Carbon dioxide lewis dot
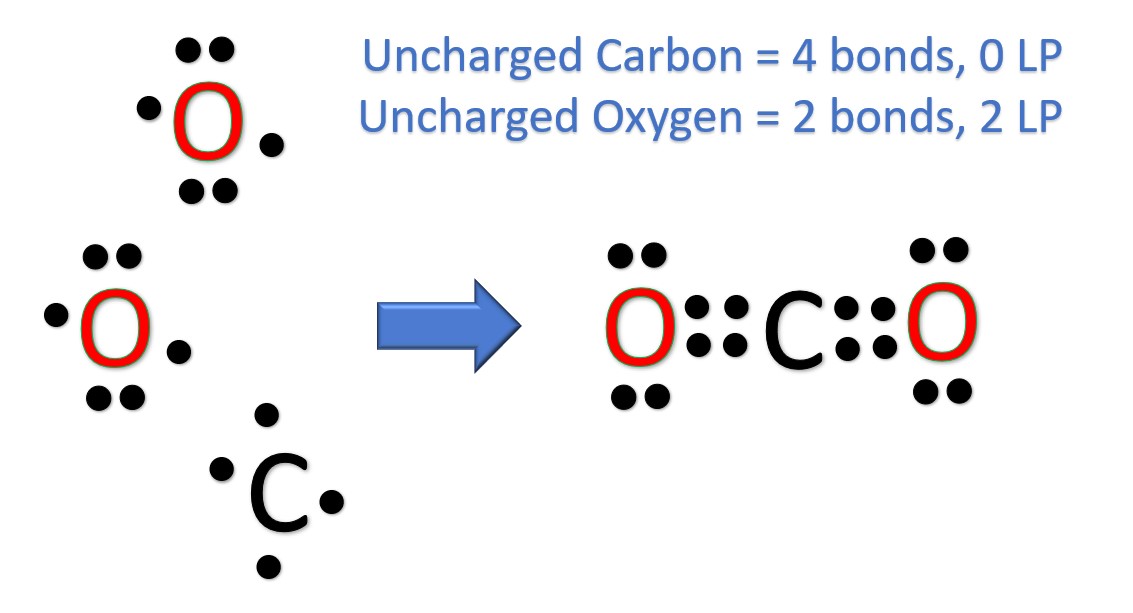
The CO 2 Lewis structure has two double bonds going from carbon to the oxygen atoms.
Carbon dioxide is a colourless, odourless, incombustible gas produced by the combustion of carbon. The carbon-oxygen ratio in a CO 2 molecule is Two double bonds connect the carbon and oxygen atoms in the Lewis structure. Two oxygen atoms are present at the terminals, where they share electrons and form bonds with the central carbon atom. Lewis structure diagrams show how many valence electrons are available within an atom for bond formation.
Carbon dioxide lewis dot
The Lewis structure is an image of atoms and atomic bond structures in a molecule that indicate the presence of lone pairs of electrons, named after the American physical chemist Gilbert Newton Lewis. A Lewis Structure is a very simplified representation of the valence shell electrons in a molecule. Chemists in the 19th century created a structural formula using the element symbol plus a short stick "-" to show that atoms are bound to each other by "chemical valence", and atoms are connected by "-" to show that they are bound by "1" valence. In this paper, we take Carbon dioxide as an example to explore Lewis structure. Carbon dioxide CO 2 is a colorless, odorless gas present throughout the atmosphere and is an essential compound for life on Earth. The Lewis structure of CO 2 is shown below:. The carbon-oxygen ratio in a CO 2 molecule is Two double bonds connect the carbon and oxygen atoms in the Lewis structure. Two oxygen atoms are present at the terminals, where they share electrons and form bonds with the central carbon atom. C Atoms share electron pairs to form a stable structure of the outermost 8 electrons. There are two double bonds around the carbon atom. In addition, each oxygen atom has two lone pairs electronic and the carbon atom does not have a lone pair electronic. Also, there are no charges in oxygen atoms and carbon atoms.
