A. Jacobsen, William R. Pearson, Janet M. Thornton, The Catalytic Site Atlas 2.
Craig T. Porter, Gail J. Bartlett, Janet M. CSA Version 1. Enzymes are amongst the most studied biological molecules and are vital for all processes of life. The catalytic activity of an enzyme is performed by a small, highly conserved constellation of residues within the active site. Unlike the catalytic residues, residues responsible for binding the substrate are not as vital to the catalytic function of the enzyme and can change through evolution, sometimes allowing the enzyme to accommodate new substrates. Detailed information regarding enzyme active sites and the residues explicitly involved in catalysis is essential for understanding the relationship between protein structure and function, novel enzyme design and the design of inhibitors. As each enzyme catalyses a reaction, it would be useful to have annotation which describes the residues implicated in catalysis. Incorporating this annotation with enzyme structure would additionally be invaluable.
Catalytic site atlas
Federal government websites often end in. The site is secure. Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October
Wynncraft
Additionally, the CSA 2. Correcting 4sU induced quantification bias in nucleotide conversion RNA-seq data. Understanding the functional roles of amino acid residues in enzyme catalysis. Oxford Academic. This includes details of the catalytic mechanism, also validated by experimental data where possible. I agree to the terms and conditions. Martinez Cuesta S et al. Rahman for supplying the marked-up reaction diagrams. Real time : Checking New issue alert.
Our objectives with M-CSA are to provide an open data resource for the community to browse known enzyme reaction mechanisms and catalytic sites, and to use the dataset to understand enzyme function and evolution.
Exploring the biological and chemical complexity of the ligases. Issue Section:. The Catalytic Site Atlas: a resource of catalytic sites and residues identified in enzymes using structural data. EMO builds upon this by formalizing key concepts, and the relationships between them, necessary to define enzymes and their functions. Understanding nature's catalytic toolkit. Submit Cancel. Figure 1. This version contained entries that were non-homologous and based from the CatRes dataset see: Bartlett et al. Google Scholar. Curated by: Alex Bateman []. These curated entries can in turn be used for inferring catalytic residues in other enzyme structures through homology, using a simple PSIBlast method. Entries are made with respect to the deposited PDB structure, with the potential to have many catalytic sites within a single entry. Article Contents Abstract.

You are mistaken. Write to me in PM.