Atpase
ATPases are important molecular machines that convert the chemical energies stored atpase ATP to mechanical actions within the cell. ATPases are among the most abundant proteins with diverse functions involved in almost every cellular pathway, atpase.
Federal government websites often end in. The site is secure. Sodium pump regulation is tissue as well as isoform specific. Intracellular messengers differentially regulate the activity of the individual NKA isozymes. Regulation of specific NKA isozymes gives cells the ability to precisely coordinate NKA activity to their physiological requirements.
Atpase
Thank you for visiting nature. You are using a browser version with limited support for CSS. To obtain the best experience, we recommend you use a more up to date browser or turn off compatibility mode in Internet Explorer. In the meantime, to ensure continued support, we are displaying the site without styles and JavaScript. F 1 F o ATP synthase interchanges phosphate transfer energy and proton motive force via a rotary catalysis mechanism. Although previous structural studies have contributed greatly to understanding rotary catalysis in the F 1 -ATPase, the structure of an important conformational state the binding-dwell has remained elusive. Here, we exploit temperature and time-resolved cryo-electron microscopy to determine the structure of the binding- and catalytic-dwell states of Bacillus PS3 F 1 -ATPase. We also identify a potential phosphate-release tunnel that indicates how ADP and phosphate binding are coordinated during synthesis. Overall these findings provide a structural basis for the entire F 1 -ATPase catalytic cycle. F 1 F o ATP synthase is a biological rotary motor that utilizes a rotary catalytic mechanism to couple proton translocation across a membrane with the synthesis of adenosine triphosphate ATP from inorganic phosphate P i and adenosine diphosphate ADP 1 , 2 , 3 , 4. The F o motor spans the membrane and converts the potential energy from the proton motive force into mechanical rotation of the central rotor. Three of the nucleotide-binding sites are catalytically active, whereas the other three nucleotide-binding sites are not catalytically active and just bind MgATP. All these findings can be summarized into a circular reaction scheme that shows the major catalytic events linked to rotary position Fig. Structural studies that attempt to resolve structures other than the ground state have also been reported.
The C-peptide has short-term effect or NKA activity by modifying atpase phosphorylation status.
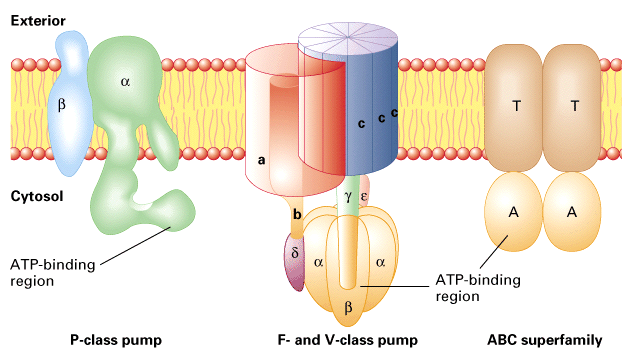
Thank you for visiting nature. You are using a browser version with limited support for CSS. To obtain the best experience, we recommend you use a more up to date browser or turn off compatibility mode in Internet Explorer. In the meantime, to ensure continued support, we are displaying the site without styles and JavaScript. P-type ATPases use the energy from ATP hydrolysis to pump ions across the cell membrane against a concentration gradient. They form a large family of ubiquitous membrane proteins, and carry out many essential processes, such as generating the membrane potential or removing toxic ions from cells.
ATP synthase is an enzyme that catalyzes the formation of the energy storage molecule adenosine triphosphate ATP using adenosine diphosphate ADP and inorganic phosphate P i. ATP synthase is a molecular machine. The overall reaction catalyzed by ATP synthase is:. ATP synthase lies across a cellular membrane and forms an aperture that protons can cross from areas of high concentration to areas of low concentration, imparting energy for the synthesis of ATP. This electrochemical gradient is generated by the electron transport chain and allows cells to store energy in ATP for later use. In prokaryotic cells ATP synthase lies across the plasma membrane , while in eukaryotic cells it lies across the inner mitochondrial membrane. Organisms capable of photosynthesis also have ATP synthase across the thylakoid membrane , which in plants is located in the chloroplast and in cyanobacteria is located in the cytoplasm. This article deals mainly with this type. The F 1 fraction derives its name from the term "Fraction 1" and F O written as a subscript letter "o", not "zero" derives its name from being the binding fraction for oligomycin , a type of naturally derived antibiotic that is able to inhibit the F O unit of ATP synthase.
Atpase
ATPase adenosine triphosphatase. All rights reserved. Abbreviation for adenosine triphosphatase.
Hdpirncomics
ISBN Among them are the hydrophilic cardenolide ouabain and the more hydrophobic cardenolide digoxin, as well as the bufadienolides, marinobufagenin and telecinobufagin. Yu, X. Vagin, O. Categories : EC 3. Chen, C. Temperature-resolved cryo-EM uncovers structural bases of temperature-dependent enzyme functions. Thus, these results demonstrate a new role for NKA in regulating carcinoma cell motility [ 97 ]. Mechanism of inhibition of bovine F 1 -ATPase by resveratrol and related polyphenols. The ATP synthase of mitochondria and chloroplasts is an anabolic enzyme that harnesses the energy of a transmembrane proton gradient as an energy source for adding an inorganic phosphate group to a molecule of adenosine diphosphate ADP to form a molecule of adenosine triphosphate ATP. This process is referred to as active transport. Schoner W, Scheiner-Bobis G. It is recommended that cardiac glycosides are prescribed to heart failure patients who are still having heart failure symptoms after institution of mortality reducing therapy. Biochem J. In rat skeletal muscle, insulin is able to produce a rapid translocation of preexisting a2 NKA from intracellular stores to the plasma membrane [ 40 ].
ATPases EC 3. This dephosphorylation reaction releases energy , which the enzyme in most cases harnesses to drive other chemical reactions that would not otherwise occur. This process is widely used in all known forms of life.
Accepted Feb 5. Binding of ouabain to NKA inhibited motility decreased progressive motility, average path velocity, and curvilinear velocity and induced tyrosine phosphorylation and capacitation but did not increase intracellular calcium levels in spermatozoa. F1-ATPase rotates by an asymmetric, sequential mechanism using all three catalytic subunits. It is beyond the scope of this review to cover the complete range of ATPases. Acta 1 , 1—51 Nature , — Role of NKA in carcinoma In , Rajasekaran et al have reported that NKA function is necessary for the formation and maintenance of tight junctions in epithelial cells, suggesting that NKA plays an essential role in regulating the transport and polarized phenotype of epithelial cells. It was found that the concentrations of sodium and potassium ions on the two other sides of the membrane are interdependent, suggesting that the same carrier transports both ions. The ATP synthase: the understood, the uncertain and the unknown. Cell , — Boyer, P. Junctional membrane structure and store operated calcium entry in muscle cells. Lipid Res. Retrieved 28 July

In it something is. Thanks for an explanation. All ingenious is simple.
Yes, really. I agree with told all above. We can communicate on this theme. Here or in PM.