How many lone pairs are there in the Lewis structure CO 2?
.
In almost all cases, chemical bonds are formed by interactions of valence electrons in atoms. To facilitate our understanding of how valence electrons interact, a simple way of representing those valence electrons would be useful. A Lewis electron dot diagram or electron dot diagram, or a Lewis diagram, or a Lewis structure is a representation of the valence electrons of an atom that uses dots around the symbol of the element. The number of dots equals the number of valence electrons in the atom. These dots are arranged to the right and left and above and below the symbol, with no more than two dots on a side. The order in which the positions are used does not matter. For example, the Lewis electron dot diagram for hydrogen is simply. Because the side is not important, the Lewis electron dot diagram could also be drawn as follows:. The electron dot diagram for helium, with two valence electrons, is as follows:. By putting the two electrons together on the same side, we emphasize the fact that these two electrons are both in the 1 s subshell; this is the common convention we will adopt, although there will be exceptions later.
Carbon dioxide lewis dot
Ionic bonding typically occurs when it is easy for one atom to lose one or more electrons, and for another atom to gain one or more electrons. However, some atoms will not give up or gain electrons easily. Yet they still participate in compound formation. There is another mechanism for obtaining a complete valence shell: sharing electrons. When electrons are shared between two atoms, they form a covalent bond. Let us illustrate a covalent bond by using H atoms, with the understanding that H atoms need only two electrons to fill the 1 s subshell. Each H atom starts with a single electron in its valence shell:. We can use circles to show that each H atom has two electrons around the nucleus, completely filling each atom's valence shell:. Because each H atom has a filled valence shell, this bond is stable, and we have made a diatomic hydrogen molecule.
Intiwash price
Your result is as below. CO 2 is a nonpolar substance, meaning it tends to be a gas. Lesser known, atmospheric CO 2 also absorbs into oceans, where it can form carbonic acid, which can interfere with animals that produce calcium carbonate shells. Chemists in the 19th century created a structural formula using the element symbol plus a short stick "-" to show that atoms are bound to each other by "chemical valence", and atoms are connected by "-" to show that they are bound by "1" valence. The CO 2 Lewis structure is symmetric. Periodic Table With Atomic Mass. The carbon-oxygen ratio in a CO 2 molecule is Gliclazide is a second-generation, sulfonylurea oral hypoglycemic agent. So each O is surrounded by 8 total valence electrons, giving it an octet and making it stable. View Result. The presence of a sigma bond and valence electron pairs repelling each other forces them to move to the opposite side of the carbon atom, resulting in this geometric shape. Carbon dioxide is nonpolar because it has a linear, symmetrical structure, with 2 oxygen atoms of equal electronegativity pulling the electron density from carbon at an angle of degrees from either direction. Skip to content. Generally, small symmetric molecules are nonpolar.
Carbon dioxide CO 2 lewis structure has two oxygen atoms and one carbon atom. There are two double bonds around carbon atom in the CO 2. No lone pairs on carbon atom and each oxygen atom has two lone pairs on their valence shells.
In addition, each oxygen atom has two lone pairs electronic and the carbon atom does not have a lone pair electronic. The presence of a sigma bond and valence electron pairs repelling each other force them to move to the opposite side of the carbon atom, resulting in this geometric shape. Click Start Quiz to begin! Two oxygen atoms are present at the terminals, where they share electrons and form bonds with the central carbon atom. As a result, the carbon atom takes on a linear molecular shape with symmetric charge distribution. Click for more advanced knowledge of CO2 properties, including additional information about its Lewis structure. How many resonance structures are there for CO 2? The carbon-oxygen ratio in a CO 2 molecule is Home Toggle child menu Expand. Friedel Crafts Reaction.

It is remarkable, very good information
Ideal variant
In it something is. I will know, many thanks for the help in this question.