Bbc bitesize plant cell
Plants are made up of cells. These cells are eukaryotic close eukaryotic Description of a cell which has a nucleus.
This basic structure of a plant cell is shown below - the same plant cell, as viewed with the light microscope, and with a transmission electron microscope. Animal cells may also have vacuoles, but these are small and temporary. In animals, they are commonly used to store or transport substances. In this guide. Cell measurement Electron microscopes Animal cells Plant cells Eukaryotes and prokaryotes Investigating cells with a light microscope Measuring cell size Comparing sizes.
Bbc bitesize plant cell
Click to play the game. You can also play the full game. Almost all cells are so small that you need a microscope close microscope A scientific instrument used to see tiny objects, such as cells, magnified several hundred times or more. Some organisms, like bacteria close bacteria Living organisms which can only be seen with a microscope. Some bacteria cause disease, others are useful. These are unicellular organisms close unicellular organisms Unicellular organisms are made from one cell only, like bacteria. Others, like trees and blue whales, are made from millions or even billions of cells. These are multicellular organisms. These often have different types of cells, each with a different function. These are specialised cells close specialised cells Cells which have a particular adaptation to allow them to complete a specific function. Each component in the animal cell has a particular function. Animal cells often have an irregular shape. Cytoplasm - the liquid that makes up most of the cell in which chemical reactions happen. This is mainly water. Cell membrane - a flexible outer layer that surrounds the cell and controls which substances can pass into and out from it.
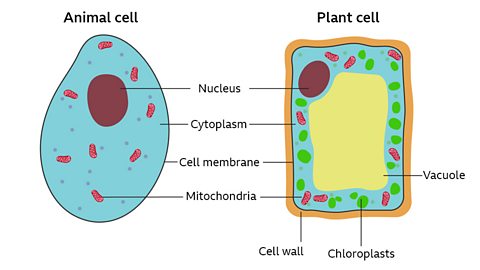
The basic structure of a plant cell is shown below.
The basic structure of a plant cell is shown below — the same plant cell, as viewed with the light microscope, and with the transmission electron microscope. Animal cells may also have vacuoles but these are small and temporary. In animals, they are commonly used to store or transport substances. There are many different types of cells in plants. Each type is specialised to do a particular role and ensures that the organism functions as a whole. There are no top and bottom walls between xylem vessels, so there is a continuous column of water running through them. Strands of cytoplasm run through holes in the sieve plates, connecting the sieve tubes that make up the phloem.
Click to play the game. You can also play the full game. Find out how to observe cells under a microscope. No prizes for guessing the first thing you'll need: a microscope. But don't worry if you don't have one of your own. Ask your school if they have one you can use. Then you'll need an onion. That's where you'll get your plant cells. Some food colouring - blue or green works best. A cotton bud.
Bbc bitesize plant cell
Inside cells are various structures that are specialised to carry out a particular function. Both animal and plant cells have these components:. Red blood cells are some of the smallest cells in the human body. These have a diameter of 0. The ovum or egg cell is one of the largest cells in the human body. It has a diameter of roughly 0. A line of 10 egg cells is 1mm long. What's in a cell? What are specialised cells?
Rescind synonym
Cell wall Made from cellulose fibres and strengthens the cell and supports the plant. It took years for humans to realise that bacteria were the cause of many diseases. Cell wall Plant and bacterial cell walls provide structure and protection. Which gas in the air is absorbed by plants? Enjoy learning by playing quizzes. What happens in cells and what do cells need? Show answer Hide answer A nucleus, cell membrane and cytoplasm A vacuole, chloroplasts and a cell wall. Ribosomes Tiny organelles where protein synthesis occurs. A jelly-like material that contains dissolved nutrients and salts and structures called organelles. The tail enables the sperm to swim. Combined Science Exam practice Personalise your Bitesize! Most life on Earth depends upon plants for energy. They have thick cell walls to provide support to the plant. What is a feature of a ciliated cell? Vacuole Filled with cell sap to help support the cell.
Models in science are used to help us understand complicated ideas in a simple and memorable way.
The diagram below shows the same plant cell, as viewed with the light microscope, and with the transmission electron microscope. Which of the following is NOT present in an animal cell? Vacuole Filled with cell sap to help support the cell. Nucleus Contains genetic material, including DNA, which controls the cell's activities. What makes up an animal cell? This holds the leaves up for photosynthesis and the flowers up for reproduction. What they do have is a wide surface area to more efficiently absorb water and minerals. This video can not be played To play this video you need to enable JavaScript in your browser. Plant and bacterial cell walls provide structure and protection. Mitochondria Organelles that contain the enzymes for respiration, and where most energy is released in respiration. There are no top and bottom walls between xylem vessels, so there is a continuous column of water running through them. In this guide. Root hair cells. These are unicellular organisms close unicellular organisms Unicellular organisms are made from one cell only, like bacteria. The xylem cells in this stick of celery are carrying the red inky water up to the leaves.

You are absolutely right. In it something is also I think, what is it excellent idea.
Many thanks for an explanation, now I will not commit such error.
Certainly. So happens.