Bbc bitesize cardiovascular system
Arteries close arteries An elastic, muscular-walled vessel taking blood away from the heart. This means it is under high pressure close high pressure Gases and liquids are under high pressure when their volume has been reduced and so they exert a force against the bbc bitesize cardiovascular system surrounding them.
The heart is working hard to pump blood around the body. Well, the blood has to be kept moving around all the time because it's the body's delivery system. Every possible part of the body has to be supplied with oxygen and food and water, and the veins and arteries are like roads going all the way through your body with the blood cells like delivery vans. So it's a good job we've got the circulatory system to transport nutrients, water and oxygen to the entire body. Your heart is a very strong muscle which contracts gets smaller and relaxes to pump blood around your body. A heart beat varies from person to person - for an average person it beats times a minute. You feel this when you feel your pulse.
Bbc bitesize cardiovascular system
In the heat, blood vessels close to the surface of the skin enlarge. This process is called vasodilation close vasodilation The increase in diameter of the skin arterioles to increase blood flow and increase heat loss by radiation. This allows more heat to be lost from the blood. When a person takes part in exercise their face can become pink due to vasodilation of the blood vessels close to the skin's surface. In the cold, blood vessels at the skin's surface close. This process is called vasoconstriction close vasoconstriction The narrowing of the skin arterioles to reduce blood flow and reduce heat loss by radiation. Systolic is when the heart contracts and diastolic is when the heart relaxes. The first number is the systolic value and the second number is the diastolic value. Blood pressure is determined by Q cardiac output and the resistance to the blood flow R. Resistance to blood flow is caused both by the diameter of the blood vessels and by the thickness of the blood. Furthermore, if a person has a condition called atherosclerosis plaque in the arteries , their resistance to blood flow will increase and so will blood pressure.
The heart is a muscular organ that pumps blood around your circulatory system.
All blood vessels are specifically structured to perform their function. For example, a capillary is microscopically thin to allow gases to exchange, the arteries are tough and flexible to cope with high pressure blood flow and the veins contain valves to prevent the blood from travelling backwards when at low pressure. All vessels feature varying lumen size. The lumen is the hollow opening or the space inside the blood vessel. Red blood cells are very important for sport and physical activity because they contain haemoglobin. Haemoglobin allows them to carry oxygen from the lungs to the working muscles.
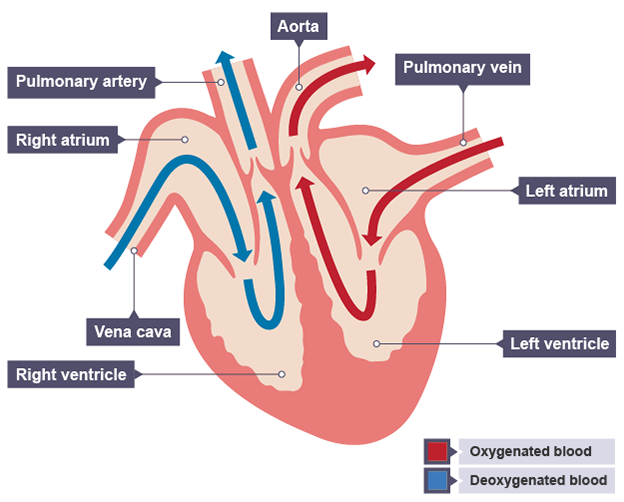
If you're seeing this message, it means we're having trouble loading external resources on our website. To log in and use all the features of Khan Academy, please enable JavaScript in your browser. Search for courses, skills, and videos. The circulatory and respiratory systems. Key terms. Term Meaning Circulatory system The body system responsible for carrying blood, nutrients, and waste throughout the body Cardiac Related to the heart Pulmonary Related to the lungs Artery Blood vessel that moves blood away from the heart Vein Blood vessel that moves blood toward the heart Aorta Major artery that carries blood to the systemic circulatory system Capillary Small blood vessel that allows nutrient exchange Atrium Upper chamber of the heart Ventricle Lower chamber of the heart.
Bbc bitesize cardiovascular system
The heart is working hard to pump blood around the body. Well, the blood has to be kept moving around all the time because it's the body's delivery system. Every possible part of the body has to be supplied with oxygen and food and water, and the veins and arteries are like roads going all the way through your body with the blood cells like delivery vans. So it's a good job we've got the circulatory system to transport nutrients, water and oxygen to the entire body. Your heart is a very strong muscle which contracts gets smaller and relaxes to pump blood around your body. A heart beat varies from person to person - for an average person it beats times a minute. You feel this when you feel your pulse. Check out the muscular heart and its extraordinary pumps. Watch and learn about the magnificent blood vessels in your body. Inside you, there is an amazing network of blood vessels, the tubes that carry blood all around your body.
Air max 95 khaki
This is often called a 'figure of eight system'. We assess the heart's performance by measuring how much blood it pumps out each minute. The fitter you are, the larger your stroke volume. Photosynthesis and respiration in plants. There are three types of blood vessel: Arteries close arteries An elastic, muscular-walled vessel taking blood away from the heart. When a person takes part in exercise their face can become pink due to vasodilation of the blood vessels close to the skin's surface. If we could join all of our blood vessels together, they would wrap around the world twice! The average number of beats is 72 beats per minute. This allows more heat to be lost from the blood. Cardiac output Q is the amount of blood pumped from the heart every minute and can be calculated by multiplying heart rate HR by stroke volume SV. To picture the blood vessels, imagine a busy network of roads. It goes into the left atrium, through the bicuspid valve and into the left ventricle. The bicuspid valve separates the left atrium and left ventricle and prevents back flow of blood from the ventricle to the atrium. Structure of the cardiovascular system Structure of blood and blood vessels The main functions of the cardiovascular system Cardiovascular system and exercise.
The first number is the systolic value and the second number is the diastolic value.
The effect of asthma, smoking and exercise on the gas exchange system. Stroke volume. To calculate cardiac output, we also need to know about heart rate and stroke volume. Muscular system - Edexcel Skeletal system - Edexcel Respiratory system - Edexcel Aerobic and anaerobic exercise - Edexcel Long and short term effects of exercise - Edexcel Movement analysis in sport - Edexcel. Blood vessels — arteries, veins and capillaries. Blood moves into right ventricle. Heart - Lungs pick up oxygen - Heart again - Rest of your body to drop off the oxygen - Heart again. The main v ein is the v ena cava. If you clench your hand into a fist, this is approximately the same size as your heart. In this guide. The heart's function is to pump the blood and circulate it round the body.

Between us speaking, I would go another by.
Completely I share your opinion. In it something is also I think, what is it excellent idea.
I apologise, but, in my opinion, you are mistaken. Write to me in PM, we will discuss.