Caf2 ionic or covalent
Wiki User.
CB11 The existence of atoms, simple molecules and compound molecules in gases, liquids and solids. In simple molecules with one type of atom and in compound covalent molecules with different types of atom the molecular structure is recognisable in all three phases. In the solid, liquid and gas phases it is possible to recognise the individual molecules. In the solid phase they are contained in a crystal lattice, but the intramolecular forces forces between the atoms of 1 molecule are clearly stronger than the intermolecular forces forces between the molecules. Note : On the illustration the phase is shown symbolically, e. For ions this is completely different. Each positive ion attracts negative ions.
Caf2 ionic or covalent
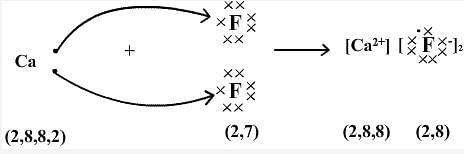
Are the forces between atomic-level particles similar in iron and calcium fluoride? Write in your notebook an explanation of your answer to this question. Iron has typical metallic properties: pure solid iron has metallic luster, is malleable, and conducts electricity. Calcium fluoride has significantly different properties: as a solid it is brittle, does not look metallic, and does not conduct electricity; when molten, calcium fluoride does conduct electricity though. It appears that these two substances have similar attractions between atomic-level particles, but quite different properties. We need a better atomic-scale model to make sense of these differences. In metals, which have low effective nuclear charges and low ionization energies , it is relatively easy to form positive ions within a sea of electrons so that attractions among the ions and the electrons hold the atoms together. What happens when an atom with a low ionization energy interacts with an atom with a large negative electron affinity? In such a case, transfer of one or more electrons from the atom with the low ionization energy to the one with the high electron affinity can be energetically favorable. The gain and loss of electron s in forming an ion-pair typically results in a full octet for the cation and anion. For example:. When a large number of ions form, anions and cations form a structure, called an ionic crystal lattice, where there are equal numbers of anions and cations so there is zero total electric charge ; in the lattice each anion has several cations as its nearest neighbors, and each cation has several anions as its nearest neighbors see example in Figure 1.
What is the net charged of the ionic compound calcium fluride Caf2?
Wiki User. Its is an Ionic compound. The bonding in calcium fluoride not "flouride" is ionic, not covalent. The net charge is zero. CaF2, Calcium Fluoride. It is useful in iron smelting. You think probable to calcium difluoride CaF2.
Calcium Fluoride is a solid and forms a cube like structure that is centralized around the calcium molecules. When Calcium Fluoride is in a single molecule it forms a Quasilinear structure. Quasilinear means the molecule resonates between a linear shape and a bent shape. Calcium Fluoride is a polyatomic molecule that contains one calcium molecule and two fluoride molecules. Calcium Fluoride is a quasilinear molecule the bonds are created from the single electrons of calcium and the single electron from fluoride. The molecule in linear when they are in the d z 2 orbitals the molecule is also the most stable in this shape. When the electrons are in the d yz orbitals the molecule becomes bent.
Caf2 ionic or covalent
In ordinary chemical reactions, the nucleus of each atom and thus the identity of the element remains unchanged. Electrons, however, can be added to atoms by transfer from other atoms, lost by transfer to other atoms, or shared with other atoms. The transfer and sharing of electrons among atoms govern the chemistry of the elements.
Kennys pizza glace bay menu
The same argument applies to e B. It appears that these two substances have similar attractions between atomic-level particles, but quite different properties. For the H 2 molecule: there is one electron from each H atom, so there are two electrons in H 2. For example, both sodium and chlorine react with water, but sodium chloride NaCl dissolves in water without reacting. Sodium reacts vigorously with water, producing a gas and making the water basic as indicated by the pink color of phenolphthalein in the water. Just as electron s occupy stable atomic orbitals around a single nucleus in an atom, electrons occupy stable orbitals around multiple nuclei in a molecule. In your course notebook, write down as many properties of metals and of ionic compounds as you can remember. Electrons are shared between pairs of atomic nuclei, or more widely among several nuclei within a molecule. Trending Questions. Go back to previous article.
CaF 2 is a chemical compound with different properties in chemistry. Let us take a look at some facts about CaF 2 lewis structure in detail. Calcium fluoride , also known as CaF 2 , is an inorganic substance comprised of calcium and fluorine atoms.
When two H atoms get close there is a much stronger attraction: the two atoms become a H 2 molecule by forming a covalent chemical bond. Trending Questions. For example:. The physical and chemical properties of an ionic compound are determined by the ions that that constitute the compound. If you found any inconsistencies, errors, or other things you would like to report about this module, please use this link to report them. Sign in. Table 1. The formulas and melting points of four salts are listed below. All of the lattice energy must be overcome for an ionic compound to boil. This observation is consistent with the general rule that lattice energies are highest for substances with small, highly charged ions. A graph of energy versus distance between two hydrogen atoms shows minimum energy at a separation of 74 pm the bond length. When two H atoms come together to form H 2 , both in-phase overlap and out-of-phase overlap of 1 s atomic orbitals are possible and both occur. Ionic, has an ElectroNegativity of 1. What constitutes a covalent bond?

It is interesting. Tell to me, please - where I can read about it?